Menu
Lesson
Print
Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Class _______________________
Modern Chemistry • CHAPTER 6
HOMEWORK 6-1
(pp. 161–163)
VOCABULARY
Define.
1. chemical bond ______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. covalent bond ______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. ionic bonding ______________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. polar-covalent bond _________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
SKILL BUILDER
Use the electronegativity values to classify the bonds that would form between atoms of each of the
following elements.
Element
Electronegativity
Element
Electronegativity
Hydrogen (H)
2.1
Oxygen (O)
3.5
Sodium (Na)
0.9
Carbon (C)
2.5
Calcium (Ca)
1.0
Cobalt (Co)
1.8
Lithium (Li)
1.0
Nitrogen (N)
3.0
Bond
H and O
Type
Bond
N and O
H and C
Li and Ca
Na and Co
N and Ca
Li and N
Na and O
Ca and H
C and O
STANDARDIZED TEST PREP
Circle the letter of the best answer.
1. A large difference in electronegativity between two atoms in a bond results in
a. polar covalent bonding.
b. nonpolar covalent bonding.
c. ionic bonding.
d. repulsion between the two atoms.
2. Which of the following happens when atoms bond with each other?
a. The atoms increase in potential energy.
b. The potential energy of the compound is maximized.
c. Their electronegativity dramatically increases.
d. They create arrangements of matter that are more stable.
Modern Chemistry
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Type
Menu
Lesson
CHAPTER 5
Print
• HOMEWORK 5-10
VOCABULARY
1. electronegativity
2. increases
3. they do not form compounds
4. the order given by the atom’s electron configuration
5. are available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds
GRAPHIC ORGANIZER
Students should list the following trends: electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, atomic
radii, and ionic radii. Answers should reflect the trends. For example, in the first box, student should list
ionization energy increases. In the second box, student should list ionization energy decreases.
STANDARDIZED TEST PREP
1. a
2. c
CHAPTER 6
• HOMEWORK 6-1
VOCABULARY
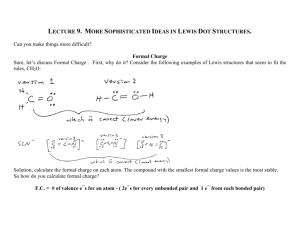
1. a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds
the atoms together
2. bonding that results from the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms
3. chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between large numbers of cations
and anions
4. a covalent bond in which the bonded atoms have an unequal attraction for the shared electrons
SKILL BUILDER
Bond
Type
Bond
Type
H and O
polar-covalent
N and O
polar-covalent
H and C
polar-covalent
Li and Ca
nonpolar-covalent
Na and Co
polar covalent
N and Ca
ionic
Li and N
ionic
Na and O
ionic
Ca and H
polar-covalent
C and O
polar-covalent
STANDARDIZED TEST PREP
1. c
2. d