Study Guide KEY
advertisement

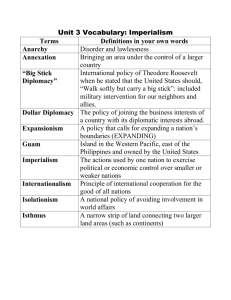
America as a World Power Study Guide Use your notes and the textbook to help you complete the study guide. Section I. Foreign Policy Spectrum Name and define each stance of the foreign policy spectrum. Be able to apply each to situations. 1. Isolationism : “loner,” do not protect or politically/militarily interact with other countries 2. Collective Security : “safety in numbers,” work with other countries to protect each other 3. Internationalism : intervene in other countries’ affairs 4. Imperialism : taking over smaller, weaker countries for your own gain Name and define the two beliefs that influence foreign policy decisions. 1. Idealism : putting others’ needs first 2. Realism : putting your own needs first Think of an example for each of these beliefs that shows what each means. List the four motivations for Imperialism. 1. Humanitarian (improving others) 3. Social Darwinism (survival of the fittest) 2. Political/military (naval bases) 4. Economic (make money) Reread your foreign policy notes. Section 2: Early American Foreign Policy Name the three influential presidents between 1790 and 1870. 1. Washington 2. Monroe 3. Polk Explain each president's foreign policy. 1. Washington: unilateralism and neutrality, avoid any political or military ties to others. 2. Monroe: Monroe Doctrine, promotes neutrality and declares the western hemisphere is closed to European colonization 3. Polk: Manifest Destiny, wants to aggressively expand America from coast to coast by treaties, purchases, and war What started the Mexican-American War? Texas border dispute Summarize the Texas Revolution of 1836, specifically the Alamo. Texas was a colony ruled by Mexico, declared they wanted independence, fought battles including the famous Battle at the Alamo where Texas rebels were slaughtered by the Mexican army, Remember the Alamo became the rallying cry of the Texan rebels who went on to win the revolution. Reread chapter 19 and outline from your notes. Section 3: Spanish-American War List the four causes of America declaring war on Spain. 1. Yellow Journalism 3. De Lome Letter 2. USS Maine explodes 4. American business interests What document was created to officially end the war? Treaty of Paris What did this document say? Cuba given independence, Puerto Rico and Guam given to the US, Philippines sold to the US for $20 million. Reread chapter 20 and review notes on the war. Section 4: Gilded Age What are the four causes for America to change their foreign policy from neutrality to imperialism? 1. New Markets 3. Global Competition 2. Militarism 4. Cultural Superiority Name the three influential presidents from the Gilded Age and their foreign policy. 1. Roosevelt : Big Stick Policy-patience and then force when necessary, Roosevelt Corollaryextension of Monroe Doctrine 2. Taft : Dollar Diplomacy-economic goals, limited force 3. Wilson : Moral Diplomacy-democratic ideals, self-determination Describe why and how America expanded to each of the following overseas locations. 1. Hawaii : Economic (sugar tax) and military (navy base) benefits, overthrew Queen Liliuokalani who wanted a “Hawaii for Hawaiians” in January 1898. 2. China : Imperial countries were dividing China into Spheres of Influence (territories where their country could only trade and set up bases), America reacted by declaring the Open Door Policy (free trade in China) to protect American trading rights in China. 3. Philippines : Economic (resources), military (set up bases), and cultural (religion) motivations, purchased following the Spanish-American War. Summarize how Roosevelt acquired territory to build the Panama Canal. Tried to negotiate with Columbia for a lease to build the Canal (Columbia owned the territory which is Panama today), Columbia refused to give Roosevelt the land, America incited or stirred up a revolt of the Panamanians against the Columbians, as a reward for helping the Panamanians in their success America given the land they needed to create the canal. Reread chapter 21 and review your notes from this chapter. Section 5: Vocabulary Be able to define and use the following vocabulary terms. Internationalism Isolationism Rough Riders Collective Security Anti-Imperialist League Imperialism Platt Amendment Idealism Open Door Policy Realism Spheres of Influence Annexation Panama Canal Ceded Big Stick Diplomacy Unilateralism Roosevelt Corollary Monroe Doctrine Dollar Diplomacy Yellow Journalism Moral Diplomacy USS Maine Treaty of Paris