CHEM101 Study Guide Test 2 (2014-15) HW Chapter 5
advertisement
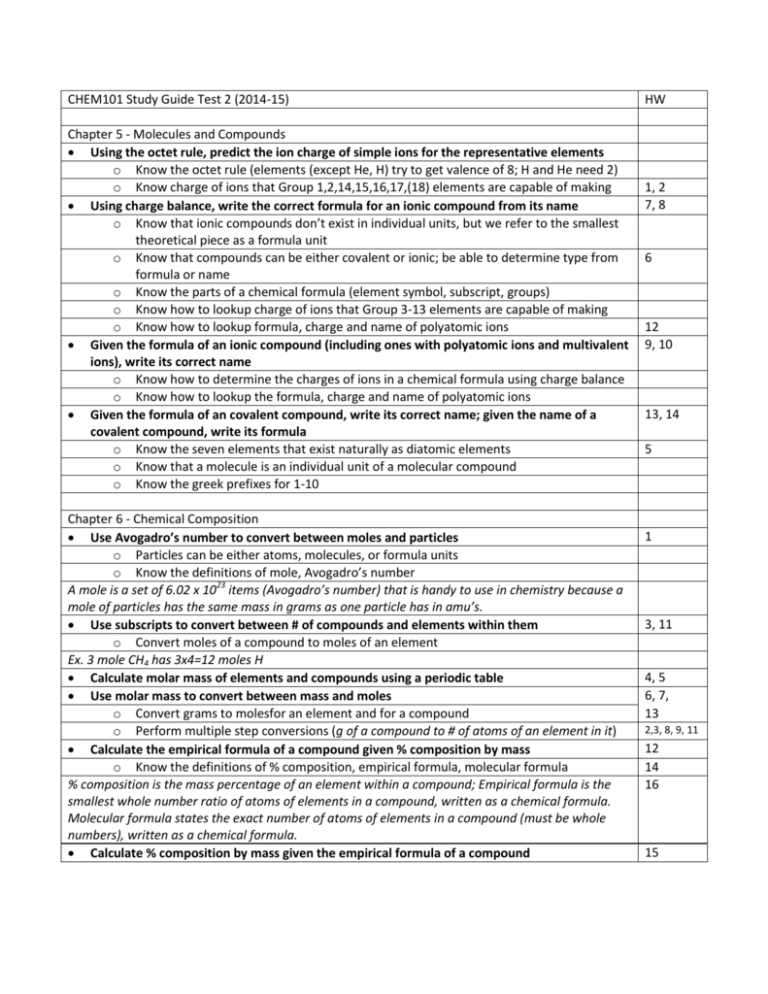
CHEM101 Study Guide Test 2 (2014-15) Chapter 5 - Molecules and Compounds Using the octet rule, predict the ion charge of simple ions for the representative elements o Know the octet rule (elements (except He, H) try to get valence of 8; H and He need 2) o Know charge of ions that Group 1,2,14,15,16,17,(18) elements are capable of making Using charge balance, write the correct formula for an ionic compound from its name o Know that ionic compounds don’t exist in individual units, but we refer to the smallest theoretical piece as a formula unit o Know that compounds can be either covalent or ionic; be able to determine type from formula or name o Know the parts of a chemical formula (element symbol, subscript, groups) o Know how to lookup charge of ions that Group 3-13 elements are capable of making o Know how to lookup formula, charge and name of polyatomic ions Given the formula of an ionic compound (including ones with polyatomic ions and multivalent ions), write its correct name o Know how to determine the charges of ions in a chemical formula using charge balance o Know how to lookup the formula, charge and name of polyatomic ions Given the formula of an covalent compound, write its correct name; given the name of a covalent compound, write its formula o Know the seven elements that exist naturally as diatomic elements o Know that a molecule is an individual unit of a molecular compound o Know the greek prefixes for 1-10 Chapter 6 - Chemical Composition Use Avogadro’s number to convert between moles and particles o Particles can be either atoms, molecules, or formula units o Know the definitions of mole, Avogadro’s number A mole is a set of 6.02 x 1023 items (Avogadro’s number) that is handy to use in chemistry because a mole of particles has the same mass in grams as one particle has in amu’s. Use subscripts to convert between # of compounds and elements within them o Convert moles of a compound to moles of an element Ex. 3 mole CH4 has 3x4=12 moles H Calculate molar mass of elements and compounds using a periodic table Use molar mass to convert between mass and moles o Convert grams to molesfor an element and for a compound o Perform multiple step conversions (g of a compound to # of atoms of an element in it) Calculate the empirical formula of a compound given % composition by mass o Know the definitions of % composition, empirical formula, molecular formula % composition is the mass percentage of an element within a compound; Empirical formula is the smallest whole number ratio of atoms of elements in a compound, written as a chemical formula. Molecular formula states the exact number of atoms of elements in a compound (must be whole numbers), written as a chemical formula. Calculate % composition by mass given the empirical formula of a compound HW 1, 2 7, 8 6 12 9, 10 13, 14 5 1 3, 11 4, 5 6, 7, 13 2,3, 8, 9, 11 12 14 16 15 Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions Write a chemical reaction equation given a written description of the chemical change o Know the definitions of: reactant, product, reaction, yields Balance a chemical reaction [change coefficients, NOT subscripts] o Know the difference between a subscript and coefficient Identify type of chemical reaction from full reaction or from reactants only o combination, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion Write molecular, ionic and net ionic equations for a precipitation reaction Define solubility and identify an insoluble salt Know select combination reactions: o metal + O2 metal oxide o metal + nonmetal binary salt (ionic compound of the ions made from each) o metal oxide + H2O metal hydroxide o metal chloride + O2 metal chlorate Know select decomposition reactions: o metal oxide metal + O2 o binary salt metal + nonmetal o metal hydroxide metal oxide + H2O o metal chlorate metal chloride + O2 o metal carbonates metal oxide + CO2 Predict products of a reaction (from just reactants) o for select combination reactions o for select decomposition reactions o for any single displacement reaction (and if it will occur based on activity series) o for any double displacement reaction 1, 6, 7,16 2-5, 12, 13, 16 10, 24-5 18, 21 17 19, 20 12,13,14,15 Chapter 8 - Quantities in Chemical Reactions definitions: stoichiometric ratio, limiting reactant, mass conservation, percent yield be able to write a stoichiometric ratio Mole-Mole conversions o convert moles of one compound to moles of another in the same reaction Mole-Mass conversions o convert moles of one compound to mass of another in the same reaction Mass-Mass conversions o convert mass of one compound to mass of another in the same reaction Determine limiting reactant from amounts of two or more reactants Calculate theoretical yield from limiting reactant Calculate % yield from moles of reactant and actual yield o use moles reactant to find theoretical yield Identify exothermic and endothermic reactions o Understand that during a chemical reaction, the system may absorb/release a fixed amount of heat per amount of reactant (called Hrxn) because the potential energy of the system is changing. Identify whether a reaction is exo- or endothermic by its Hrxn) o Exothermic reactions give off heat and have a negative Hrxn; Endothermic reactions absorb heat and have a positive Hrxn) 1, 2 4, 5, 6 7, 8, 9, 10 17 3, 18, 19 21, 22, 23, 24 25-28







