Lesson - Scholar
advertisement

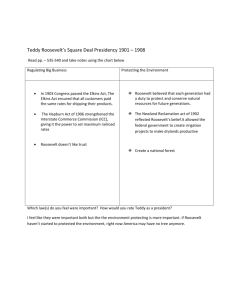
Fall Lesson Plan Template. Title: Teddy Roosevelt, Panama, and the Media Lesson Author: Brandon Sexton, Curtis Brown, Erin Weiss Key Words: Big Stick Diplomacy, Roosevelt Corollary Grade Level: 7th Time Allotted: 45 minutes Rationale/ Purpose (so what?) To help students understand the power America holds in the Americas, due in part to Theodore Roosevelt, his “Big Stick diplomacy”, and the Roosevelt Corollary. Also, to help understand the role of media in establishing Roosevelt as such a crucial person in American history Background/Context: Looking Backwards: Industrial and Progressive Eras, rise of American business and social change. Spanish American War and the rise of Teddy Roosevelt Looking Forwards: World War I, the role of America as the industry giant, Wilson and his Fourteen Points Key Concept(s): Diplomacy – The conduct by government officials of negotiations and other relations between nations. Isthmus – A narrow strip of land, bordered on both sides by water, connecting two larger bodies of land. Doctrine – A particular principle, position, or policy taught or advocated, as of a religion or government Corollary – An immediate consequence or easily drawn conclusion. Imperialism – Acquisition of territories for the advantage of the mother country NCSS Standard(s) SOL Information NCSS Theme (s) with indicators: Power, Authority, and Governance help students to explain the purpose of government and how its powers are acquired, used, and justified; guide learners to explain how governments attempt to achieve their stated ideals at home and abroad. have learners explain conditions, actions, and motivations that contribute to conflict and cooperation within and among nations; SOL* : USII.4b The student will demonstrate knowledge of the changing role of the United States from the late nineteenth century through World War I by describing Theodore Roosevelt’s impact on the foreign policy of the United States. 1 Fall Lesson Plan Template. Essential Knowledge: Essential Skills : The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine - asserted the United States’ right to interfere in the economic matters of other nations in the Americas - claimed the United States’ right to exercise international police power - advocated Big Stick Diplomacy (building the Panama Canal). Analyze and interpret primary and secondary source documents to increase understanding of events and life in United States history. (USII.1a) Make connections between past and present. (USII.1b) Guiding Question(s): What were Theodore Roosevelt’s foreign policies? What was Theodore Roosevelt’s impact on the foreign policy of the United States? How did the media portray Theodore Roosevelt in America? The day’s big question: How do countries win wars, and make others do what they want? How does media influence how people look at others? Lesson Objective(s): Obj. 1 SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of what the Monroe Doctrine said, and what the Roosevelt Corollary added to it. Obj. 2 SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of Theodore Roosevelt’s “Big Stick Diplomacy” and how it affected the building of the Panama Canal Obj. 3 SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of how the media helped define Theodore Roosevelt in the American landscape. Assessment Tool(s) to be usedAssessment 1: Informal: Student’s participation in cartoon analysis Assessment 2: Informal: Texts from the Past 2 Fall Lesson Plan Template. Materials: Historical Source(s): Additional Materials/Resources: Political Cartoons of Roosevelt (Material A) PowerPoint Presentation (Material B) Quick Notes Sheet (Material C) Cartoon Analysis Sheet (Material D) That’s a Wrap! Worksheet (Material E) Procedure/Process: 1) JUST DO IT! The “Hook”: Have students answer these questions: How did United States take the land from the Native Americans? Why? How did the Union defeat the Confederacy? What are the similarities between the two? In most wars, what do the winners usually have? 2) Instructional sequence: Obj # See above. Just do it. Transition: Objective # 1: SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of what the Monroe Doctrine said, and what the Roosevelt Corollary added to it. Transition: 3 Processing Activity and Procedure Check for Evidence of Understanding Students will answer the questions on a personal sheet of paper about how the victors in various wars defeated their enemy. Namely, they had a larger army than the other group. This reinforces the “Big Stick” diplomacy that we are talking about. Students pull out their Quick Notes sheet and prepare for a lecture Quick Notes Power Point Quick Notes sheet (Material (Material B) will introduce C) completed for ‘Monroe students to Theodore Doctrine’ and ‘Roosevelt Roosevelt, followed by an Corollary.’ The Closure explanation of the “Monroe activity (material F)will also Doctrine” and Roosevelt’s check for understanding. interpretation, known as the “Roosevelt Corollary” N/A Fall Lesson Plan Template. Objective # 2: SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of Theodore Roosevelt’s “Big Stick Diplomacy” and how it affected the building of the Panama Canal Transition: Objective #3: SWBAT demonstrate an understanding of how the media helped define Theodore Roosevelt in the American landscape. Closure: Quick Notes Power Point will help students understand Roosevelt’s “Big Stick” philosophy, how it played into the building of the Panama Canal, and how the Canal works. Quick Notes Sheet (material C) completed for ‘”Big Stick” diplomacy’ and ‘Panama Canal.’ Understanding will also be assessed on the Closure activity (material F) Students will put away their Quick Notes sheet, and set their notebook aside. They will be given the Cartoon Analysis worksheet (Material D) Students will be shown, on a Smart Board Notebook file, four political cartoons Students will be about teddy Roosevelt (Material A). The completing a first cartoon analysis will be modeled by worksheet that by the teacher, showing kids how to analysis a simple glance political cartoons. Students will then be and read, student shown three more cartoons, and they will understanding be asked to complete the next cartoon could be together as a class. The individual interpreted. students will complete the analysis of the final two cartoons. Texts from the Past: Students will define key terms discussed during the lesson in 160 characters or less (in texting lingo). They will also “send” text messages to Panama and Colombia as Teddy Roosevelt. 3) ClosureTexts from the Past: Students will define key terms discussed during the lesson in 160 characters or less (in texting lingo). They will also “send” text messages to Panama and Colombia as Teddy Roosevelt, demonstrating their understanding of how Teddy Roosevelt ‘took the isthmus’. Modifications/Accommodations for Diverse Learners: • • • • • 4 Allow students ample time to complete their Quick Notes sheet Allow work with partners on the cartoon analysis assignment Paper copies of the cartoons Give students opportunity to share verbally what they learned, if writing is an issue Sheet has multiple levels for ELLs (New ELLs can simply point out what is on the cartoon, more well adjusted ELLs can elaborate more and more) o If ELLs are Hispanic, allow them to tell the story of American Imperialism from a Latin American Standpoint Fall Lesson Plan Template. Evaluation Rubric: Complete the rubric for each lesson plan and attach cover sheet. (You should have 1 cover sheet and 10 rubrics.) Please Circle NCSS Theme and attach to the correct themed lesson. NCSS THEME I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X Rating Scale (can include half points on the scale) 1) The lesson plan is focused on a specific NCSS thematic standard, is designed to answer a specific guiding question, and has a strong content/skills focus and rationale. (Students must make sure they meet all the required criteria as detailed above.) Not focused highly focused .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________.5 Comments: The NCSS theme of Power, Authority, and Governance is clearly represented in this lesson, as it deals with the exercising of new United States power in Latin America, particularly in the case of the Panama Canal, and how Teddy Roosevelt started a wave of imperialistic thinking in America. 2) The lesson plan is designed to clearly address specific social studies SOL with a clearly focused list of Essential Knowledge, Skills, and Understandings (See SOL Resource Guide), and NCSS performance expectations and indicators. (What are students going to do based on the theme? - See Expectations for Excellence.) Not addressed Clearly Addressed .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________.5 Comments: The lesson clearly relates the SOL USII.4b which deals with the new American role in world politics up until World War II, particularly dealing with imperialism and Teddy Roosevelt’s policies in Panama. This lesson deals explicitly with Teddy and his role in American imperialism with Panama. 3) The lesson plan includes clear, motivational, intriguing and relevant guiding questions (big question). 5 Fall Lesson Plan Template. Not addressed Clearly Addressed .1__________.2__________.3__________.4_____4.5_____.5 Comments: The guiding questions are clear and straight to the point of the lesson. By the end of the lessons, students can answer about the Monroe Doctrine, Roosevelt Corollary, Teddy Roosevelt and his Big Stick policy, and America’s role in Panama. 4) The lesson plan includes well-written and explicit objectives Unclear objectives Clear objectives .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________5 Comments: The objectives are explicit in nature as they help students understand how to perform an analysis, via modeling. It is also explicit on how to do the texts from the past activity. 5) The lesson plan includes a tightly focused bell ringer/motivational hook that relates to the lesson. (1-5 minutes)- (Independent student work) (Just Do it). Unclear Objectives Clear Objectives .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________5 Comments: The Just Do It is relevant to the guiding and big question of the day and is a review of past conflicts (Indian Wars and Civil War) and how the idea of Power prevails through all conflicts. 6) The lesson plan includes detailed instructional activities that directly correlate with specific objectives. Not Focused Clearly Focused .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________.5 Comments: The cartoon analysis(instructional activity) correlates directly with the learning objectives as the students figure out how the media portrayed Teddy Roosevelt. 7) The lesson plan contains clearly focused and detailed directions for students, question frames, and lecture outlines, when appropriate, to facilitate directions and learning. (These are also part of the materials section)- A teacher should be ready to go with the lesson. 6 Fall Lesson Plan Template. Not Focused/Detailed Highly Focused/Detailed .2__________.4__________.6__________.8______9____.10 Comments: The lesson plan includes transitions and directions regarding the lesson plan. While a good amount of the lesson material is ‘lecture’ based, it requires a lot of transition on the back end, from lecture to analysis activity to texts from last night. 8) The lesson plan includes a focused and clear closure that either provides students with the opportunity to answer the guiding question (assesses student understanding) or clearly summarizes the day’s key points in relation to the key question. Not Focused Highly Focused .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________.5 Comments: The closure directly relates with the big questions and lets students express their findings in writing that is ‘age relevant’ 9) The lesson plan provides a clearly designed assessment within the closure to measure student growth/with model answer(s) that is explicitly connected to the lessons essential understandings, objectives, and the strategies for learning Not Clear and Appropriate Highly Clear and Appropriate .1__________.2__________.3__________.4__________.5 The closure assesses student learning because it relates the Just Do It, big and guiding question, and objectives. 7