SKILLS Working with Population Pyramids SKILLS
advertisement

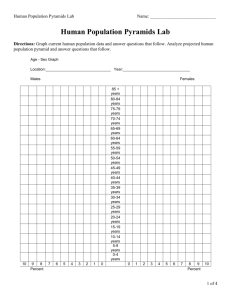
144 SKILLS SKILLS Working with Population Pyramids M1 Elements of a population pyramid A population pyramid is a common demographic chart. It graphically displays a population’s age structure and sex composition. Set-up of a population pyramid Bar graphs are a handy way to illustrate numbers. With a population pyramid demographic data (M2) are often presented as two back-to-back horizontal bar charts. Males are plotted on the left and females on the right, with a vertical axis showing age ascending in five-year intervals (five-year cohorts), from the youngest upwards to the oldest. The horizontal axis shows either the population of the cohorts in millions or in per cent. Thus each horizontal bar represents the size of an age-sex cohort as a share of the total population. Interpreting a population pyramid When drawn as a population pyramid, age distribution can hint at patterns of growth. A bottom heavy pyramid suggests high birth rates, falling or stable death rates, and the potential for rapid population growth. This type is called an expansive pyramid. A top heavy pyramid suggests negative population growth that might be due to different factors, including low birth rates or an increased emigration of people especially from the younger cohorts. This type is called a constrictive pyramid. The third type, a stationary pyramid, shows roughly equal numbers of people in all cohorts, with a tapering towards the older age. The sex ratio frequently varies in different cohorts, with the top of the pyramid often showing that females comprise a majority. This is because females typically outlive males. Pyramids also show the relationship between the dependent population (under 20 and over 64 years) and the economically productive population (between 20–64 years). Model text The population pyramid of Germany (2007) shows a narrow base reflecting a low birth rate. The wide middle part shows that the economically productive population is bigger than the dependent population. The top of the population pyramid is characteristic of a country with a high life expectancy. The sex ratio is mostly even or shows a slightsurplus of the female population in the cohorts from 70 years on. This reflects the higher life expectancy of the female population. All in all, this population pyramid is a mixture of two types, a stationary and a constrictive pyramid. For the future it shows the problem that the share of the economically productive population will markedly decrease. The shape of a population pyramid shows the development status of a country – there is a distinct difference between the pyramids of a less economically developed country (LEDC), e. g. Niger, and a more economically developed country (MEDC), e. g. France (M3). Country or area/ year/ age 145 Population both sexes Population male Population female Per cent both sexes Per cent male Per cent female 82,400,996 40,478,053 41,922,943 100 100 100 0– 4 3,489,184 1,790,721 1,698,463 4 4 4 5– 9 3,896,719 1,999,317 1,897,402 4 4 4 10–14 4,099,194 2,104,686 1,994,508 5 5 4 15–19 4,744,341 2,434,380 2,309,961 5 6 5 20–24 4,758,914 2,444,354 2,314,560 5 6 5 25–29 4,800,835 2,467,411 2,333,424 5 6 5 30–34 4,706,691 2,240,071 2,286,620 5 6 5 35–39 6,325,862 3,255,284 3,070,578 7 8 7 40–44 7,306,422 3,767,858 3,538,564 8 9 8 45–49 6,657,608 3,400,387 3,257,221 8 8 7 50–54 5,765,938 2,904,702 2,861,236 7 7 6 55–59 5,209,151 2,592,984 2,616,167 6 6 6 60–64 4,325,817 2,123,926 2,201,891 5 5 5 65–69 5,363,001 2,563,473 2,799,528 6 6 6 70–74 4,061,797 1,851,039 2,210,758 4 4 5 75–79 3,015,014 1,255,543 1,759,471 3 3 4 80 + 3,874,508 1,101,917 2,772,591 4 2 6 Germany (2007) Total, all ages Source: U.S. Census Bureau, International Data Base (all data calculated; data in per cent rounded) M2 Population of Germany by age and sex M3 Population pyramids of a less economically developed country (LEDC) and a more economically developed country (MEDC)