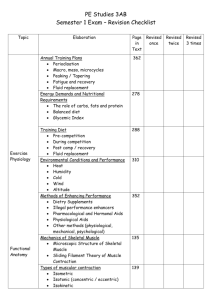
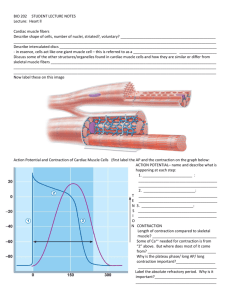
Skeletal Muscle Contraction List the 6 steps of muscle contraction
advertisement

Skeletal Muscle Contraction List the 6 steps of muscle contraction a. b. c. d. e. f. 1. Which of these steps required energy? Why? 2. Which of these steps results in the most movement? 3. Give two examples of actions you use skeletal muscles contraction to complete Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Connective tissue 1. ___________________Connect muscle to bone 2. An skeletal muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue layer called _____________. This was observed in the chicken wing dissection. What did it look like? 3. ___________________ surrounds fascicles (bundles of muscle cells) and create passages for nerves and blood vessels 4. _________________ surrounds and protects individual muscle cells/fibers Muscle Fibers 1. Sarcomeres are _________________________________________________________ 2. The movement proteins in sarcomeres are __________________ and _______________ 3. Thin filaments are made of primarily______________ 4. Thick filaments are made of primarily __________________ 5. Describe the arrangement of thick and thin in a sarcomere (Which is connected to the Z-line; which is in the middle?). 6. This arrangement causes skeletal muscle cells to look ______________ under a microscope. Which kind of muscle is also looks like this? Skeletal muscle anatomy during contraction 1. Do the thin or thick filaments move towards the center of the sarcomere during contraction? 2. Name three reasons why connective tissue important during muscle contraction Types of muscle contraction 1. What is a tetanus? What is a twitch? Give examples of each 2. Define and give two examples of isotonic contractions and isometric contractions. 3. What kind of contraction was the wall-sit? What kind of contraction is lifting a spoon? What kind of contraction is trying to pick up a table? Energy for muscle contraction 1. What molecule do muscle cells use during muscle contraction for energy? 2. Once the 4-6 seconds of stored energy in muscle cells is used, ___________________ and ___________________are the two pathways used to acquire more energy. 3. Describe anaerobic and aerobic metabolism by answering the following questions for each: a. Is the process fast or slow? b. How many molecules of ATP are produced? c. Is oxygen required? d. Is lactic acid produced?