answers here - Jodrell Bank
advertisement

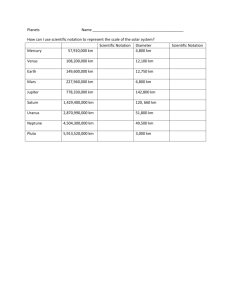
Jodrell Bank Discovery Centre Answers to students’ worksheets Key Stage 4 Planet Pavilion Questions 1. Which planet is orbiting the Sun the quickest? Mercury 2. Which planet is orbiting the Sun the slowest? Neptune 3. What force is keeping the planets in their orbits? Gravity 4. Approximately, how many times greater is the Sun’s diameter, compared to the Earth’s? Diameter of the Sun = 1.4 million km. Diameter of the Earth = 13,000 km. 1.4 million ÷ 13,000 = 108. ∴Sun is approximately 100 times wider. 5. Use the equation to calculate what the diameter of the model Earth should be. ∴ 100 = 100 = 15 ÷ Model Earth Diameter Rearrange to give Model Earth Diameter = 0.15cm (1.5mm) 6. A similar equation can be used to calculate the orrery’s Earth-Sun distance. Complete the equation below. 7. Now rearrange this equation to calculate what the model Earth-Sun distance should be, if the orrery were built to scale. Remember the real Earth-Sun distance is 150 million km. (Hint: to make the calculation easier, round up the Sun’s diameter to 1.5 million km) 15m (similar rearrangement to question 6) 8. A planetary nebula formed when a star like the Sun runs out of fuel. o Name: Ring Nebula. At the centre: white dwarf star The nearest large spiral galaxy to our own Milky Way. o Name: Andromeda Galaxy. How far away: 2.5 million light years What has been left behind after a big star exploded in 1054 AD. o Name: Crab Nebula. What is at the centre? Pulsar (spinning neutron star) A 3 light-year tall pillar where new stars are forming. o Name: Carina Nebula. What are the stars forming from? Gas and dust 1 Jodrell Bank Discovery Centre Answers to students’ worksheets Space Pavilion Questions 1. What part of the EM spectrum do the telescopes at Jodrell Bank collect? Radio Waves 2. Why is the paraboloid (bowl) shape of the telescope dish important? Reflects radio waves to a focus point 3. What is the diameter of the Lovell telescope? 76.2 metres 4. What part of the EM spectrum does this camera observe? Infrared waves 5. Have a go at experimenting with the heat camera… a. Try holding up the props which are in front of the screen. Which material is the worst insulator of heat? Black plastic bag. How can you tell? It appears transparent; infrared waves pass through it, transmitting heat energy. b. Try placing your hand on something which is not hot (like a piece of paper) for a few seconds. What form of heat transfer is occurring? Conduction c. Remove your hand from the piece of paper and show the paper to the camera. You should see a hand print. After a while, the hand print will fade away. What form of heat transfer is occurring? Radiation 6. Which animal can see infrared waves? Snake 7. What type of EM wave can a bee see? Ultraviolet 8. How many years after the Big Bang did the first atoms form? 380,000 9. How many years after the Big Bang did the Solar System form? About 9 billion 10. Roll a ball into the black hole. Write down the main energy transfer occurring as it falls. Gravitational potential Kinetic 11. List any forms of wasted energy as the ball falls. Heat & sound 12. Would these forms of wasted energy be the same for a real black hole? Why? No, there is no friction when falling into a black hole 13. Explain what happens in terms of a flow of charge when you touch the sphere. Charge flows from the centre of the plasma ball through the gas, through the person touching the ball, to the ground. 14. Which astronomer first discovered pulsars? Dame Jocelyn Bell Burnell 15. This shows one way of finding exoplanets. The amount of light from the star is being measured by a camera (in the red circle) and being shown on screen. Explain how exoplanets can be discovered by this method. Telescopes monitor brightness of stars for long periods. If regular dips in light level are detected, this could be caused by a planet orbiting that star. 16. Which planet (small or large) is easier to detect? Why? Large. The observed dips in 2 Jodrell Bank Discovery Centre Answers to students’ worksheets brightness are larger and more frequent. 17. How many exoplanets have astronomers discovered so far? Answer is updated every hour. Current figure (confirmed exoplanets) can be found at http://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu 18. What can astronomers find out about an exoplanet from studying a star’s Doppler wobble? The mass of the planet and its distance from the star 19. What type of object can you see through the telescope? Galaxy (M51) 20. This telescope is a reflecting telescope. What does it use to focus the light entering it? Curved mirrors 21. Dim the light; you should see your pupil increase in size. Why are large telescopes better at seeing things than smaller ones? Larger telescopes can collect more light/electromagnetic waves. This means they can see fainter objects. 22. Choose two telescopes; write down their names, location, size and what EM wave they observe. Answers will depend on students’ choices. Planet Path Questions 1. Which of the two inner planets are most similar in size? Venus and Earth 2. The Earth disc is about 70cm in diameter. Estimate the diameter of the Mars disc. 35cm (the diameter of Mars is around half that of the Earth’s) 3. The Earth disc lies 15m from the model Sun. How far (on average) is the real Earth from the Sun? 150 million km (1m on the Planet Path = 10 million km in reality) 4. Jupiter’s real diameter is 140,000km. What is the real diameter of the Sun? 1.4 million km (diameter of the Sun is around 10 times that of Jupiter) 5. Jupiter is 300 times more massive than the Earth (to the nearest hundred) and is 5 times further away from the Sun than the Earth is. How many more times greater is the force of gravity between the Sun and Jupiter, compared to the Sun and Earth? Considering the equation F = GMm/r2 for Jupiter, rather than the Earth; G and M will remain the same, whereas m will be larger by a factor of 300 and r will be larger by a factor of 5. Therefore F will be larger by a factor of 300/5 2 = 300/25 = 12 6. Launched in 1989 and arriving at Jupiter in 1995, the Galileo probe observed Jupiter from orbit until the end of its mission in 2003. The Galileo probe had not been sterilised before it left Earth. Why was Galileo destroyed by flying it into Jupiter and not one of its moons? To prevent one of Jupiter’s moons being contaminated with 3 Jodrell Bank Discovery Centre Answers to students’ worksheets Earth bacteria (this could be potentially hazardous to the environment). Jupiter is a gas planet and so does not contain any potentially hospitable habitats for bacteria. 7. The Cassini probe is a robot that is currently in orbit around Saturn. It arrived in 2004 and since then it has been studying Saturn and its moons. At this distance from the Sun, solar panels are not a feasible way of generating electrical power. Suggest a possible power source for Cassini and explain why you think it would be practical. Fossil fuels would not be feasible, due to their weight and lack of oxygen to burn in space. Cassini is powered by a small nuclear fission reactor. Fuel has a lifespan of many years and there are no waste products, until the end of the mission. 8. Which two planets have not been seen on the Planet Path yet? Uranus and Neptune 9. How far away from the Sun is the most distant planet in the Solar System? 4,500 million km (4.5 billion km) 10. There used to be a ninth planet, Pluto, but in 2006 it was reclassified as a Dwarf Planet. The New Horizons spacecraft was launched in 2006 and will fly-by Pluto in July 2015, transmitting the first-ever close-up pictures of its surface. The New Horizons spacecraft got a speed-boost from Jupiter’s gravity. When it arrives at Pluto, it will have travelled around 4.5x1012 m since Jupiter, in an almost straight line. The time to travel that distance will be about 3x108 seconds. At approximately what speed (in km/s) will New Horizons travel past Pluto? Speed = distance/time = 3.9x1012/2.6x108 = 1.5x104m/s = 15 km/s Telescope Path Questions 1. Sir Bernard Lovell detected these in 1945 using radar equipment. Meteors 2. Charles Husband was the engineer who built the Lovell telescope. 3. The Lovell telescope is so powerful it could detect a mobile phone signal on Mars. 4. What is the diameter of the Lovell telescope’s dish? 76metres 5. The gear racks on the Lovell telescope are recycled 15-inch gun turrets. 6. In the 1920s astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that this is expanding. Universe 7. The Lovell telescope is painted white to reflect sunlight and stop the metal warping. 8. The first artificial satellite in space (tracked by the Lovell telescope). Sputnik 9. Quasars release massive amounts of energy as gas falls into a black hole. 10. What do astronomers call the spinning collapsed core of an exploded giant star? Pulsar 11. Using radio waves we can peer deep into the heart of our galaxy. The bold squares spell out the word: OBSERVATORY 4