GENETICS STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

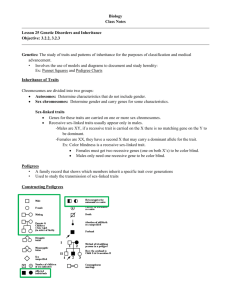
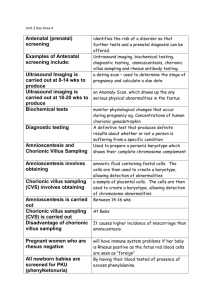
Honors Biology 2011 Ms. Lidman & Mrs. Abbott GENETICS STUDY GUIDE VOCAB TO KNOW: • heredity • genetics • homozygous • heterozygous • phenotype • genotype • dominant • recessive • allele • gene • Punnett square • test cross • • • • • • • • • • • • monohybrid cross P generation F1 generation F2 generation dihybrid cross incomplete dominance non-disjunction autosomes sex chromosomes co-dominance epistasis pleiotropy • • • • • • • • • • • • polygenic inheritance autosomal recessive autosomal dominant mitochondrial linked sex-linked (x or y) trait sex-limited trait sex-influenced trait pedigree carrier gamete zygote karyotype 1. Why did Gregor Mendel, the father of modern genetics, study peas (as opposed to humans, for instance)? Did he study traits with continuous or discontinuous variation? When (approximately)? 2. Mendel crossed pure (homozygous) round seeded pea plants with pure wrinkled seeded pea plants and all the F1 generation plants had round seeds. What would be the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F2 generation if the F1 generation selffertilized? 3. Describe Mendel’s Law of Segregation and Independent Assortment. How do these laws contribute to variability in offspring? 4. What does probability have to do with genetics? How are the principles of probability used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses? Honors Biology 2011 Ms. Lidman & Mrs. Abbott 5. In genetics, the larger the number of offspring examined, the closer the results should approach the predicted ratio. Can you think of an example outside of biology in which a large sample size is beneficial? 6. What is the binomial expansion for (a+b)3? If you flipped three coins 100 times, how many times would you expect to have all heads? 7. Why is a X2 test useful? What does a p-value of less than 5% mean? 8. What is a test cross? Give an example of when you might use a test cross. 9. Give an example of a dihybrid cross. If you cross parents that are heterozygous for two traits, what is the expected phenotypic ratio in their offspring (assuming mendelian inheritance)? 10. How could you predict the outcome of a trihybrid cross without making a 64-box Punnett square? Ex. What percentage of offspring of two pea plants heterozygous for height (Tt), flower color (Pp), and seed texture (Rr) would display the dominant traits? 11. What does it mean if a trait exhibits non-mendelian inheritance? Describe and give an example of each of the following: • Incomplete dominance vs. co-dominance • Multiple alleles Honors Biology 2011 Ms. Lidman & Mrs. Abbott • Epistasis • Pleitropy • Polygenic Inheritance • Environmental Influences: Why do identical twins not typically weigh exactly the same amount? 12. What happens during non-disjunction? What’s an example of a disorder caused by nondisjunction of sex chromosomes? 13. Why is a karyotype a useful test for diagnosing some genetic disorders? What are its limitations? What would it look like for a girl with Down Syndrome? 14. What determines gender in Homo Sapiens (i.e. Why should Anne Boleyn not have been blamed for an inability to bear sons)? 15. What are autosomes, and how many are there in humans? How many autosomes are in individuals with Downs? 16. Color blindness is caused by a recessive, sex-linked trait. How come color blindness is more common in men? What conditions must be present in a family in order for a woman to be color blind? Honors Biology 2011 Ms. Lidman & Mrs. Abbott 17. What are the most common and least common blood types in the US? Could someone with type AB blood receive a transfusion of type A blood? Could someone with type O blood receive a transfusion of type AB? What are the likely consequences of these transfusions? 18. Understand what an autosomal dominant vs. autosomal recessive pedigree would look like, as well as sex-linked recessive and sex-linked dominant. Explain the pattern of inheritance below. Assign a genotype to each of the individuals. 19. Can the traits shown in the following pedigrees be autosomal dominant? Autosomal recessive? X-linked recessive? X-linked dominant? Explain. a. b. Review practice problems (Punnett squares, blood types, binomial expansion, etc.)!