Earth's Interior Layers Worksheet: Geology for Students
advertisement
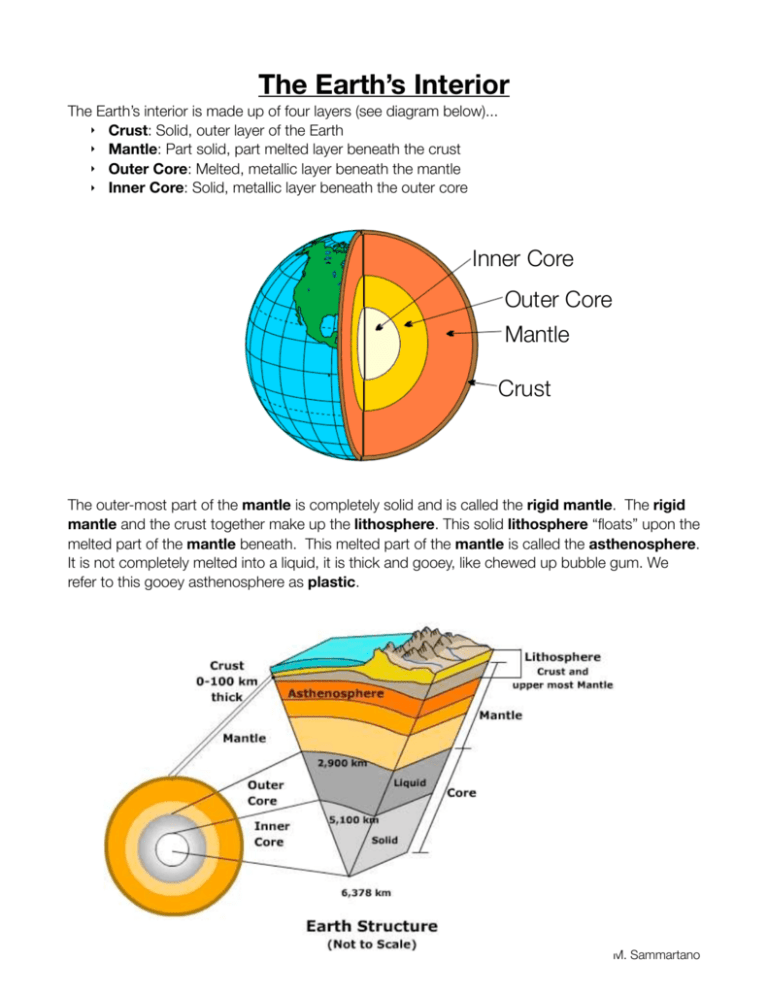
The Earth’s Interior The Earth’s interior is made up of four layers (see diagram below)... ‣ Crust: Solid, outer layer of the Earth ‣ Mantle: Part solid, part melted layer beneath the crust ‣ Outer Core: Melted, metallic layer beneath the mantle ‣ Inner Core: Solid, metallic layer beneath the outer core Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust The outer-most part of the mantle is completely solid and is called the rigid mantle. The rigid mantle and the crust together make up the lithosphere. This solid lithosphere “floats” upon the melted part of the mantle beneath. This melted part of the mantle is called the asthenosphere. It is not completely melted into a liquid, it is thick and gooey, like chewed up bubble gum. We refer to this gooey asthenosphere as plastic. M. Sammartano Inferred Properties of Earth’s Interior TIC LAN AT The diagram seen to the right can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Pay attention to the following details: IC TLANT MID-A GE RID ) RE T LE HE AN SP M O IC TH ST The MOHO is the boundary between the crust and the mantle. There are two types of crust: ‣ Continental crust which is made of a very thick layer of the rock granite and is less dense (2.7 g/cm3) ‣ ‣ Oceanic crust which is made of a very thin layer of the rock basalt and is more dense (3.0 g/cm3) Wherever the interior temperature is higher than the melting point, the material is a liquid (see the outer core. N & R 9.9–12.2 REL) COICKE RO N STI FF ER LE NT MA OU TE (I LI NO SP HE R CR RIG UST ID MA NT AS TH LE E } NO RT H 2.7 granitic continental crust 3.0 basaltic oceanic crust MOHO 3.4–5.6 RE ) COICKEL 12.8–13.1 IN N (IRO ER N& N TRENCH EARTH’S CENTER 4 3 2 1 0 7000 6000 5000 POIN T As you travel deeper down, from the crust to the inner core, the temperature increases. E LA (P CASCADES MEL TING ‣ AM ER IC A ‣ As you travel deeper down, from the crust to the inner core, the pressure increases. PRESSURE (million atmospheres) ‣ As you travel deeper down, from the crust to the inner core, the materials get increasingly dense. TEMPERATURE (°C) ‣ AN DENSITY (g/cm3) PACIFIC OCEAN ‣ OCE 4000 E UR AT R E T MP IN TE PO R O RI NG TI TE IN EL M 3000 2000 PARTIAL MELTING 1000 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 DEPTH (km) 10 Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables — 2010 M. Sammartano Layer Starting Depth (km) Ending Depth (km) Thickness (km) Pressure Range (atms) Density (g/cm3) Temp. Range (C) Phase Lithosphere Asthenosphere Stiffer Mantle Outer Core Inner Core 1. Which 2 layers make up Lithosphere? ________________________________________________ 2. Where is the crust thicker, oceans or continents? ______________________________________ 3. Where is the crust denser, oceans or continents? ______________________________________ 4. What is the outer core believed to be made up of? _____________________________________ 5. What is the inner core believed to be made up of? _____________________________________ 6. What 2 layers of the Earth are either partially or totally melted? ___________________________ 7. Between which 2 layers do you find the MOHO? _______________________________________ 8. What rock is continental crust made up of? ___________________________________________ 9. What rock is oceanic crust made up of? ______________________________________________ 10. Why are there ???’s on this chart? What does this mean? ______________________________ 11. What happens to the temperature as you travel deeper into the Earth? ___________________ 12. What happens to pressure as you travel deeper into the Earth? _________________________ 13. Why do we call the Asthenosphere “the plastic mantle” ?_______________________________ 14. What are the 3 layers of the Mantle? _______________________________________________ 15. Plates move together or apart at mid ocean ridges? ___________________________________ 16. Plates move together or apart at trenches? __________________________________________ 17. Mountains are found at mid ocean ridges or trenches? ________________________________ M. Sammartano Primary waves passthat through theshallow outer core but shear 19) C)Fossils of organisms lived in water can be waves do not. 8350 - 1 ocean - Page 1 found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great D)depths. The primary wave velocity interpreted decreases, while the - 1Earth -shear Page 2 This fact is generally by8350 most Name: ____________________________________________ wave velocity increases outer core. scientists evidence that in the 13) Which graph best represents the relationship between the 17) According toasthe Earth Science Reference Tables, at 1) differences Which statement describes the continental and Questions 7the through 11Earth refer tosurface the following: in arrivalbest times of P-waves and S-waves foroceanic 44) 4,500 below the of thekills Earth, the pressure A) kilometers cold water deep in the ocean shallow-water According to the Reference Tables, in which 17 isThe map below showsScience a weather variable recorded 14 locations The cross section below shows a sea breeze crusts? at varying distances from an earthquake? estimated to be zone oforganisms the Earth's interior is the melting point of the rock atB) noon on a certain day. Isolines show values from blowing from the ocean toward the land. The air C) of thethan Earth's crustState. have changed inferred to originated be lower the actual temperature oftheir thetravel rock? A) The continental crust is thicker and less dense than the An earthquake in New York The P-wave A) 1.4sections million atmospheres 20 to elevations 70. pressure at the land surface is 1013 millibars. relative to sea level oceanic crust. time B) for this earthquake was recorded in the data table below for 2.0 million atmospheres A) outer core C) inner core C) sunlight once penetrated to the deepest parts of the four C) widely separated seismic stations, A, B, C, and D. B) The continental crust is thinner and more dense than million atmospheres B) 2.8 mantle D) crust ocean A) the oceanic crust. D) 3.1 million atmospheres 45) Four stations data evolved from the from samespecies D) seismograph organisms that live inreceive deep water C) The continental crust is thinner and less dense than the Sea breeze earthquake. The table below shows the differences in travel 18) The composition of some meteorites supports the inference that once lived in shallow water oceanic crust. timesthe forEarth's the P-core and S-waves recorded that is composed of at each station. D) The continental crust is thicker and more dense than 20) Which Wherestation are earthquakes most place? isand closest to the likely epicenter of the earthquake? 20 to take A) magnesium potassium the oceanic crust. A) along the core-mantle interface 1013 mb B) silicon and oxygen 2) Recent volcanic activity in different parts of the world D) where the composition of the Earth tends to be uniform 8350 1 Page 2 C)B) iron nickel 3and 0the supports the inference that volcanoesOcean are located mainly in C) near Earth's Equator the 17) B)According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, at D) aluminum and calcium D) near a fault zone A) the central regions of continents 8350 - 1 - Page 4 r 4,500 kilometers below the surface of the Earth, the pressure 19) Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water8350 can-be 1 - Page 4 (Not drawn to scale) B)estimated zones oftocrustal activity is bemarine 30) The presence of fossils at elevations high above sea 35) The diagram below of the Earth shows the observed pattern A P-wave reachessedimentary a seismograph station 2,600 kilometers 8350 - 1 - Page 4 21) found in horizontal rock layers at great ocean 30) level The presence of marine fossils at elevations high above sea 35) The diagram below of the Earth shows the observed pattern 40 C) zones in late stages of erosion 13 The data table below shows the origin depths of the 7) If the first P-wave arrived at seismic station A at provides good evidence for waves recorded after an earthquake. from an earthquake epicenter at 12:10 p.m. According to 14) A) A large belt of mountain ranges and volcanoes surrounds 1.4 million atmospheres depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth ve sea 35) The diagram below of the Earth shows the observed pattern level provides good evidence for waves recorded after an earthquake. The air pressure at the ocean surface a few miles 10hrs:22min:30sec, what was the origin time for the D) the centers of landscape regions all large-magnitude earthquakes over a 20-year Earth Science Reference Tables, at what time did the the Pacific Ocean. Which events are most closely B) 2.0recorded million atmospheres A) volcanic eruptions scientists as evidence waves after an earthquake. A) A B) Dthat C) B D) C from the shore isrepresents most likely earthquake? A) volcanic eruptions period. earthquake occur? associated with these mountains and volcanoes? 3) Which graph best the relationship between C) 2.8 million atmospheres B) crustal erosion A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water B) crustal erosion A) 02hrs:02min:30sec C) volcanic activity and earthquake in an area? (1) mb (3)activity 1013 mb A)organisms 12:01 p.m. C) 10hrs:14min:10sec 12:19 p.m. D) 3.1 million atmospheres C) continental glaciation A)994 tornadoes C) sandstorms 50 D) 10hrs:22min:30sec Data Table C) continental glaciation B) 10hrs:30min:50sec (2) 1005 mb (4) 1017 mb C) B) 12:15 p.m. D) 12:05 p.m. uplift B) crustal earthquakes D) hurricanes 18) D) The B) sections of the Earth's crust have changed their D) composition crustal uplift of some meteorites supports the inference itelevations takes 50 seconds the level P-wave to arrive Depth Below ofat that the Earth's core is composed of relative toinner sea 22) IfThe inference that thefor coreNumber of the Earth is Buffalo, solid is 31) epicenter anEarth earthquake located near Massena, 15) The According to of the ScienceisReference Tables, in which 8) 31) New The epicenter of an earthquake is located near Massena, about how long would it60 taketofor the S-waveparts fromof this Surface Earthquakes based on analysis of York. According to the Earth Science Reference C) sunlight once penetrated the deepest thesame group are the zones of the Earth's interior correctly arranged C) A) magnesium and potassium 15 An instrument usedtotothemeasure a weather varina, New York. According Earth Science Reference earthquake to arrive at Buffalo? [Refer to the Earth Science Tables, the greatest difference arrival times of the P- and in order of increasing average in density? A)ocean seismic (km) data B) silicon and below. oxygen able is shown Tables, the greatest difference in arrival times ofinthe P- and Reference Tables.] S-waves for this earthquake would be recorded D) organisms that live in deep water evolved from species A) crust, mantle, inner core, outer core B) crustal rock C) iron and nickel - and 0–330 27,788 S-waves for this earthquake would be recorded in A) 0min50sec that once lived in shallow waterC) 4min00sec N A) Utica, New York B) aluminum crust, mantle, core, inner core C) radioactive data D) and outer calcium 70 A) Utica, New York B) 6min40sec D) 1min40sec 34–100 17,585 B) Newcore, Yorkmantle, crust C) Binghamton, inner core, outer D) meteorite composition 20) Where are earthquakes most likely to take place? 19) Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be B) Plattsburgh, Binghamton, New York C) New York 9) What is the approximate distance between earthquake's D) outer core, inner core, mantle, crust along the interfaceReference 101–300 7,329the 23) A)According tocore-mantle the Earth Science Tables, the rate found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great ocean C) Albany, Plattsburgh, New York B) D) epicenter and station A? [Refer to the Earth Science D) New York of temperature increase below the Earth's surface is greatest This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth B) where the composition of the Earth tends to be uniform 16) D)depths. To get a sample material from the mantle, drilling will be D) Albany, New York 301–700 3,167 Reference Tables.] between depths ofEquator scientists astoevidence that done through theEarth oceanic crust rather thanTables, throughthe the 32) According the Science Reference C) near the Earth's Which atmospheric variable is most likely 32) temperature According toofthe Earth Science Reference Tables, the A) 7,500 km 4000 5,100 km continental because crust rock located 1,000 kilometers below the D) a fault zone A)near 3500 and kmisolines onC) C) 1500 and 2500 km A) the coldcrust water deep in oceanic the ocean killsisshallow-water represented by the this2,400 map? temperature of is rock located 1,000 kilometers below the B) 1,130 km D) km Earth's surface about organisms A) younger than continental crust B) 250 and 500 km D) 2500 and 3500 km According to these data, most these 21) A P-wave reaches a seismograph station 2,600 of kilometers 4) Folded sedimentary rock layers are usually caused by Earth's surface is about (1) snowfall instation inches B) sections of the Earth's crust have changed their 10) Which seismic could be located in New York State? B) more dense than continental crust A) 200DC C) 2,800DC earthquakes occurred within Earth’s from an earthquake epicenter at 12:10 p.m. According to the 14) AA) largecrustal belt ofmovement mountain occurring ranges and volcanoes surrounds after (2) wind speed in knots A) 200DC C) deposition 2,800DC elevations relative toevents sea crust level C)Pacific thinner than continental The lack of S-waves 3 can best explained B) 2,100DC D) 3,200DC Earth Science Reference Tables, atC) what time did theD)byAthe A) lithosphere D B) inC zone Bbe the Ocean. Which are most closely (1) stiffer mantle B) deposition of sediments in folded layers (3) pressure in(3) millibars Thebarometric lack of S-waves in zone B) 2,100DC D)volcanoes? 3,200DC C) once penetrated toand the deepest parts of the D) sunlight softerwith than continental crust presence within the Earth of 3 can best be explained by the earthquake occur? associated these mountains C) alack riseofinto sea deposition 11) (2) Which of within the four seismic stations isFahrenheit located farthest from 33) According thelevel Earth Science Reference Tables, asbythe asthenosphere (4) outer core The ocean S-waves inafter zone 3 can best be explained the (4) air temperature in degrees presence the Earth of 33) A) According tothe thein Earth Science Reference Tables, as the a solid A)A) p.m.inner core C) 12:19 p.m. tornadoes C) sandstorms the12:01 epicenter? depth within Earth's interior increases, the D) differences sediment during deposition presence within the Earth ofdensity the D) organisms live in deepiswater evolved A) 12:15 a solid inner core cells depth within thethat Earth's interior increases, the from Which weather variable by species this mantle B)B) p.m.convection D)C) 12:05 B) D)measured hurricanes A) B B) C cells D p.m. D) A A) density, temperature, and pressure A) earthquakes a solid inner core 5) The time that an earthquake occurs be inferred by that once lived in shallow watercan decrease B) amantle convection 14 What is the largest sediment that can be 18 Which combination of temperature and pressure instrument? C) liquid outer core A) density, temperature, and pressure decrease The inference that the inner core of the Earth is solid istime B) increases, but and pressure 15) According to convection the Earth Science Reference Tables, in which 22) B) density mantle cellstemperature knowing the 12) transported A seismograph station recordsthat a difference arrival C) a liquidto outer by acore stream hasstiffer a in velocity of 20) Where are earthquakes mosttemperature likely to take place? isD) inferred occur within Earth’s mantle? density changes B) density increases, but and pressure based on analysis of decrease (1) wind direction (3) wind speed group are the zones of the Earth's interior correctly arranged C) a liquid outer core between the Sand P-wave of 4 minutes. About how far A) distances between seismograph stations D) density changes 125 cm/sec? decrease A) along the core-mantle interface in order of increasing average density? 36) A) The thinnest section the Earth's crust istofound beneath C) density and temperature increase, but pressure (1) 3500°C and 0.4ofmillion atmospheres (2) air pressure (4) time amount ofP-waves rainfall D) density changes seismic away is thedata earthquake epicenter? [Refer the Earth B) epicenter distance and arrival of the The thinnestand section of the Earth's crust is found beneath C) decreases densitythe and temperature pressure B) where composition ofincrease, the Earthbut tends to be uniform 36) (1) cobbles (3) sand (2) 3500°C 2.0 million atmospheres Science Reference coastal plains Tables.] C) mountain regions mantle, core, outer core B)A) crustal rock C) travel time ofinner the of S-waves 36) A) Thecrust, thinnest section the Earth's crust is found beneath decreases C) near the temperature, Earth's Equator A)pebbles coastalregions plains C) mountain regions (2) clay2,600 density, and pressure (3) 5500°C and atmospheres B) desert D) oceans B)D) crust, mantle, outer core, inner core increase C) radioactive data0.4 million(4) D) arrival time of P-waves A) 1,000 km C) km A) near coastal plains C) mountain regions 16 Mt. Marcy often the coldest nighttime D) density, temperature, pressure increase D) a fault zone hasand B) desert regions D) oceans (4) 5500°C and 2.0 million atmospheres inner core, outer core, mantle, crust D) meteorite composition 34) C) It is suggested that the outer core of the Earth is liquid. B)part 5,200 km zone of the Earth'sD)interior 1,900iskm of which inferred to B)issandstone desert regions D) oceans in York State because ofliquid. its 6) temperatures A layer isthe found tilted at angle of 75D from the 37) A 34) It suggested thatNew outer core ofan the Earth 21) A P-wave reaches a core, seismograph station 2,600 is kilometers 37) The A part of to which zone of theshows Earth's interior is inferred to to is core, the strongest evidence for this? D)Which outer inner mantle, crust have a density of 10.0 grams per cubic centimeter? [Refer 23) According the Earth Science Reference Tables, the rate 15 photograph below a valley. d. horizontal. What probably this 75DAccording tilt? Which isearthquake the strongest for this? 37) (1) A part of which zone ofevidence thecaused Earth's interior is inferred to the latitude and planetary winds from an epicenter at 12:10 p.m. nds have a density of 10.0 grams per cubic centimeter? [Refer Earth Science Reference Tables.] A)getP-waves disappear as they move through ofthe temperature increase below the Earth's surface is greatestto 16) To aa sample material from the drilling the willouter be have density of 10.0 grams permantle, cubic centimeter? [Refer to Earth Science Reference Tables, at what time did the A) Nearly all sandstone layers are formed from wind(2) latitude and elevation the Earth Science Reference Tables.] P-waves disappear as they move through the outer core. the oceanic crust rather than through the between depths done through A) outer core of C) crust thelongitude Earth Reference Tables.] er deposited sands. earthquake occur? core. Science (3) and planetary winds A) outer core C) 1500 crust B) S-waves disappear as they move through the outer continental crust because oceanic crust is B) inner core D) mantle A) 3500 and 4000 km C) and 2500 km B) The formed layer were A) longitude outersediments coredisappear C)sandstone crust p.m. S-waves as they this move through the outer (4) and that elevation A) 12:01 p.m. C) 12:19 B) inner core D) mantle core. A) younger than continental crust B) 250 and 500 km D) 2500 and 3500 km that er 38) The analysis of seismic data from an earthquake shows originally deposited a 75D tilt. core. B) S-waves inner p.m. core D) through mantle B) 12:15 D) 12:05 p.m. speed up asatthey move the outer core. 38) The analysis of seismic data from an earthquake shows that B)C) more dense than continental crust some locations received both P-waves and S-waves, but S-waves speed up as they move through theto outer core. C) This sandstone layer has recrystallized due contact P-waves are transmitted through the outer 38) D) Thethinner analysis of seismic data from earthquake shows inference that the inner core ofanthe Earth is core. solid is that which some locations locations received received only both P-waves. P-waves and S-waves, but than continental crust er core. 22) C)The other What is the best D) P-waves arereceived transmitted outer core. but somemetamorphism. locations boththrough P-wavesthe and S-waves, based on analysis of anged other locations received only P-waves. What is the best D)D) softer than continental crustchanged position due to inference that can be made from these observations? This sandstone layeronly has otherseismic locations received P-waves. What is the best inference that can be made from these observations? A) data A) A zone of liquid rock exists within the Earth. crustal movement. inference that can be made from these observations? A) S-waves A zone ofare liquid exists within the Earth. B) crustal rock B) veryrock weak. A) radioactive A zone of liquid C) data rock exists within the Earth. B) S-waves are very weak. C) Some seismographs are more sensitive than others. B) meteorite S-waves are very weak. P.S./E. Sci.–Jan. ’09 [5] [OVER] C) Iron Someinseismographs are moreS-waves sensitive thantraveling. others. D) composition D) some rocks prevents from M. Sammartano C) Some seismographs are more sensitive than others. D) Iron in some rocks prevents S-waves from traveling. 23) According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, the rate 39) Earthquakes generate compressional waves (P-waves) and D) Iron in some rocks prevents S-waves from traveling. of temperature increase below the Earth's surface is greatest 39) shear Earthquakes generate compressional (P-waves) e waves (S-waves). Compared to waves the speed of shearand A) B) 16 De occ (1) (2) (3) (4) 17 Th lay rai Wh res (1) (2) 18 Wh de in (1) (2) 19 Ox in (1) (2)