Ch. 2 HW
advertisement

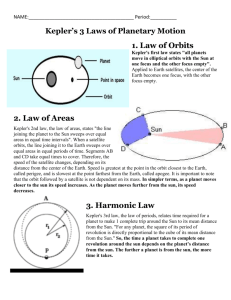
Name _____________________ Chapter 2 Homework 1. Why does the moon appears larger when it rises than when it is high in the sky? 2. What does Kepler's third law state? 3. By how much are the paths of the planets on the sky are tilted with respect to the celestial equator? 4. Why did Copernicus' heliocentric model fail to work as well as it might have to predict the positions of planets? 5. What were a couple of things that Tycho Brahe's proved that became major contributions to astronomy? 6. Who was the first person to measure the circumference of the Earth. 7. What is one of the methods used to date supernova remnants (the remains of exploded stars) today 8. Which objects passes through the zodiac? 9. How do stars move with respect to the celestial sphere? 10. What is retrograde motion? 11. What is the size of an object located at a distance of 1 km and that has angular size A = 2? 12. What was a crucial observation of Galileo in rejecting the geocentric system? 13. What model Sun is assumed as the center of the solar system. 14. During retrograde motion, how does a planet move relative to the stars? 15. During retrograde motion, how does a planet move relative to the horizon. 16. Who’s extensive records of planetary positions did Kepler use to discover that the orbits of the planets? 17. What does Kepler's first law state? 18. What does Kepler's first law state? 19. Suppose you were an alien living on the fictitious warlike planet Myrmidon and you wanted to measure its size. The Sun is shining directly down a missile silo 1000 miles to your south, while at your location, the Sun is 36° from straight overhead. What is the circumference of Myrmidon? What is its radius? 2-1 20. Suppose a planet were found with an orbital period of 64 years. How might you estimate its distance from the Sun? If its orbit is circular, what is its radius? 21. Suppose you received a message from aliens living on a planet orbiting a star identical to our Sun. They say they live 4 times farther from their star than the Earth is from the Sun. What is the length of their year compared to ours? 22. The great galaxy in Andromeda has an angular diameter along its long axis of about 5°. Its distance is about 2.2 million light-years. What is its linear diameter? 23. A shell of gas blown out of a star has an angular diameter of 0.1° and a linear diameter of 1 light-years. How far away is it? 24. A small robot probe is exploring a spherical asteroid. As the probe creeps over the surface, it drills holes to take soil samples. At one hole, scientists on Earth notice that the Sun shines straight down the hole. At the same time, 10 km due "north," the shadow of the vertical antenna on the main landing craft allows the scientists to deduce that the Sun is 15° from directly overhead. What is the radius of the asteroid? How many times smaller or bigger is its radius than Earth's? 25. A planet is discovered orbiting a nearby star once every 125 years. If the star is identical to the Sun, how could you find the planet's distance from its star? If the planet's orbit is a perfect circle, how far from the star is the planet in AUs? 26. Observations with the Hubble Space Telescope revealed a planet about 16 AU from a star whose mass is the same as our Sun's mass. How long does it take the planet to orbit the star? 2-2