Population Pyramids
advertisement

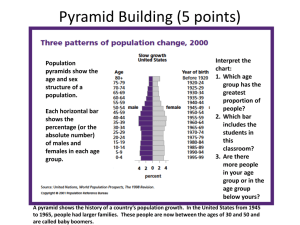
Grade 9 Geography – Unit 2 Lesson 13 Population Pyramids A Population Pyramid is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population. Most often, a population pyramid consists of two back-to-back bar graphs. Population is plotted on the X-axis and age on the Y-axis. One bar graph shows the males, while the other graph shows females in a particular population. The ages are made up of five-year age groups (also called cohorts). Males are shown on the left and females on the right. The number of males and females may be shown as absolute numbers or as a percentage of the total population. Types of Pyramids Pyramid shapes differ from country to country, or within a country, region to region. However, four general pyramid shapes, as determined by fertility rates and mortality rates, have been noted. ? Expansive — A broad base, indicating a high proportion of children, a rapid rate of population growth and a low proportion of older people. The pyramid points upward. Fertility is high so the many children are born replacing the parents. In Canada, Nunavut is an example of an expansive type population pyramid. ? Stable growth — A structure with indentations that even out and reflect slow growth over a period. The Northwest Territories is an example of a stable type population pyramid. ? Stationary — A narrow base and roughly equal numbers in each age group, tapering off at the older ages. The base and the centre of the pyramid make a box shape. In this case, fertility equals mortality. Manitoba is an example of a stationary type population pyramid. ? Declining — This pyramid has a small base suggesting a low proportion of children to many older people. The pyramid points downward. Fertility is so low that the number of children born does NOT replace the parents. In summary, a high proportion of aged persons and declining numbers. Newfoundland and Labrador is an example of a declining type population pyramid. Total Fertility Rate Another element of Population Pyramids is Total Fertility Rates (TFR). It is the single most important factor in determining future population. TFR is the average number of babies born to women during their reproductive years OR the sum of the age-specific birth rates of women in five-year age groups. Note - Fertility rate is the number of children born alive per thousand fertile women per year. ? A TFR of 2.1 is considered the replacement rate. Once TFR reaches 2.1, the population will remain stable assuming no immigration or emigration takes place. ? When TFR is greater than 2.1, a population will increase. ? When it is less than 2.1, a population will decrease, although due to the age structure of a population it will take years before a low TFR is translated into lower population. Although still high in many parts of the world, TFR has been declining dramatically over the past decade. As shown in Table 1, the TFRs in the developed countries (e.g., Canada are below the replacement rate, although in many of these countries population continues to grow due to the age structure of the population as well as immigration. Currently 61 countries have a TFR of 2.1 or less (Canada’s 1998 TFR was 1.7). The TFR for less developed countries is twice as high as the developed countries. However, it is falling -- TFRs in less developed countries dropped almost 40 percent from 4.7 in 1990 to 3.1 in 2000. Although the cause is debated, there is no doubt that women all over the world are having fewer children. Table 1. World Total Fertility Rates (Observed and Predicted). Region 1990 TFR 2000 TFR 2010 TFR 2020 TFR World 3.4 2.8 2.5 2.3 Less 4.7 3.1 2.7 2.4 Developed Countries Developed 1.9 1.6 1.7 1.7 Countries Source: www.overpopulation.com/faq/basic_information/total_fertility_rate In 2005, Niger has the world’s highest TFR at 8.0 children. How do you calculate TFR? This is the data for Canada. ? Divide Number of Live Births / Female Population in the Age Group to determine the Age Specific Birth Rate ? Sum the Age Specific Birth Rates ? Multiply by 5 to calculate the TFR. Table 2. Age of Mother 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-49 Number of Live Births 367 15 267 30 613 42 245 39 105 17 378 2 808 94 Female Population in the Age Group 387 341 408 422 403 191 397 398 446 488 469 810 458 439 413 377 SUM Age Specific Birth Rate 0.0009 The TFR is the sum of the age-specific birth rates multiplied by five. What is Canada’s TFR? From the above information, is Canada’s childbearing population is replacing itself? Provide an explanation with your answer. Grade 9 Geography – Unit 2 Lesson 9 Population Pyramid – India All information is from the 2007 CIA World Factbook. India is the second most populous country in the world with a 2006 population of just less than 1.1 billion people. Population Density is 368.4 persons / km2 Population Growth Rate is 1.38%. Fertility Rate is 2.73 children / woman (2006 estimate). Life Expectancy is 64.7 years. Infant Mortality Rate is 54.6 deaths / 1 000 live births. Median Age is 24.9 years Slightly over 30% of the population is under the age of 15. Literacy Rate (15 years and older who can read) is 59.5% Annual GDP per capita (Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)) is $3 700. Unemployment Rate is 7.8% Over 25% of the population lives below the poverty line. About 80% of the population is Hindu. India has 14 official languages. India’s debt is about $132 billion, and India receives $2.9 billion in aid annually. A population pyramid can reveal much information about a country’s population, age structure, future service needs and priorities, potential, etc. Construct a Population Pyramid of the following datasets. Table 1 . Percentage of Males and Females in Various Age Groups for the 2000 India Population Age % Female % Male 0-4 11.9 12.2 5-9 11.1 11.4 10-14 10.4 10.6 15-19 9.9 10.0 20-24 9.3 9.3 25-29 8.7 8.6 30-34 7.6 7.6 35-39 6.5 6.5 40-44 5.5 5.5 45-49 4.6 4.6 50-54 3.8 3.8 55-59 3.2 3.1 60-64 2.6 2.5 65-69 2.0 1.8 70-74 1.4 1.2 75-79 0.8 0.7 80+ 0.6 0.4 Note: Total India population in 2000 was just over 1 billion people. Table 2. Projected Percentage of Males and Females in Various Age Groups for the 2050 India Population Age % Female % Male 0-4 6.4 6.6 5-9 6.4 6.6 10-14 6.5 6.7 15-19 6.5 6.8 20-24 6.5 6.9 25-29 6.5 6.9 30-34 6.4 6.9 35-39 6.4 6.9 40-44 6.4 6.8 45-49 6.4 6.7 50-54 6.2 6.4 55-59 5.7 5.8 60-64 5.2 5.2 65-69 4.8 4.6 70-74 4.2 3.8 75-79 3.5 2.9 80+ 5.8 3.6 Note: Total ESTIMATED population for India by 2050 is 1.8 billion people. Answer the questions… 1. Describe the general shape of the two population pyramids? 2. What were the major similarities and differences between the two years targeted for review? 3. What are the implications for India if the projection occurs? 4. Offer some possible solutions (e.g., reduced birth rate)