Bio202studentlecturenotesHeartll
advertisement

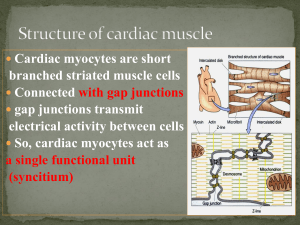
BIO 202 STUDENT LECTURE NOTES Lecture: Heart ll Cardiac muscle fibers Describe shape of cells, number of nuclei, striated?, voluntary? ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Describe intercalated discs ____________________________________________________________________________ - in essence, cells act like one giant muscle cell – this is referred to as a _____________________ __________________ Discuss some of the other structures/organelles found in cardiac muscle cells and how they are similar or differ from skeletal muscle fibers ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Now label these on this image Action Potential and Contraction of Cardiac Muscle Cells (first label the AP and the contraction on the graph below: ACTION POTENTIAL– name and describe what is happening at each step: 1. ________________________ : ______________________________________ ______________________________________ 2. _________________________: T ______________________________________ E ______________________________________ N 3. _________________________: S ______________________________________ I ______________________________________ O N CONTRACTION Length of contraction compared to skeletal muscle? _______________________________ Some of Ca⁺⁺ needed for contraction is from “2” above. But where does most of it come from? _________________________________ Why is the plateau phase/ long AP/ long contraction important?___________________ ______________________________________ Label the absolute refractory period. Why is it important?______________________________ _______________________________________ Discuss the difference in how an AP starts in cardiac muscle and how it contracts as a unit versus motor units in skeletal muscle ____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Why do cardiac cells have lots of mitochondria? __________________________________________________________ They also have myoglobin. What does myoglobin do? _____________________________________________________ Intrinsic Conduction System Specialized cardiac muscle cells that do not ______________________ but can initiate and distribute _______________ What does autorhythmic mean? _______________________________________________________________________ How does an unstable resting potential relate to autorhythmic cells? __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ What are five types of these cells found in the intrinsic conduction system and indicate which is the fastest (which one sets the pace?) 1. _______________________________ 2. _______________________________ 3. _____________________________ 4. __________________________________ 5. ___________________________ The depolarization wave of the action potential spreads throughout the heart by the intrinsic conduction system and then by spreading through gap junctions between cells in the atrium and between cells in the ventricle. Why do the atrial cells not spread the AP through gap junctions to the ventricular cells? __________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ Then how does the AP go from the atrium to the ventricles? _______________________________________________ In going through this structure, there is a delay of about 0.1 sec. – why is this important? ________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Label the different “parts” of the intrinsic conduction system and indicate the direction of the action potential on the image to the right: What is an ECG (=EKG)? _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________ How many “leads”(tracings) are there? ________________________ Below, draw a normal ECG of a single heart contraction. Label the different waves and intervals and then with each, briefly indicate what is occurring electrically in the heart. Extrinsic control of heart rate: ANS can change the rate and force of contraction: The overall cardiac center in the ________________ of the brainstem is composed of three component centers, two of which are: 1. cardioaccelatory center What division of ANS? ____________________ What three areas does it innervate, and what are its effects? 1. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 2. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 3. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 2. cardioinhibitory center What division of ANS? ____________________ What two areas does it innervate, and what are its effects? 1. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 2. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Heart Sounds: What causes the first heart sound (“Lub”) _______________________________________________________________ What causes the second heart sound (“Dup”) ____________________________________________________________ What is a heart murmur? ____________________________________________________________________________ What is often the cause of murmurs in adults? ___________________________________________________________