Intramembranous ossification
advertisement

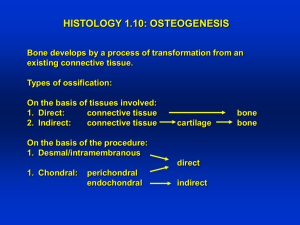
Osteogenesis g Intramembranous ossification Mesenchymal osteoblast Secrets osteoid Endochondral ossification Hyaline cartilage eroded Osteoblast invade Osteogenesis imperfecta: ↓Collagen C ll I Defecte collagen I fracture Intramembranous ossification In flat bone condensed layer of Embryonic mesenchym Ossification centers Progenitor cell differentiation Osteoblast around vessels Osteoid secretion Calcification Woven trabecula formation Lacuna formation Ossification centers fusion Compact bone surrounded spongy bone Remaining connctive tissue forms: Endosteum periosteum Stages of o Intramembranous t a e b a ous Ossification Oss cat o Stages g of Intramembranous Ossification Endochondral ossification Most M tb bones (l (long b bones)) Bone Collar Stages g of Endochondral Ossification Secondary Secondary ossification center Hyaline cartilage Epiphyseal blood vessel Deteriorating Deteriorating cartilage matrix Spongy bone bone formation Primary Primary ossification center Bone collar i l Articular cartilage Spongy bone Medullary cavity Epiphyseal plate cartilage Blood vessel of periosteal bud 1 Formation of Formation of bone collar around hyaline cartilage model. 2 Cavitation of the hyaline cartilage within the cartilage model. 3 Invasion of internal cavities by the periosteal by the periosteal bud and spongy bone formation. 4 Formation of the medullary cavity as medullary cavity as ossification continues; appearance of secondary ossification centers in the epiphyses in preparation f for stage 5. 5 Ossification of the O ifi ti f th epiphyses; when completed, hyaline cartilage remains only in the epiphyseal plates and articular cartilages Figure 6.8 Bone g growth in epiphyses pp y Rickets: In children Calcium deficiency Epiphys deformation Impaired growth malntririon Vit. D deficiency Osteomalacia O t l i In adult Impaired calcification Much decalcification Bone g growth,, remodeling g & repair p Metabolic role of bone PTH Calcitonin Growth hormone Liver Somatomedian (IGF) Epiphysial growth Pituitary dwarfism Gi Gigantism ti Acromegaly Rheumatoid Rh id Arthritis A h ii Synovial membrane inflammation & thickening Collagenase & hydrolitic enz. Cartilage defect Joints Synarthrosis Diarthrosis Synarthrosis 1. Synostosis (sutures) 2. Syndesmosis (distsl tibiofibular & sacroiliac j) 3. Symphysis (pubis symphysis) Joints Diarthrosis Joint cavity Synovial fluid Synovial membrane 1. 2. Macrophage like synovial cell (A type) Fibroblastic synovial cell (B type)