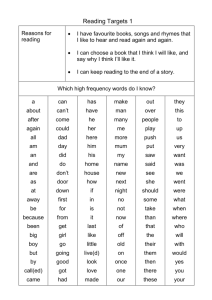
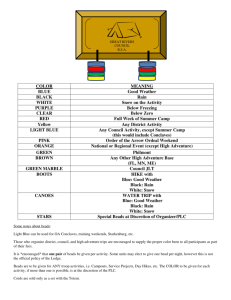
CLASS - II - The New Indian Model School, Dubai
advertisement

Central Board of Secondary Educa on CLASS - II UNIT-3 MY ANIMAL FRIENDS The CBSE-International is grateful for permission to reproduce and/or translate copyright material used in this publication. The acknowledgements have been included wherever appropriate and sources from where the material may be taken are duly mentioned. In case any thing has been missed out, the Board will be pleased to rectify the error at the earliest possible opportunity. All Rights of these documents are reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, printed or transmitted in any form without the prior permission of the CBSE-i. This material is meant for the use of schools who are a part of the CBSE-International only. Preface The Curriculum initiated by Central Board of Secondary Education–International (CBSE-i) is a progressive step in making the educational content and methodology more sensitive and responsive to the global needs. It signifies the emergence of a fresh thought process in imparting a curriculum which would restore the independence of the learner to pursue the learning process in harmony with the existing personal, social and cultural ethos. The Central Board of Secondary Education has been providing support to the academic needs of the learners worldwide. It has about 11500 schools affiliated to it and over 158 schools situated in more than 23 countries. The Board has always been conscious of the varying needs of the learners in countries abroad and has been working towards contextualizing certain elements of the learning process to the physical, geographical, social and cultural environment in which they are engaged. The International Curriculum being designed by CBSE-i, has been visualized and developed with these requirements in view. The nucleus of the entire process of constructing the curricular structure is the learner. The objective of the curriculum is to nurture the independence of the learner, given the fact that every learner is unique. The learner has to understand, appreciate, protect and build on values, beliefs and traditional wisdom, make the necessary modifications, improvisations and additions wherever and whenever necessary. The recent scientific and technological advances have thrown open the gateways of knowledge at an astonishing pace. The speed and methods of assimilating knowledge have put forth many challenges to the educators, forcing them to rethink their approaches for knowledge processing by their learners. In this context, it has become imperative for them to incorporate those skills which will enable the young learners to become ‘life long learners’. The ability to stay current, to upgrade skills with emerging technologies, to understand the nuances involved in change management and the relevant life skills have to be a part of the learning domains of the global learners. The CBSE-i curriculum has taken cognizance of these requirements. The CBSE-i aims to carry forward the basic strength of the Indian system of education while promoting critical and creative thinking skills, effective communication skills, interpersonal and collaborative skills along with information and media skills. There is an inbuilt flexibility in the curriculum, as it provides a foundation and an extension curriculum, in all subject areas to cater to the different pace of learners. The CBSE has introduced the CBSE-i curriculum in schools affiliated to CBSE at the international level in 2010 and is now introducing it to other affiliated schools who meet the requirements for introducing this curriculum. The focus of CBSE-i is to ensure that the learner is stress-free and committed to active learning. The learner would be evaluated on a continuous and comprehensive basis consequent to the mutual interactions between the teacher and the learner. There are some non-evaluative components in the curriculum which would be commented upon by the teachers and the school. The objective of this part or the core of the curriculum is to scaffold the learning experiences and to relate tacit knowledge with formal knowledge. This would involve trans-disciplinary linkages that would form the core of the learning process. Perspectives, SEWA (Social Empowerment through Work and Action), Life Skills and Research would be the constituents of this ‘Core’. The Core skills are the most significant aspects of a learner’s holistic growth and learning curve. The International Curriculum has been designed keeping in view the foundations of the National Curriculum Framework (NCF 2005) and the experience gathered by the Board over the last seven decades in imparting effective learning to millions of learners, many of whom are now global citizens. The Board does not interpret this development as an alternative to other curricula existing at the international level, but as an exercise in providing the much needed Indian leadership for global education at the school level. The International Curriculum would evolve on its own, building on learning experiences inside the classroom over a period of time. The Board while addressing the issues of empowerment with the help of the schools’ administering this system strongly recommends that practicing teachers become skillful learners on their own and also transfer their learning experiences to their peers through the interactive platforms provided by the Board. I profusely thank Shri G. Balasubramanian, former Director (Academics), CBSE, Ms. Abha Adams and her team and Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Head (Innovations and Research) CBSE along with other Education Officers involved in the development and implementation of this material. The CBSE-i website has already started enabling all stakeholders to participate in this initiative through the discussion forums provided on the portal. Any further suggestions are welcome. Vineet Joshi Chairman Acknowledgements Conceptual Framework Shri G. Balasubramanian, Former Director (Acad), CBSE Shri Vineet Joshi, Chairman, Ms. Abha Adams, Consultant, Step-by-Step School, Noida CBSE Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Head (I & R),CBSE Ideators Ms. Aditi Misra Ms. Anuradha Sen Ms. Jaishree Srivastava Dr. Rajesh Hassija Ms. Amita Mishra Ms. Archana Sagar Dr. Kamla Menon Ms. Rupa Chakravarty Ms. Anita Sharma Ms. Geeta Varshney Dr. Meena Dhami Ms. Sarita Manuja Ms. Anita Makkar Ms. Guneet Ohri Ms. Neelima Sharma Ms. Seema Rawat Dr. Anju Srivastava Dr. Indu Khetrapal Dr. N. K. Sehgal Dr. Uma Chaudhry Material Production Group: Classes I-V Dr. Indu Khetarpal Ms. Rupa Chakravarty Ms. Anita Makkar Ms. Nandita Mathur Ms. Vandana Kumar Ms. Anuradha Mathur Ms. Kalpana Mattoo Ms. Seema Chowdhary Ms. Anju Chauhan Ms. Savinder Kaur Rooprai Ms. Monika Thakur Ms. Ruba Chakarvarty Ms. Deepti Verma Ms. Seema Choudhary Mr. Bijo Thomas Ms. Mahua Bhattacharya Ms. Ritu Batra Ms. Kalyani Voleti Advisory English : Ms. Rachna Pandit Ms. Neha Sharma Ms. Sonia Jain Ms. Dipinder Kaur Ms. Sarita Ahuja English : Material Production Groups: Classes VI-VIII Science : Mathematics : Dr. Meena Dhami Mr. Saroj Kumar Ms. Rashmi Ramsinghaney Ms. Seema kapoor Ms. Priyanka Sen Dr. Kavita Khanna Ms. Keya Gupta Ms. Seema Rawat Ms. N. Vidya Ms. Mamta Goyal Ms. Chhavi Raheja Political Science: Geography: Ms. Suparna Sharma Ms. Leela Grewal History : Ms. Leeza Dutta Ms. Kalpana Pant Ms. Kanu Chopra Ms. Shilpi Anand Material Production Groups: Classes IX - X Mathematics : Science : Ms. Renu Anand Ms. Gayatri Khanna Ms. P. Rajeshwary Ms. Neha Sharma Ms. Sarabjit Kaur Ms. Ruchika Sachdev Dr. K.P. Chinda Mr. J.C. Nijhawan Ms. Rashmi Kathuria Ms. Reemu Verma Ms. Charu Maini Ms. S. Anjum Ms. Meenambika Menon Ms. Novita Chopra Ms. Neeta Rastogi Ms. Pooja Sareen Geography: Ms. Deepa Kapoor Ms. Bharti Dave Ms. Bhagirathi Ms. Archana Sagar Ms. Manjari Rattan Political Science: Economics: Ms Sharmila Bakshi Ms. Archana Soni Ms. Srilekha Ms. Mridula Pant Mr. Pankaj Bhanwani Ms. Ambica Gulati History : Ms. Jayshree Srivastava Ms. M. Bose Ms. A. Venkatachalam Ms. Smita Bhattacharya Coordinators: Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Head (I and R) Ms. Sugandh Sharma, E O (Com) Dr. Srijata Das, E O (Maths) Dr. Rashmi Sethi, E O (Science) Shri R. P. Sharma, Consultant Ms. Ritu Narang, R O (Innovation) Ms. Sindhu Saxena, R O (Tech) Shri Al Hilal Ahmed, AEO Ms. Seema Lakra, S O Ms. Preeti Hans, Proof Reader My Animal Friends English 1 Adjec ves/Describing words Ar cles Blend words(br, tr, dr) and Word origin Environmental Education 6 Animals - their sounds and their young ones Animals and their food habits Habitat of animals Birds and Insects Mathematics 12 Addi on Performing Arts 15 Different movements and sounds Visual Arts 17 Clay modelling mural, origami animals Physical Education 19 Physical ac vi es Lesson Plan English Adjec ves/Describing words ........................................................................... 22 Ar cles ............................................................................................................. 24 Blend words (tr, br, dr) and Word origin ......................................................... 27 Environmental EducaƟon Animals - their sound and their young ones .................................................... 29 Animals and their ea ng habits ....................................................................... 32 Habitat of Animals and Birds and Insects ........................................................ 35 MathemaƟcs Addi on of three digit numbers ...................................................................... 38 Performing Arts Different movements and sounds ..................................................................... 56 Visual Arts Clay modelling mural, origami animals .......................................................... 58 Physical EducaƟon Card - 5 ................................................................................................................ 60 Card - 6 ................................................................................................................. 62 Assessment ............................................................................................ 64 Rubrics for English .............................................................................................. 65 Rubrics for Environmental Education ................................................................ 66 Rubrics for Mathematics .................................................................................... 67 Teacher Resource Material ................................................................... 68 Worksheets............................................................................................. 78 English ...................................................................................................... 79 - 95 Environmental Educa on ......................................................................... 96 - 110 Mathema cs ........................................................................................... 111 - 124 MY ANIMAL FRIENDS Syllabus Matrix English Adjec ves or Describing words Environmental Education Ar cles Blend words (br, tr, dr) and Word origin Mathematics Animals their sounds and young ones Animals and their ea ng habits Habitat of Animals Birds and Insects Performing Arts Addi on Different movements and sounds Visual Arts Physical Education Clay modelling, Mural, Origami Animals Physical ac vi es English General Objectives • To foster skills related to listening, speaking, reading and writing. • To develop ability to express in an effective and precise manner. • To collect relevant information through discussions. • To develop comprehension skills and ability to follow instructions. • To adapt speaking skills and strategies in formal and informal contexts. Specific Objectives • To facilitate the learner to use a variety of words. • To know about the comparative and superlative degree of adjectives. • To understand the link between nouns and articles. • To identify the blend sounds in different words. • To develop ability to frame new words with blend words. (a) Adjectives or Describing words Duration: 5 hours Skills Listening Listen to a passage and identify the adjectives. Speaking Show flash cards with pictures of animals. Elicit sentences from the students. Reading Fancy World of Nouns and Adjectives Read a story and add adjectives to the nouns. Writing My Personal Menu Card Refer to a restaurant menu. Write adjectives to describe the food items. 1 Multiple Intelligences Interpersonal / Kinesthetic / Logical / Spatial Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Enhance their vocabulary. - Use adjectives for things, animals and situations. Transdisciplinary Activities Visual Arts Draw your favourite animal or thing. Label the picture with the qualities you like the most about it. Critical Thinking Imagine our language without descriptive words. • Pick a paragraph or two (depending on the length of the paragraph) from your favourite book. • Let each student rewrite that paragraph without using any adjective. • Each student reads the original paragraph aloud, followed by the adjective free paragraph written by them. Discuss why it is important to use adjectives. Life Skills/SEWA Take students for a nature walk and ask them to describe the things in the surroundings using describing words. 2 (b) Articles Duration: 5 hours Skills Listening Listen to the words and interpret which kind of noun the words refer to - singular/plural and common/proper. Story time Speaking We are the Best Read aloud the words to identify whether the word begins with a vowel sound or a consonant sound. Share the rules of using articles with your friends. Reading Identify the picture and read the corresponding words. Use appropriate articles with them (Worksheet on Articles). Sorting Game Writing Use suitable articles for the objects in the classroom. Complete the life cycle of a butterfly by filling articles in the blanks. Multiple Intelligences Musical / Logical / Kinesthetic / Spatial Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Use articles appropriately. - Respond confidently to the kind of noun where an article is to be used. 3 Transdisciplinary Activities Visual Arts Write the names of the animals you know or have seen/heard about. Use ‘a’/‘an’ as required, e.g. a panda, an ostrich etc. Draw their pictures and put the pictures on the display/bulletin board. Critical Thinking Read a write-up from a children’s magazine or a newspaper and observe how frequently articles have been used. Ask the students to encircle the articles and count them. Life Skills/SEWA Find out the names and the habitat of extinct and endangered animals. (c) Blend words (br, tr, dr) and Word origin Duration: 3 hours Skills Listening Listen to the blend words and identify the correct blend. Speaking Form a circle and each student shares as many blend words as possible. Practice blending the sounds into words for reading decoding. The Blender Game Speak a word that starts with the given blend sound. Break the word into two parts - its base word and prefix/suffix e.g. bed+ ridden= bedridden Find out words which are from other languages but are used commonly in our day-to-day language, for e.g. ciao (Italian) means bye, tete-a-tete (French) means person to person discussion. 4 Reading Read the sentences and circle all the blend words used in them. Write ten blend words and frame sentences from them. Writing Multiple Intelligences Learning Outcomes To enhance the vocabulary related to blending words, form words and frame sentences using these words. Musical / Logical / Kinesthetic / Spatial / Interpersonal The students will be able to : - Read and write the blend words correctly. - Know the meanings of the foreign language words which are used in English language and learn to use them in their day-to-day life. Material Required A short story, pencil, paper, flash cards, coloured marker, worksheets, stars with blend words, blank blend cubes. Transdisciplinary Activities Visual Arts Students look for or draw pictures of the objects whose name begins with the blends e.g. trunk, dress, brush etc. Life Skills/SEWA Analyse and understand the interdependence of languages on one another. 5 Environmental Education General Objectives • To develop inquisitiveness about living organisms. • To observe and understand the role of each animal in the environment. • To appreciate the role of animals in maintaining a balance in the environment. • To develop an understanding of animal sounds, their young ones, their adaptation to the natural habitats and their feeding habits based on observation, exploration, comparison and classification. Specific Objectives • To recognize, compare and distinguish between sounds of various animals. • To get acquainted with the names of various animal and their young ones. • To classify animals on the basis of their food habits by observing, exploring and comparing. • To understand the relationship between the body structure of animals and their habitats. • To explore the wonderful world of birds and insects and understand their physical features. • To appreciate the role of animals and birds in maintaining the ecological balance. (a) Animals - their sounds and their young ones Duration: 4 hours Skills Conceptual Powerpoint presentation on various animal Learning sounds. Story time ‘Small piglet looks for Mommy’ Observation Game : Follow the Leader– Act like an animal. Visit a neighbourhood or biodiversity park. 6 Learning by Doing Nature walk Poem : Old McDonald had a farm Write the names of animals from the story ‘Small piglet looks for Mommy’ in the alphabetical order. Application Dramatization of the story – ‘Small piglet looks for Mommy’ Game : Animals and their young ones. Activity: Turtle / Kitten mask. Create a picture glossary of animals and their food. Multiple Intelligences Logical / Spatial / Kinesthetic / Interpersonal / Intrapersonal / Linguistic Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Recognize, identify, distinguish and name the sounds of various animals. - Name the young ones of various animals. 7 (b) Animals and their eating habits Duration: 3 hours Skills Conceptual Learning Powerpoint presentation on eating habits of animals. Observation Visit a zoo, a bird sanctuary or an aquatic museum. Observe animals/pets around you and write about them. Learning by Doing Game of fortune - Know your group. Game : Fire in the jungle, run, run, run. Create an animal album with pictures. Application 8 Food habits of animals (Worksheets). Multiple Intelligences Logical / Kinesthetic / Interpersonal / Intrapersonal / Linguistic Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Classify animals based on their food habits. - Identify the physical features of various animals and the manner in which they eat their food e.g. chew, suck, tear etc. Duration:3 hours (c) Habitat of animals Skills Conceptual Learning Powerpoint presentation - Habitat of different animals. Poem : Down in the ocean Observation Watch the movie ‘The Lion King’ or ‘Nemo’. Discuss about the different types of animals and their habitat. Learning by Doing Activity - Draw a picture of a bird and label its body parts. Find my place. Application Animals and their habitat (Worksheets). Multiple Intelligences Logical / Spatial / Interpersonal / Intrapersonal / Linguistic Learning Outcomes The students will develop the ability to: - Explore, observe, identify and classify animals based on their habitat. - Identify the special physical features of animals that help them in adapting to their habitats. 9 Duration:3 hours (d) Birds and Insects Skills Conceptual Learning Powerpoint presentation on birds and their beaks. Poem: Birds Observation Identify and name the birds that fly high and the ones that do not. Learning by Doing Dummy bird activity -To reinforce the concept of physical features of a bird. Know your feathered friend - Collect information about different types of birds. Application Identify birds and insects (Worksheets). Multiple Intelligences Logical / Spatial / Interpersonal / Intrapersonal / Linguistic Learning Outcomes The students will be able to distinguish between birds, insects and animals. Material Required Movie video or CD, powerpoint presentation, A-4 size sheets, scrapbooks, glue stick, crayons, wool, scissors, 3 paper plates, outer half shells of pistachio, walnut and groundnut, gluesticks, picture of animals, hanging cards with names of parent animal and their young ones written on them, picture of animals, cards with the names of carnivorous, omnivorous and herbivorous animals written on them, craft paper, cut out of pictures of animals, model of an aquarium, dummy of a bird and an insect. 10 Transdisciplinary Activities Visual Arts Make a turtle with outer shells of pistachio, walnut and groundnut. Make a mask of a kitten with paper plates, two small circles, a pink triangle and wool. Physical Fire in the jungle run, run, run (reinforce the concept of Education classification of animals on the basis of feeding habits) Birdie fly (reinforce the concept of classification of animals based on their habitats). Performing Dramatization of the story of ‘The Three Little Pigs’ or any Arts other story relevant to the topic. Life Skills/SEWA Animals are becoming endangered for a variety of reasons. Write a report and send it to your local newspaper. 11 Mathematics General Objectives • To understand the process of addition. • To appreciate the use of Mathematics in everyday life. • To develop the ability to translate the mathematical terms into mathematical operations and perform simple calculations. Specific Objectives • To develop the ability to add the numbers using place value blocks and abacus. • To solve 3 digit addition problems with and without regrouping. • To understand and use the terms - add, plus, sum, total and addend. • To recognize and solve a variety of problems that involve addition. Addition Duration:13 hours Skills Observation Story time- ‘Friendship Day’ and Identification Identify the situations where addition is applied. Magic with beads Observe the patterns when multiples of ten and hundred are added. Kitty finds her mate Identify and observe that the sum of numbers remain the same irrespective of the order they are added in. Logical and Mental I can do it myself Develop the ability to add numbers using abacus. Clap and tap Mentally add the combinations of one digit and two digit numbers or multiples of 10 and 100 through this activity. 12 Lets judge Visualize and comprehend the pictures. Solve the problems of addition. Correlate the solution of a word problem in the addition of 3 digit numbers. Application Lets work together Calculate sum by using addition with addends containing 2 digits or 3 digits. Solve word problems with the help of picture flash cards. Multiple Spatial / Linguistic / Logical / Kinesthetic / Intelligences Naturalistic Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Develop ability to add numbers using value blocks. - Apply the knowledge of addition in their day-to-day situations. - Compute the addition of multiples of ten and hundred mentally. - Acquire aptitude for comprehending and solving picture stories and word problems. - Demonstrate various methods of addition with 2 digit or 3 digit numbers. Material Required Place value cards, plain paper, pencil, beads (red-Hundreds, green-Tens, yellowOnes), flash cards with pictures for word problems, addition sums for commutative property, tiger toy, garland with two different coloured beads. 13 Transdisciplinary Activities . Visual Arts Picture stories with numbers. Physical Education Number games on addition (Flash Cards). Performing Arts Enact a rhyme with numbers. Add numbers to it as you sing. Life Skills/SEWA Appreciate the use and value of addition in our daily life and understand that many lives would be incomplete in the absence of numbers and addition. Visit a pet shop with your mother. Observe the different varieties of pets / animals / birds. Write the names of pets / animals / birds of your choice. 14 Performing Arts General Objectives • To develop an aptitude for music, dance movements and co-ordination. • To use basic vocabulary of performing arts in order to name and describe a performance. • To analyze and develop sensory information. Specific Objectives • To create and imitate movements in response to musical beats. • To use specific actions and sounds to imitate animals. • To integrate the components of rhythm, music and movement. • To create and communicate a simple sequence of movement with a beginning, a middle and an end. Different movements and sounds D Duration: 3 hours Skills Aesthetic Use basic vocabulory of dance and music in order to name and describe a performance. Learning by doing Listen to a variety of musical selections and perform various movements - turn and stretch, bend and twist, hop and skip. Dance on the song choreographed by the teacher following beat and tempos. Application Dance to the music showcasing the various movements learnt. Create sounds and movements using fast and slow tempos. Animal mask dance Multiple Intelligences Intrapersonal / Kinesthetic 15 Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Develop a variety of basic locomotor skills. - Identify how musical elements communicate ideas or moods. - Perform in small and large groups with coordination. Material Required Audio or CD player, songs with strong and weak beats, video of ‘Dance with the Animals by Rock ‘N’ Learn’. Transdisciplinary Activity Visual Arts Collect photographs and information of artists who perform and compose music. Life Skills/SEWA Identify animal characters in stories and cartoons from different cultures. 16 Visual Arts General Objectives • To develop creative and aesthetic sensibilities. • To enhance intellectual abilities that make cross curricular connections using the medium of art. Specific Objectives • To use the elements of art namely line, shape, texture to draw animals. • To develop fine and gross motor coordination and spatial awareness. • To use materials such as clay, paper, paper bags and paper plates to make 3D animals. Clay modelling, Mural, Origami Animals Duration: 3 hours Skills Observation Look for pictures of animals with smooth and rough texture. Visit a library. Collect information of animals and their habitat for the mural. Observe the distinct features of various animals and make a clay model of your favourite animal. Learning by Doing Mould the clay to form an animal, insect and a bird of your choice. Using any pointed tip, add features and texture to the animal. Assemble it to create a mural. Use knowledge of line, shape and texture to draw a jungle or a zoo scene. 17 Make an animal hand or glove puppet with paper bags. Origami animals - cat, cow, fish, frog. Expression Use the given material to depict the features of an animal. Make a family of animals, e.g. cat and kitten, dog and puppy etc. Add features and texture and paste it in the scrap book. Multiple Intelligences Linguistic / Logical / Spatial / Kinesthetic Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Create 3D animals using various mediums. - Use lines and shapes to draw animals. - Work amicably in groups to create a work of art. - Identify the elements of art in the objects and things in nature. Material Required Coloured chalk, drawing paper, sketch pens, construction paper, cartridge paper, brown paper, glue, cellotape, charcoal, sketch pens, drawing paper, oil pastels, drawing paper, pencil. Transdisciplinary Activities Environmental Education Make a book on a to z of animals. Write the name of the animals, their young ones, food habits, habitat etc. Performing Arts Puppet performance depicting jungle scene Life Skills/SEWA Create a drawing to depict how animals are man’s best friend. 18 Physical Education General Objectives • To maintain physical fitness through regular exercise and physical activites. • To demonstrate skills, techniques and strategies while performing activities. • To develop competency in combining movement and motor skills. Specific Objectives • To understand what being athletic means, like being able to run a specific distance without feeling breathless. • To develop the quality of true sportsmanship. • To demonstrate appropriate social skills during a physical activity. Duration: 3 hours Physical activities Skills Learning by Doing Various rigorous physical activities like walking, jumping, hopping, skipping, galloping. Bean bag relay (PEC-5). Throwing and catching (PEC-6). Application Perform aerobic activities in order to maintain endurance. Participate in physical activities like relay race, collecting and chasing objects. Multiple Intelligences Linguistic / Intrapersonal / Naturalistic 19 Learning Outcomes The students will be able to : - Demonstrate competency and proficiency in many physical activities. - Compare and contrast locomotor movements performed on even and uneven beats. Physical Education Cards Material Required Physical Education Cards, PEC Kit. Transdisciplinary Activities Environmental Education Find out the role of animals in different sports. Life Skills/SEWA Value of experimenting while trying new activity. 20 Lesson Plans 21 English Lesson Plan-a Topic: Adjectives/Describing words Duration – 6 hours Brief Description–This lesson involves explaining the concept of adjectives. Extensive use of adjectives helps in improving vocabulary. Individual and team activities, colourful worksheets further strengthen the understanding of the concept. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Recognize and identify adjectives in a sentence. • Write adjectives for the characters of various stories. • Use a specific adjective in a variety of sentences and use it effectively in writing. • Differentiate between the positive, comparative and superlative degrees of adjectives. Material Required A short story, pencil, paper, flash cards, coloured marker. Teacher T Activity Introduce the topic by picking up real life objects e.g. a colorful book, a pencil box, stuffed toys. Ask the students to randomly describe the objects using adjectives. Write the sentences on the board and underline the adjectives with a coloured marker. Example - It is a small pencil. This is a thick book. Show flash cards with pictures of animals, dresses, trees etc. Elicit as many sentences as possible describing the pictures on flash cards. Write the sentences on the board and underline the adjectives with coloured marker. Explain that adjectives are usually placed or written before a noun. 22 Student Activity Activity 1: Fancy World of Nouns and Adjectives Set up two boxes, one labelled as ‘NOUNS’ and the other as ‘ADJECTIVES’. Take 30 index cards (depending on the number of students in the class) and write one noun on each card, for example - dinosaur, centipede and monster. Put them into the box labelled as ‘NOUNS’. Now, write one adjective each on the other 30 or more index cards and put them into the box labelled as ‘ADJECTIVES’. Choose adjectives that are interesting and visual, for example - purple, good, beautiful, young, big and striped. Each student will choose one noun card and at least one adjective card from the boxes. Then, put the adjectives and nouns together and make a drawing (or a collage) of what they describe. The picture must be interesting. Note : If the adjective and noun together represent something realistic, for example big dog, black horse; students will need to choose other adjective. Activity 2: My Menu Card • Give each student a restaurant menu card. (It can be a menu card from a restaurant or one that has been created). • The students write adjectives to describe the food items. Students are likely to come up with words like juicy, tempting, chessy, delightful to describe a burger or sandwich. • In groups of two or four, the students design their own menu card. • For each item on the menu card, one or two adjectives have to be written. • The students can illustrate their menu cards on computer or on a construction paper. Review • Fill the correct adjectives. (Worksheets) • Make sentences (without adjectives) and then analyze the appropriate adjectives that could be used to fill those gaps. 23 English Lesson Plan-b Topic: Articles Duration – 4 hours Brief Description–Articles are used before nouns or noun groups. These are - a, an and the. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Comprehend ‘What is an article?’ • Name the articles and use them appropriately. • Understand that articles are always used with nouns. • Use articles correctly in sentences. Material Required A suitable short story, some stationery items and flash cards with pictures of animals, birds and insects. Teacher Activity Read the story ‘Small piglet looks for Mommy’. On the board, write the words from the story which have an article before it. Explain the correct use of articles. ‘An’ is used before words that begin with vowel sounds e.g. an apple, an emu, an inkpot. ‘An’ is also used before a word beginning with a silent h, e.g. an heir, an honest man, an hour. We use ‘a’ before words that begin with consonants e.g. a pool, a pond, a lake, a river. It is also used before vowels which have the sound ‘yu’, e.g. a unison, a university, a unit. Both ‘a’ and ‘an’ are used only before common nouns. We use ‘the’ before some proper nouns. Example: The Agra Fort, the Bible, the Statue of Liberty. 24 We use ‘the’ before specific nouns which are one of its kind or unique, e.g. the moon, the sky, the earth. The teacher explains further by taking the following examples. a) There is a book on the table. b) The book is on the table. In sentence (a), a book refers to any book. The word ‘a’ makes it clear that we are not talking about a particular book. The word ‘the’ used with the table, however, makes it clear that we are referring to a particular table. In sentence (b), the book refers to a particular book. ‘A’ and ‘an’ are known as indefinite articles whereas ‘the’ is known as definite article. Activity Sorting Game The students will play a “sorting game”. They will look for objects in the classroom and sort them according to the article being used before it e.g. a horse, an elephant, a pen etc. Student Activity Insert the suitable articles in the story read by the teacher. (The teacher reads out a story with the articles missing in them.) There was____ beautiful forest. Many animals lived in _____ forest. They were all great friends and lived happily. One day ____ animal came into the forest. It was _____ fierce lion. _____ lion roared and stamped his feet and asked fiercely, “Is there ___ king in the forest? _______ other animals did not say anything. _____ lion roared more ferociously and said , “I’m ______ new king of the forest ! I shall be _____ honest king. I want you to send me ____ animal as food every day. Then I will not kill you all!” 25 Review We are the Best The class will be divided into two teams. One team will speak out a noun. The other team has to tell which article will be used before it. The teams can pick up tricky words like university, honest man, European etc. The team which responds quickly and gives the correct answer wins the title ‘We are the Best’. Assessment Ask the following questions from the class. 26 • Name all the vowels. Can you identify vowels by their sound? • Write 5 sentences using the articles. • Frame two or three sentences without using any articles. English Lesson Plan-c Topic: Blend words (tr, br, dr) and Word Origin Duration – 3 hours Brief Description–This lesson involves knowledge about blend words and enriches students’ vocabulary by making them aware of the word origins. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Identify the words with blend sounds by listening to them. • Provide suitable examples of blend words. • Understand and learn the words, that have originated from other languages, and their use in English. Material Required Stars with blend words written on them, blank cubes, marker pen. Teacher T Activity “Snail Talk” Hang a few stars in the class with blend words (tr, dr, br) on them. Read out the words in the stars and explain the meaning of each word to the students. Now, the teacher reads out some words and asks the students to tell the initial blend word they hear at the beginning of the word, for e.g. for the word drill, the students will answer ‘dr’. If a students finds this difficult, at first, say the word several times, emphasizing the initial blend until he/she is able to tell the blend word. Encourage the students to frame sentences with the words. Student Activity On a cube, mark each cube face with different phonic blends. Ask the students to form a circle. 27 Each student takes a turn and rolls the cube. She/he says a word with the blend word that the cube lands on, i.e. “tr - tree”. Each student attempts to say a word with that blend word. If she/he is unable to think of a word, then that student has to go in the Blender, i.e. - they have to move in and out of all the gaps in the circle until they arrive at their starting point. Continue till each student has made an attempt to say a blend word and all the blend words have been used to frame words. Know the use of foreign language words in English. Make a collage of words of other languages and their use in English. Put it on the display board to review for a specific time period. p Review Write few words of foreign language used in English. Find the meaning of the root word and the prefix added to it. 28 Environmental Education Lesson Plan-a Topic: Animals - their sound and their young ones Duration: 5 hours Brief Description – Through this lesson, the students will learn the sounds of different animals and the names of their young ones. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Recognize, compare and distinguish between sounds of different animals. • Differentiate between the names and terms used for sounds of animals. • Identify and relate young ones to their parent animals. • Familiarize themselves with the names of young ones of different animals. Material Required Movie DVD or CD, A4 sheets, scrap book, glue stick, crayons, wool, scissors, two paper plates, shells of pistachios, groundnut and walnut, pictures of different animals, flash cards of names of animals and their young ones. Teacher T Activity Discussion (Animal sounds) Initiate a discussion on how living beings communicate with each other. Elicit responses from the students such as talking, writing, actions etc. Discuss whether animals can talk or write letters to each other. Allow the students to answer as per their observations. Explain that animals also make sounds to express themselves or to raise alarm to alert other animals. Nature Walk Take students for a nature walk to help them gain first hand experience by listening to the sounds of various animals and birds. Instruct the students to listen to various sounds carefully. Powerpoint presentation (sounds of animals) Show a powerpoint presentation of different animals and emphasize the sounds that animals make. 29 For example:Cow : moos Horse : neighs Lion : roars Hen : clucks Story: Small Piglet looks for Mommy Narrate the story about a piglet who is searching for its mummy and meets the young ones of many animals on its way. Reinforce the concept through flash cards of animals and their young ones. Student Activity Follow the leader The students form a circle and choose a leader. The leader enacts and says, “We were going through the woods, We came across a monkey, The monkey chattered khao khao…” The students follow the leader. Poem: Old McDonald had a farm Learn the song on different farm animals with their sounds. Add the name of animals to the song. Writing activity From the story, write the names of animals and their young ones whom the piglet met while searching for its mummy. Make a mask (kitten) Make a kitten mask with the help of two paper plates. Use one paper plate to make the face and cut the other paper plate into two halves to make the ears. With two small circles make the eyes, a pink triangle for mouth and some wool to make its moustaches. Picture Glossary Create a picture glossary of various animals and their young ones. Review Worksheets • 30 Match the baby animals with their parent animals. Write their names and colour the pictures. Write the name of the animals, their young ones and the sound they make. Find your young one and run Divide the students into 2 groups. Group A: Parent animals and Group B: Baby animals. Draw two lines at a distance of 50m. The students dressed as animals stand on one side and the students dressed as baby animals stand on the other side. With the blow of the whistle, run and fetch your young ones and come back to the starting line. 31 Environmental Education Lesson Plan-b Topic: Animals and their eating habits Duration : 5 hours Brief Description: Through this lesson, the students identify the different animals on the basis of their eating habits and classify them as herbivore, carnivore, omnivore. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Observe, identify and differentiate between herbivorous, carnivorous and omnivorous animals. • Classify animals on the basis of their eating habits. • Compare the physical features of various animals and their eating habits. Material Required Powerpoint presentation based on the topic, A4 size sheets, gluestick, picture of animals, hanging cards, scrap book. Teacher Activity Introduction Discuss with the students why we classify things such as tools, food, flowers and so on. Explain that classification - the arrangement of objects, ideas or information into groups—makes things easy to find, identify, talk about and study. Relate the topic eating habits of animal to that of human beings. Elicit response from the students about their eating habits and favourite dishes. Continue the discussion explaining the different types of eating habits of animals and let the students share their previous knowledge related to this concept. Visit to a zoo Visit a zoo to provide an opportunity to the students to closely observe the eating habits of different animals and birds. Speak to the person in-charge and collect information related to the eating habits of the animals from the zoo. After the classification activity, introduce the terms herbivorous, carnivorous and omnivorous animals. Talk about the shape of the mouth and teeth of different animals. 32 Explain the same through the powerpoint presentation by showing shapes of mouth, jaws and teeth of different animals as well as their eating habits. • Cow, buffalo and camel nibble food. When they relax, they bring back part of the food from inside and chew it properly. These animals are called chewing animals. • Animals like lion, fox, wolf and cat tear the flesh with their sharp pointed teeth. After that they chew it. • Giraffe’s long neck helps it to eat leaves from tall plants and trees. • Elephants eat with the help of their trunk. • Butterflies and bees suck nectar from the flowers. Elicit responses from the students. Explain the statement with relevant examples. ‘Man is an omnivore’. Justify the statement. Student Activity Guided activity Record the eating habits of the animals seen in the zoo. Explain that the food that the animals consume depends on the shape of their mouth and teeth. After recording the data, compare and classify animals according to their eating habits. Animals that eat only plants Animals that eat only flesh of other animals Animals that eat both animals and plants Elephant Lion Bear Cow Tiger Crow Horse Leopard Rat Game of fortune To play the game, name the groups as herbivorous, carnivorous and omnivorous. Call out the names of different animals and students of that group stand accordingly. For example - if the teacher says camel, immediately the herbivorous group stands up. Through this activity, the concept of classification of animals according to their eating habits will be reinforced. 33 Animal Album Paste pictures of different animals, write the food items that they eat and categorize them according to their eating habits. Observe animals and pets around you. Write a few lines about their eating habits. Review Look at the pictures and categorize the animals according to their eating habits. (Worksheets) Pick up the names of animals from the word maze and write them in the correct column. Provide hanging cards to the students with the names of different animals written on the cards. Make 3 more cards with herbivorous, carnivorous and omnivorous written on them. Paste these cards in 3 different corners in the classroom. On hearing,’fire in the jungle run, run, and run’, students start running and make groups of herbivorous, carnivorous and omnivorous as per their hanging card. Those who are able to join their particular group will be safe. For example: a student who has lion written on his hanging card will join carnivorous group and if found otherwise will be out of the game. Assessment The students can be assessed on the basis of their responses to the following questions: 34 • Give 4 examples of each - Herbivorous, Carnivorous and Omnivorous. • Give two examples of animals who tear their food before eating. • What is the difference between herbivorous and omnivorous animals? Environmental Education Lesson Plan-c & d Topic: Habitat of Animals and Birds and Insects Duration : 3 hours Brief Description–Through this lesson, the students will learn and understand the habitats of animals as well as about birds and insects. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Compare and categorize the animals on the basis of their particular habitat i.e. terrestrial animals, aerial animals, aquatic animals, amphibians and arboreal animals. • Classify different types of animals and their habitat. • Understand how the body structure of different animals is suited to their particular habitat. Material Required Pictures of various animals, cut-out of animals, full size picture with sky, land, trees and water drawn on it, powerpoint presentation, glue stick, craft paper, crayons, A4 size sheets, aquarium. Teacher T Activity Discuss about animals and how they are different from each other in shape and size and why some live on land and others live in water. Habitat of animals Introduce the terms terrestrial and aquatic animals by explaining in detail about these terms and habitat of animals. The animals living on land are known as terrestrial animals and the animals living in water are called aquatic animals. With the help of powerpoint presentation, explain how various animals adapt to their surroundings. Terrestrial Animals: These animals live in desert, like camel. Camel’s hump acts like a storage space for food and water so that it can survive in the desert without food for many days. 35 Similarly, show pictures of habitation of polar bear and reindeer on ppt. Explain that their body structure is designed in a particular manner to suit the habitat and viceversa. Polar bear has thick fur which protects it from the cold and reindeer has broad hooves that help it to walk on snow. Arboreal Animals: Ask simple questions like ‘Name the animals that live on trees? ‘Why do these animals live on trees?’ Elicit responses from the students. The animals that live on trees are called Arboreal animals. Show an aquarium or a model of it to students and ask questions to trigger their logical and critical thinking. • “If you take out a fish from the aquarium, will it be able to live for long?” Give reasons to support your answers. • Can you breathe under water? • How do fish breathe inside the water? After listening to the answers, display pictures of the parts of a fish and explain that a fish swims with its fins, changes its direction with the help of its tail and breathes with the help of gills. Show the pictures of aquatic animals such as dolphins and whales and make students aware of the fact that whales and dolphins also use fins to swim but they do not have gills and they come to the surface of the water to breathe. Explain the concept of amphibians by showing a ppt with clipping of tortoise, crocodile, frog etc. To make the lesson more interactive, discuss the shape of a frog’s back legs that help it to hop and swim. Elicit response for why human beings cannot fly. Ask ‘how will it feel to fly?’ Show picture of birds and explain that the wings of birds help them to fly and they have light bodies and hollow bones which further help them to stay in the air. These types of animals are called Aerial animals. Student Activity To check the previous knowledge of students provide a worksheet with animals drawn on it and ask the students to write ‘Land’ for the animals that live on land and ‘Water’ for the animals that live in water. Students will complete this worksheet based on their observation and knowledge of animals in their surroundings. Draw a fish and a bird. Label its features. 36 Find my place On a board, place a scenery or a poster showing land, water, trees and sky. Give each student a cut-out of an animal and ask him/her to place it on the poster categorising it as terrestrial, arboreal, aerial or aquatic animal. Review Worksheets Give two examples each of aerial, terrestrial, aquatic, amphibians and arboreal animals. Read the clues and solve the animal puzzle. Name, draw and colour two terrestrial and two aquatic animals. Down in the ocean Recite the poem with rhythmic body movement. Be Quick Sit in a circle and blindfold a student’s eyes. The students will move in a circle and point towards another student and call out the names of different categories of animals on the basis of their habitat like arboreal. The student towards whom he/she points will have to name an arboreal animal within a fraction of seconds. If unable to name the animal of that particular category, the student will be considered out. Assessment The students’ knowledge and understanding can be assessed on the basis of the following questions: • Classify the following animals on the basis of their habitat i.e. terrestrial, arboreal, amphibian, aquatic and aerial. Squirrel, frog, polar bear, elephant, monkey, snake, fox, fish, shark, kiwi, ostrich, parrot, pigeon, lion, octopus, crocodile, alligator. • What are arboreal, amphibian and terrestrial animals? 37 Mathematics Lesson Plan Topic: Addition of three digit numbers Duration : 13 hours Brief Description - In this lesson, the students learn and appreciate the addition of 3 digit numbers. This is successfully achieved through the use of abacus, use of place value blocks, adding with and without regrouping, solving word problems through pictures, verbal description and through stories. The lesson also deals with commutative property in addition, adding zero to a number and adding multiples of ten and hundred mentally. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to: • Add 3 digit numbers with and without regrouping. • Comprehend and solve word problems. • Mentally add multiples of ten and hundred. • Express and represent things in data through mathematical operations. Material Required Abacus, place value cards, plain paper, pencil, beads (red - Hundreds, green - Tens, yellow - Ones), flash cards with pictures for word problems, addition sums for commutative property, tiger toy, garland with two-coloured beads. Teacher Activity Take 5 red beads and 7 blue beads in two different jars. Put them together in one jar. Ask the students to count the total number of beads in the jar. Now, increase the quantity of beads in the jar by 10. Ask the students to count the number of beads again. Recall that addition means bringing things together and there are two situations in the addition: when two or more quantities are combined to get a single quantity and when a quantity is increased by some amount. Write the addition sentences for the above two situations. Bring a bag with number flash cards. Ask the students to take out two numbers from the bag and add them. 38 Here is how you do it. Shake and take two cards 5 + 7 = 12 12 + 10 = 22 Show the bigger number Explain that the numbers we add are called addends and the result obtained is the sum. The final result is always greater than the numbers we add. Student Activity Explain that the purpose of this lesson is to make the addition of large numbers easier, i.e. addition of three-digit numbers through the following activity. Activity : ‘I can do it myself’ Show the abacus where the hundreds place is located in reference to ones and tens place. Divide the whole class into groups of 3-4 students. Each group is given the following things a) Abacus b) Colourful beads ( 20 of each colour) c) Plain paper d) Pencil Take place value cards and arrange them in three piles. Example One pile of hundreds One pile of tens One pile of ones 39 Call two students from each group. First, one student picks up a card from each pile to make a three digit number. For example 6 2 3 So the number formed is 623 Now, the second student picks up one card from each pile and forms a 3 - digit number For example 2 4 5 So another number formed is 245. The two students write both the numbers on a plain paper and join their group. The group finds the sum of these two numbers with the help of an abacus. First separate out the beads according to their colours, i.e. red - Hundreds, green - Tens, yellow - Ones. Arrange the beads to make the number 623 on the abacus. H 40 T O Now the next number is 245. So the students add: 2 more red beads in hundreds. 4 more green beads in tens. 5 more yellow beads in ones. H T O Count the number of beads in each rod to find the sum of 2 numbers . Observe the number of beads. 8 red beads in hundreds. 6 green beads in tens. 8 yellow beads in ones. So, 623 +245 = 868 To learn simple addition of 3 digit numbers, repeat the activity with more numbers. Explain step by step addition of 3 digit numbers by writing in columns. H T O Step 1 6 2 3 Add ones: 3 ones + 5 ones = 8 ones + 2 4 5 Step 2 8 6 8 Add tens: 2 tens + 4 tens = 6 tens Step 3 Add hundreds: 6 hundreds + 2 hundreds = 8 hundreds Reinforce the concept though worksheets. 41 Activity: 3 digit numbers with regrouping The place value cards are arranged in such a way that addition of two 3 digit numbers require carry over. For e.g. if the first student picks up one card from each pile, the number is 368. i.e. One pile of hundreds One pile of tens 300 60 One pile of ones 8 The second student picks up the following cards - 100 70 4 The number is 174. The students note down both the numbers on a plain paper. Now, they arrange these numbers on the abacus in the following manner. H 42 T O Count the beads in ones row and the number of beads in ones = 12 Explain that since total number of beads in ones is 12, i.e. 10+2. So, 10 yellow beads can be removed from ones and in place of that one green beads can be added to tens rod as 10 ones = 1 ten Ask the students to count the number of green beads in tens rod. There are 14 tens now. 10 tens = 1 hundred So, 10 green beads can be removed from tens rod and in place of that one red bead is added to hundreds rod. So, total number of beads in the abacus are as follows: H Red T Green O Yellow Therefore, the sum of 368 +174 is 542 Give few more numbers to practice addition of 3 digit numbers with regrouping. (Worksheets) Explain that by adding 368 and 174, the answer is 542 i.e. 5 hundreds, 4 tens, 2 ones. Regrouping is further explained by using the board. Arrange the same numbers on the board by making columns on the board, like - 43 Regrouping + Step 1 H T O 3 6 8 1 7 4 5 4 2 Add ones: 8 ones + 4 ones = 12 ones 12 ones = 1 tens + 2 ones Step 2 Add tens : 6 tens + 7 tens + 1 tens = 14 tens 14 tens = 1 hundred + 4 tens Step 3 Add hundreds : 3 hundreds + 1 hundred+1 hundred = 5 hundreds Give few more problems to the students to reinforce the concept of regrouping in addition. Activity : Magic with beads Make a garland using a long string and coloured beads. Put 10 red and 10 white beads in alternate groups with a total of 100 beads along with number tags of 100, 200……….900. Show the string to the students and ask the following questions. Q1. Name the colour of the beads you find in the string. Q2. How are they arranged ? Q3. Count the total number of beads. Students count 1,2,3……………100. Explain that since counting so many beads together in such a manner is a long method. So, we arrange the beads in groups of 10. Student count the number of tens on the string along with the teacher like 10, 20, 30, and so on. Total number of beads is counted as 100. Now each group of beads here represents 1 ten. 10 tens = 1 hundred Hang the tags of 100, 200, 300 and so on after 10 beads each. 44 Ask the following questions : Q1. What is the value of each bead now? Q2. How many beads form one hundred? Write two numbers on the board 134 and 257. Ask the students to find the sum of these numbers using the beads on the string. Write the expanded form of the numbers as – 134 : 1 hundred + 3 tens + 4 ones 252 : 2 hundreds + 5 tens + 2 ones Count single beads to get (4+2) ones i.e. 6 ones, Take 10 ones = 1 ten So, 3 tens + 5 tens =8 tens For adding hundreds take one bead as 10. Count total number of hundreds as 100, 200 and put the marker on 300. Thus, 134 + 252 = 386 Addition of multiples of hundred mentally Further, explain how to add two numbers mentally. 400 + 300 = 700 Add numbers at hundreds place 4 + 3 = 7 45 Commutative Property of addition: Explain the commutative property of addition or also called order property of addition. This property means that addends can be added in any order and the sum obtained always remains the same. Explain the commutative property by taking the following examples using two coloured beads. 3 + 2 =5 + = + = or 2+3=5 The students observe when 2 green beads are added to 3 red beads or vice versa, the total number of beads in both the cases is 5. To develop problem solving aptitude and ability to comprehend and solve picture stories and word problems among students, take up the following activities. Material Required: Picture sheets. Distribute the worksheet to each child and tell them to look at the picture. Large Fish 125 How many fishes are there in the sea? 46 Small Fish 115 Students look at the picture carefully and answer the following questions: Q1. How many large fishes are there? Q2. How many small fishes are there? Read the sentence given below the picture. Then, draw a key diagram for the problem on the board like:- 125 + Number of large fishes 115 = Number of small fishes Total fishes in the sea Explain that the number in the first circle represents the number of large fishes and the number in the second circle represents the number of small fishes, ‘+’ sign represents total. Ask the students to solve the problem 125 + Number of large fishes + 115 Number of small fishes = 240 = Total fishes in the sea Provide more word problems by drawing pictures on the board or by giving worksheets of same kind to the students . 47 Activity : Story Time Narrate a story “Rabi Celebrates Friendship Day”. Once there was a rabbit whose name was Rabi. One day, he was watching his favourite cooking show on the television when the door bell rang. He opened the door and was surprised to see his best friend Sami, the turtle, in front of him. He hugged his friend and asked him to come inside the house. Sami was meeting his friend after five years. So, he was very happy. As it was too hot outside, Rabi switched on both the fans and the room-cooler. Sami Rabi 48 Q: How many things did Rabi use to keep the room cool? Continue the story. Sami said to Rabi, “Can you get me something to drink. I am feeling thirsty.” Rabi said, “Oh! Yes”. He went and brought 2 cans of mango drinks and 3 cans of mixed fruit juice for him from the fridge. The teacher asks Q: How many cans did Rabi take out from the fridge? After some time Rabi said, “I want to make this day memorable. I will make a ‘chocolate cake’ for you. Would you help me?” Sami said, “Why not?” They both went into the kitchen. Rabi took out 4 eggs from the egg carton, 1 packet of flour, 1 packet of castor sugar, 1 can of drinking chocolate, 1 packet of butter and 2 glasses of milk. Q: Can you tell me how many ingredients did Rabi use to make the cake? Rabi mixed all the ingredients and kept the cake in the microwave oven for 5 minutes. The cake needed some more time to be baked. So, he kept it for three more minutes. Q: How long did it take to bake the cake in the microwave? Once the cake was ready, Rabi decorated it with the icing writing ‘Happy Friendship Day’. Sami had tears in his eyes when he saw the cake. Both of them ate the cake together, played a lot of games and made their meeting memorable. Ask the following questions. 1. 4 eggs + 3 eggs = _________________ eggs. 2. 5 cans of juice + 4 cans of juice = _______________ cans of juice. 3. 4 cups of flour + 4 cups of flour = _______________cups of flour. 4. 3 packets of butter + 3 packets of butter = 5. 2 bottles of milk + 7 bottles of milk = _____________ packets of butter. __________________ bottles of milk. 49 Activity: ‘Let’s judge’ Enter the class with the following picture cards and a tiger toy. TEAM A TEAM B Narrate the following story. Once there was a jumping competition in the jungle. All the animals gathered in the jungle. Two teams were made - Team A and Team B. Show the picture card of Team A to the students and ask them the following questions. Q1. Can you recognize the animals in Team A? Ans: Yes, - rabbit, deer, cat and bear. Q2. How many members are there in this team? Ans: 4 Show the picture card of Team B and ask similar questions. Now, call and ask one of the students to hold the toy tiger. Make the tiger, the Judge of the competition. The tiger explains the rules of the competition to both the teams. 50 a) Number of times each animal jumps, it gets a score of one. b) If any animal is not able to jump at all, the score will be 0. c) Each one has to jump on one leg. Team A After this, the tiger whistles and the competition starts. The performance of Team A is like this:Rabbit jumped - 50 times Deer jumped - 20 times Cat jumped - 30 times Bear could not jump at all. Write the score of each animal on the board . Score of Team A Rabbit - 50 Deer - 20 Cat - 30 Bear - 0 Team B The performance of Team B is like this – Tortoise could not jump at all. Mouse jumped - 60 times Fox jumped - 10 times Monkey jumped - 50 times Score of Team B Tortoise Mouse Fox Monkey - 0 60 10 50 51 Add the score of both the teams on the board. Team A :- 5 tens + 2 tens +3 tens + 0 = 10 tens + 0 = 1 hundred + 0 = 100 + 0 = 100 Team B :- 0 + 6 tens + 1 tens + 5 tens = 0 + 12 tens = 0 + 10 tens + 2 tens = 0 + 1 hundred + 2 tens = 0 + 100 + 20 = 120 Q: Which team is the winner? The judge gives a trophy to the winning team, i.e. Team B. Conclude the story. Zero when added to any number gives the number itself. Add the scores of the other team members with the member who scored zero. 60 + 0 = 60, 100 + 0 = 100 and so on. Activity : Clap and tap Explain the rules of the game. • Be alert and listen carefully to the number of times tapping is done and the number of times clapping is done. • 1 tap is equal to 100 1 clap is equal to 10 Select one student as the LEADER. Whisper a number, e.g. 320 in his/her ear. The student demonstrates the number through claps and taps to the whole class. The rest of the students have to guess the number and the student who gives the right answer first is declared the WINNER and is called upon to be the LEADER. For 320, the 52 student taps the table 3 times, says plus and claps 2 times. Explain that this means 300+20 i.e. 320. In this way, each student gets a chance to demonstrate the number whispered in his ears through action. Ensure to whisper only those numbers which are multiples of 10 so that students can add up mentally. The numbers can be 410, 460, 720 and so on. Activity : Kitty finds her mate Distribute flash cards with simple addition problems to each student. Half of the problem is written on one flash card and the other half of the same problem is written on the other flash card only with addends reversed. Give a cut out of a kitty to each child. Mix up all the cards so that the flash cards with the same problem are not placed next to each other. 300 40 + + 40 300 Ask the students to add up the numbers given on the flash card and write the answer on the cut-out of kitty. When all the students finish solving the sum, they find out the mate of their kitty, the cat. All the three numbers have to match, e.g. one student announces the number on his kitty as 340. It is possible that 3 - 4 students may raise their hands as their kitty could also have the same number i.e. 340. The student have to announce the number on the flash card also. If all the cards match, only then it is declared that kitty has found her mate. 53 The game continues till every flash card gets matched with the other flash card of the same problem and the same answer. 300+40 = 40+300 = 340 Wind up the game by explaining that, whatever may be the arrangement position of addends in the problem, the answer remains the same. Take up few more examples by writing the numbers on the board. 100 + 50 = 50 + 100 = 150 200 + 300 = 300 + 200 = 500 Activity: Let’s work together Flash cards with a word problem written on each one of them. Ask the students to work in pairs. Each pair is given a flash card. Example : There are 150 frogs and 100 toads in a pond. How many frogs and toads are there in all ? Frogs 150 54 Toads 100 Review Worksheets will be given to the students to practise addition. Assessment Students are assessed based on their knowledge related to the topic, participation in class activities and how efficiently they are able to apply the concept in their day to day life. 55 Performing Arts Lesson Plan Topic: Different movements and sounds Duration: 3 hours Brief Description– The students will understand and learn a variety of combinations of locomotor skills and sounds. Learning Objectives As a result of this lesson, the students will be able to: • Identify and create sounds and movements using fast and slow tempos. • Perform simple repetitive movements and steps in accordance to the beat of the music. Material Required Audio or CD player to play songs with strong and weak beats, camera, video “Dance with the Animals by Rock ‘N Learn”. Teacher Activity Introduce the lesson based on the previous knowledge of students related to beats. Play a piece of music and ask them to clap or move with the music. Again play the music, ask the students to listen and tap to the beat and invite them to share their experience. Continue further by dividing the class in two groups where they respond to music through purposeful movement e.g., swaying, marching, tapping, clapping to a variety of musical selections. Play a marching music where one group has to march and explain that it is because of the rhythmic and marching beats. The other group claps to the beat. Play a contrasting piece of music (lullaby) and encourage the students to move according to the music. Explain why they moved in such a way and whether they could clap along with the beat. Link the topic with the real life situations. Discuss about the regular beating of the heart – listen to the sound of a heartbeat. Explain why sometimes it is faster and sometimes slower. Think of other things that have regular beats e.g. a clock. 56 Sing songs with strong pulse – the Grand Old Duke of York, Pop go the weasel – and ask the student to observe whether they sit still or move along the song as it is played or sung. Before taking the next activity work out atleast one sample of choreography for each meter depending upon students’ abilities. The choreography consists of simple marching (left-right-left-right) to a duple meter, reserving steps, hops, turns and other weight-shifting movements for strong beats. The teacher demonstrates same on the beat: step forward on one, back on two. Kicks, foot slides and shuffles can be performed on weaker beats. Try using claps, finger snaps and other action that don’t involve shifting the entire body. Teach the choreography to the students and encourage them to “dance” to the music. Student Activity Perform the learnt choreography and try to incorporate new steps. Show the video ‘Dance with the Animals’ by Rock ‘N Learn. Encourage the students to imitate movements and sounds of the animals shown in the video. Wear your favourite animal’s mask and take part in the ‘mask dance competition’. Imitate sounds and movements of animals and use them in your performance. Review The students choreograph their own moves according to the beat and the meter. They imitate sounds and movements of animals and use them in their performance. Assessment The students are assessed based on their ability to learn movements correctly following the beats and the meter and whether they can do the activities independently or not (without stopping to imitate the teacher or other students). 57 Visual Arts Lesson Plan Topic: Clay modelling mural Duration: 3 hours Brief Description–This lesson introduces the students to clay modeling and making animals with origami. Learning Objectives By the end of this lesson, the students will be able to : • Draw animals giving emphasis on minute details. • Make animals with the help of origami and clay. • Work amicably in groups. Material Required Construction paper, pastel sheets, mount board, reusable boxes, paper bags, paper plates, paints, googly eyes, buttons, string, glue, staplers. Teacher Activity A corner of the class is chosen where a mural of a jungle with a variety of animals will be depicted. The mural also incorporates a puppet theatre where students use animal puppets to narrate a story, sing animal songs etc. Some of the animals can be a part of the mural while others can be made as puppets to be used for the performance. Make mobiles of few animals/birds to hang. Student Activity Students are divided into two groups. One group draws trees, bushes etc. and the other group draws animals, birds, insects etc. for the mural. Students are allowed to trace outlines of animals if they wish to. Paint the objects. In consultation with the English/EE teacher, a story is decided and hand/glove and stick puppets necessary for the storyline are made during the art class. A table is set up with paper plates, paper bags, buttons, googly eyes, crepe paper etc. Students are given basic instructions on how to convert a paper plate/paper bag into stick and hand/glove puppets. They are, then, divided into groups. A bowl of paper slips with the names of animals is circulated and each group picks two. They perform 58 their next task with the names of animals given in these slip. The Task Make 2 animal puppets and present a performance with them. The Scene: • A story • A song on animals in their habitat. The puppet performance can be made open for viewing for other classes. The performance of students is evaluated as per the rubric. A sample rubric is given below. Creativity of the Can you identify material used the animal clearly? Performance Teamwork Suggestions Review The puppet making task reflects the creative skills of the students. Suggested activities : • A visit to an animal farm and/or a zoo before starting the unit will be visually enriching for the students. • Diorama of an aquarium can be created / drawn. • Use imagination to draw/create a 3D diorama - a fantasy habitat with fantasy animals. • Aluminium foil sculptures of animals. Assessment Assess the students’ work based on the following details : • Application of their previous knowledge of line, shape, texture in order to draw animals. • Work together in groups to create a work of art. • Follow step by step instructions. 59 Physical Education Card 5 Bean bag relay Use these activities to: • improve speed over short distances. • change direction while moving. • improve the bending skills needed to play games like Kho Kho. • explain the directions used in Kho Kho. How to play In teams • • • 60 First player has two bean bags, one red and one green. Run and place the red bean bag in first circle and the green bean bag in second circle. Run around the cone and return to the starting point collecting the green bean bag and red bean bag and pass them to the next player. Variations • Place bean bag onto a cone rather than in a hoop. • Reduce/increase the distance between the hoops. • Once both bean bags have been collected, throw them to the next player. Equipment • 2 bean bags per team, one red and one green. • 2 hoops per team. Ropes can be used to create circles or draw the circles with lime powder. • One cone per team. • Lime powder or markers. Safety Measures • Make sure that there is enough space between the groups so they have enough room to run without bumping into each other. • Watch out for others’ safety. • Make sure that the surface is not slippery. Links to other subjects English: Comprehension through pictures • Place the names of animals in one hoop and the names of their babies in the other e.g. cat and kitten. Children run and pick up the name or picture of an animal from the first hoop. They run to the second hoop and find its baby. Mathematics: Geometry • Place numbers into hoops: tens in one hoop and ones in the other hoop. Children run and pick up a number from the first hoop (e.g. 4 ‘tens’) and a number from the second hoop (e.g. 3 ‘ones’). What is the number you have made with the tens and ones (e.g. 43)? Compare it with other players. Curriculum links • Linked to the learning objective no. 14 in the CBSE School Health Manual and the Theme on Movement Awareness in the NCERT Syllabus: What are the other forms of movements? Self Assessment • Can I explain the game to a friend? 61 Physical Education Card 6 Throwing and catching Use these activities to: • improve throwing and catching skills. • learn to work with others safely. • use throwing and catching skills in simple games. Activities In groups • • • • • 62 Throw and catch to self. (1) Throw and catch to a wall. (2) Drop a ball and catch it. (3) Bounce a ball downwards 2 or 3 times and catch it. (4) Throw a ball up, clap (one, two, three) and catch the ball. (5) • Play simple versions of Gitte: (6) • throw a small ball up, pick up an object before the ball is caught . Variations • Set challenges: how many catches can you make before the ball is dropped? • Use the widest range of soft throwing objects possible. Equipment • A variety of balls and other objects that can be thrown: bean bags, rings. • Lime powder or markers. Safety Measures • Use lightweight or soft balls only • Space activities. • Watch out for others’ safety particularly when collecting and chasing objects. Links to other subjects English: read simple words • Throw a ball at letters placed on the ground or on a wall. Have three or four attempts and try to make a word. Mathematics: Geometry • Children throw and catch the ball themselves while walking in straight and curved pathways and in triangular, square and circular pathways. Curriculum links • Linked to the learning objective no. 5 in the CBSE School Health Manual and the Theme on Movement Awareness in the NCERT Syllabus: What are the other forms of movements? Self Assessment • How good am I at throwing a ball to another player? How good are my catching skills? 63 Assessment 64 English By the end of this unit, the students will be able to : • Acquire a complete knowledge of adjectives. • Use appropriate words to describe a noun. • Identify vowel and consonant sounds and use articles accordingly. • Speak various words with blend sounds. • Know about words that originated in languages other than English. Rubrics for the unit Expected Learning Outcomes Indicators of the student’s performance Developing Achieved The student is able to : The student is able to : The student is able to : Understand the use of adjectives to an extent though needs assistance to describe a noun as per its appearance. Use an appropriate describing word for a noun. Clearly understand the use of vivid adjectives with nouns. Provide words to describe a noun with the given clues. Use them properly in the writing process. Knowledge about articles and their use Understand that articles are used before common noun but does not apply it aptly. Use articles but lacks in their correct application at certain places. Use articles without assistance and knows where to omit them. Ability to recognize blend words and word origin Read the blend words but finds it difficult to identify them on listening. Identify blend words by their sound and frames a few words with the same blend sound. Identify blend words and frame sentences using them. Familiarity with the use of describing words with nouns Beginning Use words of foreign origin without knowing the origin of the word. Use words of foreign origin independently. Use a few words of foreign origin. 65 Environmental Education By the end of this unit, the students will be able to : • Recognize, identify, name and distinguish between sounds and the young ones of animals. • Classify animals on the basis of their habitat and eating habits. • Identify features of birds and insects. Rubrics for the unit Expected Learning Outcomes 66 Indicators of the student’s performance Beginning Developing Achieved The student is able to : The student is able to : The student is able to : Animals - their sounds and their young ones Recognize a few sounds of animals and identify babies of common animals. Name the sounds and young ones of animals most of the time. Explain and specify the sounds and young ones of animals. Animals and their eating habits Classify animals on the basis of their habitat i.e. wild, domestic, farm animals but is unable to classify on the basis of eating habits. Classify the animals on the basis of their eating habits with guidance and support. List the eating habits as well as the manner in which animals eat i.e. chewing, tearing, etc. Habitat of Animals Tell and classify animals based on their habitat i.e. wild and pet animals though cannot connect to the extended density of the given concept. State the habitat of common animals and classify them into herbivore, carnivore and omnivore. Compare and contrast the habitat of various animals and state reason for the difference in their habitat. Birds and Insects Distinguish between birds, insects and other animals and name only a few features like wings and eyes. Understand the types of beaks and can distinguish between birds and insects that can fly. Categorize birds and insects according to their physical features. Mathematics By the end of this unit, the students will be able to : • Add 3 digit numbers with and without regrouping. • Comprehend and solve word problems. • Add multiples of ten and hundred mentally. • Understand the significance of addition and use it in their real life. Rubrics for the unit Expected Learning Outcomes Indicators of the student’s performance Beginning Developing Achieved The student is able to : The student is able to : The student is able to : Addition of three digit numbers with and without regrouping Solve the addition sums on abacus and in columns without regrouping but needs support in solving addition sums with regrouping. Solve the addition sums on abacus and in columns with and without regrouping. Solve addition sums with accuracy using abacus place value blocks with and without regrouping and also use mental skills to find the solution. Understanding the commutative property of addition Relate the commutative property of addition but is unable to apply it. Define the fact that the sum is the same even if numbers are added in any other order but needs help in applying it as a commutative property. Understand and apply the commutative property of addition independently. Pictorial problems in addition and creation of stories Comprehend the pictures but is unable to solve the problems. Comprehend and solve the problems with simpler operations. Comprehend and solve any kind of word / picture problem and can create own stories and statements. Application Apply knowledge with limited effectiveness when solving the sums in steps on Abacus and paper by mentally adding numbers. Apply knowledge with considerable effectiveness when solving the sums in steps on Abacus and paper by mentally adding numbers. Apply knowledge with high level of effectiveness when solving the sums in steps, on Abacus and paper by mentally adding numbers. Demonstrates the use of the concept in real life situations. 67 Teacher Resource Material 68 Teacher Resource Material English Material Required A short story, pencil, paper, flash cards, coloured marker, a suitable short story, some stationery items, worksheets, stars with blend words, blank blend cubes . Books: Hairy, Scary, Ordinary: What Is an Adjective? by Brian P Cleary Websites for Reference teacherexpress.scholastic.com www.K-3TeacherResources.com www.superteacherworksheet.com Environmental Education Material Required Movie video or CD, powerpoint presentation, A-4 size sheets, scrapbooks, glue stick, crayons, wool, scissors, 3 paper plates, outer half shells of pistachio, walnut and groundnut, gluesticks, picture of animals, hanging cards with names of parent animal and their young ones written on them, picture of animals, cards with the names of carnivorous, omnivorous and herbivorous animals written on them, craft paper, cut-outs of pictures of animals, model of an aquarium, dummy of a bird and an insect. Books: The Jungle Book by Diane Wright Landalf Audio-video: : Powerpoint presentation - Animal sounds, Eating habits of animals, Habitat of different animals, Tails of animals and Birds and their beaks Websites for Reference http://petcaretips.net/bird-poem.html http://www.teacherexpress.scholastic.com Mathematics Material Required Abacus, place value cards, plain paper, pencil, beads (red- hundreds, green tens, yellow-ones), flash cards-with pictures for word problems, addition sums for commutative property, picture cards, tiger toy, garland with two different coloured beads. Websites for Reference www.lessonplanet.com www.coolmath4kids.com math.pppst.com www.lessonplanspage.com 69 Performing Arts Material Required Audio or CD player to play songs with strong and weak beats. Books: Carnival of the Animals: Classical Music for Kids Camille Saint-Saens (Author), Barrie C. Turner (Author), Sue Williams (Illustrator) The Animal Boogie PBWCD (Sing Along With Fred Penner) Debbie Harter (Author) Audio-video: Dance with the Animals by Rock ‘N Learn. Websites for Reference www.songs4teachers.com www.lessonplanspage.com www.emusic.com/album/Songs www.musicroom.com/Song www.rhymes.org.uk Visual Arts Material Required Colour chalk, drawing paper, sketch pens, construction paper, cartridge paper, brown paper, glue, cellotape, charcoal, sketch pens, drawing paper, oil pastels, drawing paper, pencil, clay, books from the library, reference books, construction paper, pastel sheets, mount board, reusable boxes, paper bags, paper plates, paints, glue, staplers, origami paper, instruction sheets (Annexure 1) Books: Art for the Very Young: Ages 3-6 [Paperback] Elizabeth Kelly (Author), Joanne Mcconville (Author) Websites for Reference www.origami-fun.com www.enchantedlearning.com 70 Blend words dr Blends List drab drawer drink draft dread drip drag dreadful drive dragon dream drop dragonfly dreary dreary drown drain dress drum drama dribble drummer dry drastic drift brother bracelet brainwave broken brilliant bracket branch breakfast brass bravado breakdown breakthrough bristle brittle brute breath breathe bridge bribe broadcast broomstick bright bridesmaid brought bread trace track trade trail train trait transit trap trauma tread treat trend triangle trick tried trim trolley trophy trouble trowel truce true trumpet trunk truth br blend words tr blend words 71 Story: Small piglet looks for Mommy The small piglet cannot find her mother. She runs to the field and sees the cow. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the calf. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the pond and sees the duck swimming. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the duckling. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the big house and sees the dogs playing. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the puppy. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the stable and sees the horse standing. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the foal. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the hill and sees the sheep grazing. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the lamb. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the orchard and sees the goat eating leaves. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the kid. “This is my mommy.” 72 The small piglet runs to the old garage and sees the owl dozing. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the owlet. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the kitchen and sees the cat drinking milk. “Mommy?” she calls. “This is not your mommy.” says the kitten. “This is my mommy.” The small piglet runs to the sty and sees the pig. “Mommy?” she calls. “There you are!” cries the mother pig. “Where have you been, small piglet?” “I was looking for you,” answered the small piglet. “And I was looking for you,” said the small piglet’s mommy. By: Vivekananda Roy Ghatak 73 Down in the ocean Down in the ocean what do you see? A big fish, a small fish, swimming in the sea Swimming, swimming aha-ha-ha-ha Up in the blue sky, what do you see? A big bird, a small bird looking at me Flying, flying aha-ha-ha-ha Out in the garden, what do you see? A white butterfly, a colourful butterfly Sucking nectar, sucking nectar aha-ha-ha-ha Up on the tree, what do you see? A big monkey, a small monkey, jumping on the tree Jumping, jumping aha-ha-ha-ha Birds Look at the bird Up in the treetop Building its nest With no time to stop Hatching its eggs So smooth and so round Then feedings its babies Worms from the ground Look at the bird With the beak for a mouth When it gets cold The birds will fly south When it gets warm The birds return Let’s watch how the birds live And see what we learn 74 Pop Goes The Weasel Half a pound of tuppenny rice, Half a pound of treacle. That’s the way the money goes round, Pop! goes the weasel. A penny for a spool of thread, A penny for a needle. That’s the way the money goes, Pop! goes the weasel. All around the cobbler’s Bench The monkey chased the weasel. The monkey thought t’was all in fun, Pop, goes the weasel. A penny for a spool of thread, A penny for a needle. That’s the way the money goes, Pop! goes the weasel. That’s the way the money goes, Pop! goes the weasel The Grand old Duke of York. The Grand old Duke of York he had ten thousand men He marched them up to the top of the hill And he marched them down again. When they were up, they were up And when they were down, they were down And when they were only halfway up They were neither up nor down. 75 Annexure 1 Origami- Sitting Dog Origami - Dog 76 Origami- Pelican Origami- Twirling bird 77 78 English (a) Adjectives/Describing words Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. Circle the adjectives that describe the underlined nouns. II. a) I stepped into the room. It was cold and uninviting. b) Plant eating animals are called herbivores. c) The miners stood, alert and watchful, as the fuse was lit. d) The lion is the king of the jungle. e) Strange creatures, wild and untamed, roam around the high mountains. Place the most appropriate adjective before the noun. a) ______________ apples. (red, bitter, huge) b) _____________ geese. (wild, tiny, colourful) c) _____________ lion. (thick, tasty, angry) d) ______________ horse. (fast, black, tall) e) _____________ dog. (faithful, sweet, wild) 79 Adjectives/Describing words I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Add –er and –est to form the correct degree of adjective. tall fast taller faster tallest fastest loud safe wet low large II. Fill in the blanks by using the correct degree of adjective. a) I have a small dog but Tina‛s dog is small_____. b) Who is the fast_____ person in your class? c) Ali and I are young but I think you are the young_____. d) 80 Are you old____ than your sister? Adjectives/Describing words I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Help Simba to complete this crossword with the help of the given clues. 1 8 9 10 2 11 3 12 14 4 13 5 6 7 Help me please! Note: All the answers are adjectives. 81 82 Across Down 1. a period of hundred years 8. replace a letter from the word ‘tasty‛ with ‘n‛ to make it the opposite of pleasant 2. add ‘s‛ to the word mall 9. the colour of grass 3. the opposite of old 10. the opposite of thin 4. the number after nine 11. “weight of the feather”, rhymes with night 5. the size of an elephant 12. not kind 6. February – the ________ month of the year 13. the word that means good, rhymes with ice 7. the number of moons our earth has 14. the number of toes our left foot has (b) Articles I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Put a tick mark against the correct answer and write the same in the given space. 1. ______ owl. i) a ii) an 2. _______ angel. i) a ii) an 3. ________ European. i) a ii) an 4. ________ yatch. i) a ii) an 5. ________ horse. i) a ii) an 83 II. Fill in the blanks with ‘a‛ or ‘an‛. 1. __________ elephant has big ears. 2. _______ goat is _______ animal with horns. 3. ___________ alligator looks like ___________ crocodile. 4. ________________lamb is the baby of ____________ sheep. 5. 84 _______ eagle is ________ bird. Articles I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Fill in the blanks with ‘a‛, ‘an‛ or ‘the‛. Butterflies lay their eggs on leaves. When _______ egg hatches, it is called ________ larva. The larva eats and grows until it becomes___ caterpillar. As a caterpillar, it continues to grow. ________few weeks later, ________ caterpillar sheds its skin and covers itself with a newgreen skin. It covers ______ whole caterpillar. Now the caterpillar is called ___ pupa. The pupa rests inside ______ cocoon while its body changes completely. Now_________ pupa breaks open ________ cocoon. It is now _______ beautiful butterfly. 85 (c) Blend words and Word origin Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Colour ‘br‛ blends words with blue colour and ‘tr‛ blend words with red colour. 86 tribe trash brain brake tree drip trace trumpet branch trip trim broom trap brake track trade tribe bronze train brought trunk tail beak break shrimp fin brunch crow prawn brown Blend words and Word origin I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Fill in six blend words in the boxes. Blend words Dice Cut along the lines and fold the paper to make a blend words dice. 87 Blend words (dr) and Word origin I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Complete the crossword with the help of the given clues. 1 2 3 4 6 5 7 8 9 Across Down 1. to swallow a liquid 2. opening in a bathtub to empty its water 4. the opposite of wet 3. a feeling of fear 5. a play or performance 4. what you pull out in your dresser 6. to make a picture 7. a musical instrument 7. an imaginary beast 8. thoughts when you are asleep 9. to let something fall Source : Cherry Carl, 2008 88 II. Fill in the blanks with the ‘dr‛ blend words given in the word bank. 1. A ________________ looks like a giant lizard. 2. Please don‛t _______________ your feet. 3. All the soapy bubbles went down the _______________ . 4. A _______________ landed on my fishing pole. 5. May I please _____________ a glass of water? 6. My mom always says that I should _____________ milk. 7. I had a funny __________________ last night. 8. The bus _______________ said we had to stay in our seats. 9. My sister wore a pretty ________________ for the party. 10. The opposite of worker (female bee) is __________. 11. The _______________ is my favourite piece of chicken. 12. It‛s my turn to ________________ the dinner dishes. Word Bank dragonfly dragon dry drag dress drain dream drone drumstick drawbridge driver drink 89 Blend words and Word origin Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Many English words come from Latin. Vorare is a Latin word meaning to eat or to devour. So, English words that end in vore mean eater. Herbivore, carnivore, omnivore and insectivore are four words that end in vore. I. Answer the following in your own words. 1. A herbivore [Hint: Herb is Latin for plant.] ____________________________________________ 2. A carnivore [Hint: Carn is Latin for flesh or meat.] ____________________________________________ 3. An omnivore [Hint: Omni is Latin for all or everything.] ____________________________________________ 4. Horses, camels and cows _____________________________________________ 5. Anteaters and bears _____________________________________________ 6. 90 Tigers and lions _____________________________________________ II. Label the animals below as herbivore, carnivore, omnivore or insectivore. _____________________________________________ 91 Blend words and Word origin Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Directions: In each case, write the meaning of each root or prefix and then determine the meaning of the word. Write the meaning in the blank. 1, re means _____________________________________ build means ____________________________________ rebuild means __________________________________ 2. port means ____________________________________ able means ____________________________________ portable means _________________________________ 3. im means ______________________________________ mature means __________________________________ immature means ________________________________ 4. trans means ___________________________________ form means ____________________________________ transform means _______________________________ 5. inter means ___________________________________ ject means ____________________________________ interject means ________________________________ 92 6. em means _____________________________________ body means ____________________________________ embody means __________________________________ 7. de means ______________________________________ duct means ____________________________________ deduct means __________________________________ 93 Naming words (recap) Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ All people, animals, places and things have names. I. Identify the nouns and circle the adjectives. Rewrite the sentences where articles are to be put before the nouns. 1. Elephant is large but mouse is small. ________________________________________ 2. Ant has fifteen legs. ________________________________________ 3. My dog is healthy. It likes to have bones. ________________________________________ 4. She is in garden watching squirrels climbing up and down green trees. ________________________________________ 5. Monkeys are agile and they love to play on trees. ________________________________________ 94 II. Identify the following animals. Write down their names with adjectives. ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ 95 Environmental Education (a) Animals-their sounds and their young ones I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Take the animal babies to their moms and also write their names. Cat Dog Sheep Pig Hen 96 Animals-their sounds and their young ones Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. :___________ Complete the following table. Animal Young one Sound Cow Elephant Horse Chick Kid Pup Cat Piglet Lamb Bird Nestling Monkey Cub Roars Brays Duckling Hen Owl 97 (b) Animals and their eating habits I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Classify and write the names of animals in the correct column. horse, sparrow, lion, cow, tiger, goat, rat, elephant, giraffe, wolf, eagle, bear, vulture, crow, buffalo, cat Carnivorous 98 Herbivorous Omnivorous Animals and their eating habits Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Find out the names of animals from the word maze and put them in the correct column based on their eating habits. START HORSE LION CAT BUFFALO FOX MOSQUITO RAT RABBIT DOG BUTTERFLY COW FINISH Chew Tear Suck Grind 99 Animals and their habitat Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Identify the animals. Write ‘Land‛ for the animals that live on land and ‘Water‛ for the animals that live in water. 100 (c) Habitat of Animals Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. II. :___________ Give two examples for each of the following. a) Terrestrial animals __________ __________ b) Arboreal animals __________ __________ c) Aquatic animals __________ __________ d) Amphibians __________ __________ e) Aerial animals __________ __________ Who am I ? a) I have a very long neck. _____________________________________________ b) I have a hump and I store food and water in it. _____________________________________________ c) I live in cold regions and my body is covered with fur. _____________________________________________ d) I have broad hooves that help me walk on snow. _____________________________________________ 101 III. Draw the picture of a fish. Label its fins, gills, tails, scales, mouth and eyes. 102 Habitat of Animals Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Solve the puzzle. 1 D P 2 A 3 4 T D 5 p F 6 C C I T 7 C D L S E Clues: E 1. An aquatic animal that comes to the surface of water to breathe. 2. The largest terrestrial animal. 3. Animal that has flippers. 4. A water bird. 5. Animal that breathes through its gills. 6. An amphibian. 7. Animal that can live without food and water for more than fifteen days. 103 Habitat of Animals Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. Match the following. Camel Long tail Fish Fur Bird Hooves Reindeer Wings Polar Bear Humps Monkey Flipper shaped feet Turtle Gills II. List three things that help a bird to fly. _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 104 III. List two examples for each of the following. a) Birds that can fly only for a very short distance. ____________________ ____________________ b) Birds that cannot fly high in the sky. ____________________ ____________________ c) Birds that can fly very high in the sky. ____________________ ____________________ d) Birds that cannot fly. ____________________ ____________________ IV. Draw a bird and label its parts. 105 V. Draw your favourite animal. 106 Eating habits of birds Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ The shape of the beak tells you about the type of food a bird eats. Look at the picture and tell the type of beak the following birds have and what do they eat. Type of beak Bird Food it eats parrot woodpecker d k duck eagle sparrow 107 Birds and Insects Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. Name the following. 108 (a) A bird that eats flesh ______________________ (b) A bird that eats insects ______________________ (c) A bird that eats grains ______________________ (d) A bird that eats fruits ______________________ II. Name the following. (a) Two insects ______________ ________________ (b) Two insects that can fly ___________ __________ (c) Two insects that suck nectar _________ ________ (d) Two insects with eight legs __________ _________ III. Write the names of the animals that have Two legs Four legs Six legs 109 IV. Draw an insect showing feelers and its six legs. 110 Mathematics (a) Addition I. Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Look at the place value cards arranged in the column below. Write the numbers and find their sum. H T 100 100 100 O 10 10 10 10 1 1 1 1 1 -Hundreds -Tens Count and Write -Ones Sum (a) - H T 100 100 100 10 O 10 10 10 1 1 1 1 1 -Hundreds Count and Write Sum = Sum (a) = -Tens -Ones Sum (b) + Sum (b) + = 111 Addition Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. :___________ Count the number of beads in the abacus and write the numbers in the boxes. H T O First Number = H + T O Second Number + = II. 112 Find the sum for the following pairs of numbers. 536 664 379 +768 +186 +137 468 669 489 +944 +607 +221 609 986 878 +527 +519 +744 Addition Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. :___________ Add to find the sum. Each sum represents a letter. A. + A H T O N. H T O A. H T 5 1 6 2 1 8 4 0 + 2 3 7 + 1 1 4 N N. H T O + 7 1 5 0 3 6 N B. O 3 4 1 8 A. H T O A H T O 4 1 + 4 0 7 2 B 2 + 1 3 4 3 5 A Write the letter for each of the sum in the box to find the answer to the riddle given below. 819 689 859 879 637 378 The favourite fruit of monkeys. ________________________ 113 Addition I. Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Convert the number words to numbers and perform the required operation. a) Three hundred one + eight hundred seventy two H b) c) T O Five hundred forty two + four hundred fifty nine H T O One hundred forty three + three hundred two H 114 :___________ T O II. The anacondas have got entangled in the numbers. Add the numbers so that they can reach their hole. + 30 = + 80 Hole + 40 20 +500 +200 = +100= + 50 = + 50 = Hole = +5= + 15 = + 300 = Hole 115 III. Help the squirrels to find their right hollows in the tree. Draw lines to match the squirrels to their respective hollows. 315 + 0 399 + 1 0 + 111 999 315 717 111 1 + 998 400 510 + 5 515 116 2 + 715 Addition Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Bruno, the puppy has come to stay in a hotel with his master Ben. It has lost its way. Help him reach room no. 192 with the help of clues given below. Colour the boxes showing answers to the clues. Room No. 192 10 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 9 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 8 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 7 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 6 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 5 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 4 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 3 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 2 110 Floor 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 I 100 Floor 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 Ben‛s Room HELP ME 117 a) Bruno is standing in front of room no. 124. b) Go 10 rooms forward to reach in front of room no. _____ c) Go 5 rooms forward to reach the end of IV floor. ______ d) Count the rooms on V and VI floor. Total no. is. ___________________________________________ e) On which floor is Bruno now. ______________________ f) Now Bruno is on 159, cross 3 floors and go two rooms forward to reach room no. 192. ___________________________________________ 118 Addition Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Add the number in the centre to the surrounding numbers. 40 + ___ + 280 = ____ ____ = + 110 ____ ____ + 280 = ____ ____ = 260 + ____ ____ = 350 + ____ ____ + 390 = ____ ____ = 700 + ____ ____ + 400 = ____ 119 Addition Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ I. Tell whether the fishes given below are each others‛ mate or not. Pair them up and colour them. 400+5+10 600 +200 30 + 360 60+5+700 5+10+400 225 + 25 25 + 225 25 + 225 360 + 30 120 200 + 600 Addition Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Look at the p pictures g given below. 115 105 Birds Tree 1 Birds Tree 2 Find out how many birds are there in all on both the trees? Solution: No. of birds on the first tree = ____________ No. of birds on the second tree = ____________ Total no. of birds = ____________ H T O 121 Addition 1. Name: ___________ Class Date : ___________ Subject :___________ There are 252 small animals and 168 big animals in the ocean. How many total aquatic animals are there in the ocean? Number of small animals Number of big animals + Solution 122 :___________ Addition - Worksheet contd. 2. There are 95 hens and 105 sheep in the farm. Find the total number of animals in the farm. No. of hens No. of sheep + + Solution 123 Addition Name: ___________ Class :___________ Date : ___________ Subject :___________ Tom has to catch Jerry. To catch him, Tom has to find the sum of the numbers. Help him in adding the numbers according to the given directions: Tom (Start) 145 +3 +3 + + + 5 5 5 +3 +3 Jerry (Finish) 124