Cell Cycle, Ch 10, Unit Science Department
advertisement
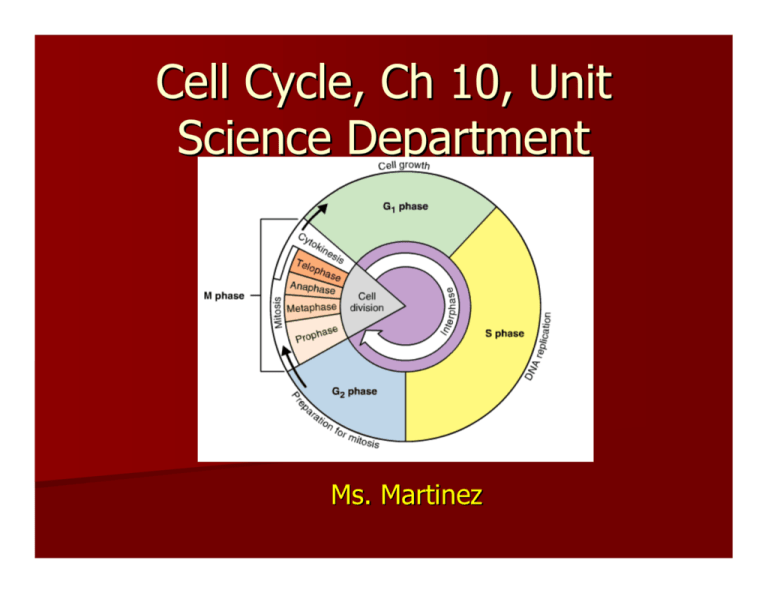
Cell Cycle, Ch 10, Unit Science Department Ms. Martinez 1. What are TWO reasons why cells divide rather than continually grow indefinitely? 10-2 1. What are TWO reasons why cells divide rather than continually grow indefinitely? From HW: 1. The larger the cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on it DNA 2. The more trouble the cell as moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane 2. What is DNA “overload?” 10-1 2. What is DNA “overload?” As a cell increases in size, it does not make extra copies of DNA. If a cell were to grow without limit, it would have way too much DNA or an “information” crisis 3. As the length of a cell increases, what happens to its volume? 10-1 3. As the length of a cell increases, what happens to its volume? It increases, and the surface area would get smaller 4. What is cell division? 4. What is cell division? The process by which a cell divides into two new, identical daughter cells 5. What are the 3 components of the cell cycle? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell cycle? 1. Interphase 2. Mitosis 3. Cytokinesis 6. ________________________ is the period during the cell cycle between cell divisions, during which DNA replication and protein synthesis take place. 6. ________________________ is the period during the cell cycle between cell divisions, during which DNA replication and protein synthesis take place. S phase 7. ______________________is the process by which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell. 7. ____________________ is the process by which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell. -Cell Division 8. _________is the process by which the cytoplasm divides forming two distinct cells. 8. _________is the process by which the cytoplasm divides forming two distinct cells. -Cytokinesis 9. ______- are structures in the cell that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next. 9. ______- are structures in the cell that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next. Chromosomes 10. During the cell cycle, a cell ______________, prepares for __________, and ____________ to form two ________ cells, each of which then begins the cycle again. 10. During the cell cycle, a cell grows ______________, prepares for divides division __________, and ____________ Identical daughter to form two ________ cells, each of which then begins the cycle again. 11. What are the three main parts of Interphase? 11. What are the three main parts of Interphase? G1, S, G2 12. What happens during the G1 phase? 12. What happens during the G1 phase? cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles 13. What happens during the S phase? 13. What happens during the S phase? chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place 14. What happens during the G2 phase? 14. What happens during the G2 phase? many of the organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced 15. Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: _______________, __________, _______________, and _______________. 15. Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: Prophase Metaphase _______________, __________, Anaphase _______________, and Telophase _______________. 16. _____—the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the centrioles separate (in animal cells), and the nuclear membrane breaks down 16. _____—the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the centrioles separate (in animal cells), and the nuclear membrane breaks down Prophase 17. ____—the chromosomes line up across the midline of the cell and each chromosome is attached to a spindle fiber and centromere. 17. ____—the chromosomes line up across the midline of the cell and each chromosome is attached to a spindle fiber and centromere. Metaphase 18. ___—sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes 18. ___—sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes Anaphase 19. ____—chromosomes move to opposite sides of the dividing cell, and two new nuclear envelopes form. 19. ____—chromosomes move to opposite sides of the dividing cell, and two new nuclear envelopes form. Telophase 20. What is the name of structure “A”? 20. What is the name of structure “ A” ? Cell Plate 21. What is the structure labeled A in the figure below is called? 21. What is the structure labeled A in the figure below is called? Centromere 22. What is the structure labeled B in the figure below is called? 22. What is the structure labeled B in the figure below is called? Sister Chromatids 23. During which phase(s) of mitosis are structures like the one shown in below visible? 23. During which phase(s) of mitosis are structures like the one shown in below visible? Prophase 23. According to the figure below, what is the correct order of Mitosis? 23. According to the figure below, what is the correct order of Mitosis? C, B, A, D 24. What are centrioles? 24. What are centrioles? one of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope 25. What is cytokinesis? 25. What is cytokinesis? The cytoplasm pinches in half and two identical daughter cells are produced. 26. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter with how many chromosomes? 26. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter with how many chromosomes? 4 27. What is the process called by which Prokaryotes divide? 27. What is the process called by which Prokaryotes divide? Binary Fission 28. What is the nucleiod region of a prokaryote? 28. What is the nucleiod region of a prokaryote? The single chromosome of a prokaryote 29. Binary fission produces 2 identical ___________ cells. 29. Binary fission produces 2 identical ___________ cells. daughter 30. How fast can Binary Fission occur? 30. How fast can Binary Fission occur? In as little as 20 minutes 31. Cancer is the ____________ growth and division of cells 31. Cancer is the ____________ growth and division of cells uncontrollable 32. As the tumor grows, it _____________________ neighboring cells and tissues 32. As the tumor grows, it destroys _____________________ neighboring cells and tissues 33. What are two types of cancer? 33. What are two types of cancer? Benign and Malignant 34. What type of cancer describes cells that grow in a ball, do not affect other cells? 34. What type of cancer describes cells that grow in a ball, do not affect other cells? Benign 35. What type of cancer describes cells where unorganized growth that can spread to other parts of the body or tissues? 35. What type of cancer describes cells where unorganized growth that can spread to other parts of the body or tissues? Malignant 36. What is a tumor? 36. What is a tumor? A group of cancer cells 37. Which diagram below shows cancer cells? 37. Which diagram below shows cancer cells? A Study! Practice Questions A. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the cell cycle? a. C, M, G1 , S, G2 b.G1, S, G2 , M, C c. S, G1, G2, M, C d.None of the above A. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the cell cycle? a. C, M, G1 , S, G2 b.G1, S, G2 , M, C c. S, G1, G2, M, C d.None of the above B. What are the first three phases of the cell cycle are collectively known as? B. What are the first three phases of the cell cycle are collectively known as? Interphase C. The phase of mitosis that is characterized by the arrangement of all chromosomes along the equator of the cell is called C. The phase of mitosis that is characterized by the arrangement of all chromosomes along the equator of the cell is called Metaphase D. Unlike plant cells, animal cells contain _____. D. Unlike plant cells, animal cells contain _____. centrioles E. What is a tumor? E. What is a tumor? a mass of cancer cells F. Many organelles and molecules needed for cell division are formed after DNA replication and before mitosis. In which phase are they formed? F. Many organelles and molecules needed for cell division are formed after DNA replication and before mitosis. In which phase are they formed? G2 G. Which three phases make up interphase? G. Which three phases make up interphase? G1, S, G2 H. ________________—sister chromatids separate into individual chromosome H. ________________—sister chromatids separate into individual chromosome Anaphase I. _______________—the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the centrioles separate (in animal cells), and the nuclear membrane breaks down I. _______________—the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the centrioles separate (in animal cells), and the nuclear membrane breaks down Prophase J. __________—chromosomes move to opposite sides of the dividing cell, and two new nuclear envelopes form. J. __________—chromosomes move to opposite sides of the dividing cell, and two new nuclear envelopes form. Telophase







