The British Acts
advertisement

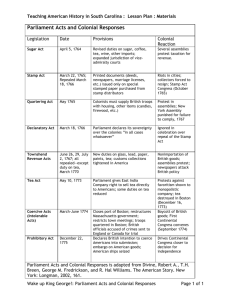
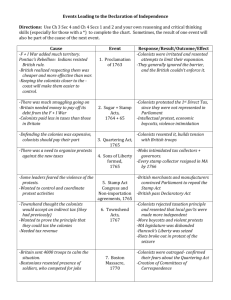
The British Acts 1660,1663,1673- The Navigation Acts 1st law- closed colonies to all trade except goods carried in English ships 2nd law- all goods had to pass through England to be taxed 3rd law- taxed coastal trade, appointment of customs officials to enforce acts 1762- Writs of Assistance -blanket search warrant to search ships and colonists homes for smuggled goods 1763- Proclamation of 1763 (Reaction to Pontiac’s Rebellion) -colonists could not settle West of Appalachian Mountains 1764- Currency Act -colonists could not print their own currency 1765- Quartering Act -colonists could be forced to accommodate British soldiers who were there to “protect” them 1765- Stamp Act -first direct tax- all legal documents and printed material required the purchase of a government stamp Colonial Reaction: slogan of “no taxation without representation” develops, Stamp Act Congress meets, leads to British repeal of Stamp Act 1765- Declaratory Act -Parliament asserted its right to regulate the colonies in “any way whatsoever” 1767- Townshend Duties -taxes on imported goods like lead, glass, tea; England also suspends colonial legislature Colonial Reaction: Sons of Liberty gains influence, more boycotts and protests, Boston Massacre takes place 1773- Tea Act -colonists must buy tea from British East India Company in order to avoid high taxes, tax remains on tea (other taxes are repealed) Colonial Reaction: Boston Tea Party 1774- Coercive Acts (Intolerable Acts) -closed Boston Harbor, limited colonial government, quartering act broadly expanded, designed to punish the colonists Colonial Reaction: First Continental Congress meets, grievances sent to King, begin preparing for war Bang!!!- First fighting begins at Lexington and Concord Debate Rounds Round 1- Writs of Assistance, Proclamation of 1763, and Currency Act Round 2- Quartering Act, Stamp Act, Declaratory Act, and Townshend Duties Round 3- Tea Act and Coercive Acts