Exam 1 Review a and b
advertisement

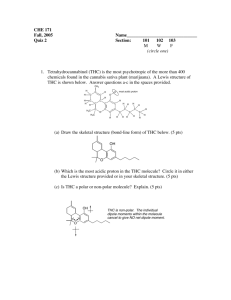
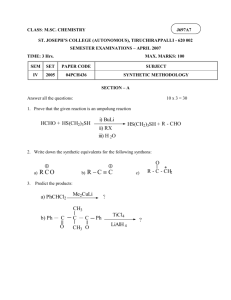
Draw the resonance structure indicated by the arrows. 1) 2) O O 3) O O Label each atom with the correct hybridization. 4) sp3 sp3 HO sp3 sp3 O sp3 sp3 5) sp3 N sp2 sp2 sp3 sp2 6) O sp sp sp2 sp3 7) Draw H2NCH2+ in its second best resonance structure. H H N CH2 H N H CH2 H N CH2 H 8) Draw the best Lewis structure for CH3CHO, a neutral molecule O C H3C H 9) Draw the Lewis structure for CH3COOH, a neutral molecule. O C H3C OH 10) Draw the Lewis structure for N2H2, a neutral molecule. HN NH 11) Draw in the electron flow arrows in on the left hand structure that lead to the resonance structure on the right. O O 12) In the empty box, draw the best resonance structure of the lefthand compound, and draw one or more electron-flow arrows on the preexisting structure that lead to the new structure. O O 13) O O 14) Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl 1 Cl Cl Cl 4 3 2 Label each of the following as an ionic or covalently bonded compound. a) NaF ionic b) BrCl covalent c) NaOCHe ionic Calculate the formal charge of nitrogen in each of the following compounds. FC = 5 – (4 + (1/2(4))) = -1 a) N b) N N FC = 5 – (2 + (1/2(6))) = 0 FC = 5 – (0 + (1/2(8))) = +1 Draw the Lewis structure. H a) (CH3(OH2))+ H H b) CH3NO2 C O H H H C N H O H O Draw all possible isomers of C2H4O. O HO C H3C H C H O CH2 H2C CH2 Are each of the following pairs isomers or resonance structures? a) H3C CH3 H3C C H2 CH2 C H2 Neither, different formulas b) O O Isomers, same formula but different arrangement of atoms. Draw a resonance structure of each, and identify which is the major contributor. O a) H b) O NH2 H NH2 O O H3C C C H CH2 H3C C C H CH2 Draw all possible resonance structures of the compound below and it’s resonance hybrid. CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 Predict the geometry around each indicated atom. H2 C a) H3C CH3 C H2 tetrahderal CH2 b) H3C OH Trigonal planar Draw the three dimensional structure of the following. a) CH3OH H H C H O H b) (CH3)2NH H H H H C H N H H Convert each molecule into a skeletal structure. a) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH(CH3)2 H b) H H H H H3C C C CH H H H H3C CH3 Convert into Lewis structures. a) (CH3)3COH CH3 H3C O H CH3 b) CH3COCH2Br H O H H Br H H What is the hybridizatio of th eindicated atom. a) sp3 sp2 sp2 b) CO2H sp Which is the weakest of the indicated bonds? b a c A is the weakest bond due to it being composed of a sp3 and sp2 hybridized orbital, thus having the least amount of S character NH2 HO a b B is the weakest, b/c bond strength increases across a row in the periodic table and N is to the left of O. Draw the products and label each part. O O OCH3 + + OH O A B CA CB + H A CH3 HO + NaNH2 B CB Na NH3 CA Draw the products and determine if the reaction occurs. O O + F3C O + CH2CH3 OH F3C pka=0.2 pka=16 O + NaCl + O OH reactants favored CH2CH3 O Products favored O pka=5 HO HCl pka=-7 Which is the strongest base? HBr, HCl or HF HF, b/c it is the weakest acid. Identify the most acidic hydrogen. H H b c H a H C is the most acidic hydrogen b/c it’s bonded to an sp hybridized carbon. H Draw the products of each reaction and label the starting materials as a Lewis acid and base. Cl Cl Cl + Cl B LB Cl Cl Cl LB Cl Cl LA O B Cl Cl + B B Cl Cl LA O Cl 1) Complete the following acid-base reaction. H O O + O OH + 2) Complete the following acid-base reaction. Draw only the organic products. KOH OH H OH + O O H O H K 3) O H H OH O + OH 4) Choose the strongest acid. H Cl H Br H S H H Br Both Cl and Br are further right than S. And Br is further down than Cl. So most acidic. 5) SH SH PH2 OH Both O and S are further right than P. And S is further down than O. So most acidic. 6) Choose the weakest acid. OH CH3 SH CH3 C is further left than O and S so weakest acid. 7) The following compound has two stereoisomers. One has a dipole of 0 D, and the other has a dipole moment of 2.95 D. Draw the structure of the stereoisomer with dipole moment of 2.95 D. Cl Cl Cl H Cl Cl H Cl H H Cl H Cl Cl H Cl H H 8) Rank the three compounds from least acidic (rank 1) to most. OH 3 SiH3 2 CH3 1 We know Si is more acidic than C because it is below C in the same column. Although Si and O can’t be compared directly, O is much more acidic. 9) Rank the following compounds from most acidic (rank 1) to least. O H3C H2 C O OH H3C Cl H2 C OH Br 3 2 O O H3C H2 C 1 OH OH H3C H2 C H2 C OH 4 Acidity is based on the electron withdrawing effect of the four different substituents. O is the most electronegative, furthest up and to the right, and thus gives the most acidic compd. And Cl is more electronegative than Br b/c electronegativity increases up the column. 10) Draw the electron-flow arrows that lead from starting materials to products in this acid–base reaction. H H H N H H H H H 11) O O H O N N NH O 1) Draw an aldehyde. O RCHO R H 2) Draw an ester. O R R O RCOOR or RCO2R 3) Draw a sulfide. S R RSR R 4) Draw 1,1-dimethylcyclohexane. 5) Draw 2,2,4-trimethylhexane. 6) Draw trans-1,3-dibromocyclobutane. Br H Br H Br Br Br H Br Br Br H 7) Draw cis-1-chloro-3-isopropylcyclopentane. Cl Cl Cl H H H 8) Draw sec-butylcycloheptane H Cl 9) Draw 2,2,4,4-tetramethylhexane 10) Draw the structural formula of an alkane that has eight carbons and only primary hydrogens. CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 CH3 Primary hydrogens are attached to carbons attached to only one other carbon. 11) Draw the conformation favored by 1,2-dichloroethane at equilibrium in the liquid phase by following this procedure. H H H Cl Cl H anit H Cl H H Cl H gauche The gauche conformer is favored in the liquid phase due to a polar effect. However, for this class I would accept the anit conformer as your answer, which would be correct if in the gas form. 12) Draw cis-3-ethyl-1-isopropylcyclohexane in its lowest energy conformation H H 13) Draw trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane in its lowest energy conformation Br H H CH3 1) Draw the Lewis structure of HNO3. O HO N O 2) What is the formal charge of the following compound? H H C H FC = 4 – (2 + (1/2)(6)) = -1 O 3) Draw all resonance structures O O O O 4) What are the hybridizations of the numbered carbons? sp3 1 2 sp2 5) Which of the following compounds has the largest net dipole? Draw the contributing dipoles of the compound you choose. CO2 H2O CHCl3 O H H 6) Draw the product of the following reaction. (Label the Lewis Acid and Base) LA LB 7) Which molecule plays the role of acid? HNO3 + H2SO4 → HSO4– + H2NO3+ acid O H 8) Using pKa values from the table, determine if the following reaction will occur. pKa HA 3.7 HCOOH 4.2 C6H5COOH 4.75 CH3COOH 15.5 CH3OH O + NaOCH3 OH 4.75 O HO CH3 15.5 + O pKa of the conjugate acid is larger than that of the acid so the reaction favors the products. 9) Which is the strongest base? LiOH LiF LiCH3 LiCH3 is the strongest base because the acid it forms when the anion is protonated is very weak. 10) What intermolecular forces does the following molecule exhibit? O O It possesses Van der Waals and dipole-dipole interactions. 11) Which of the following has the highest boiling and why? CBr3CH3 CH3OCH3 CH3NH2 CH3NH2 has the highest boiling point because it possesses the same intermolecular forces as the first two molecules, but also has hydrogen bonding capabilities. 12) Label the electrophile and nucleophile. Then if the reaction occurs, draw the products. O O + E CH3 Nu 13) Name the following compound. 2-sec-butyl-4-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane 14) Which of the following has the highest melting point? Why? a) 2-methylbutane b) 2,2',3-dimethylbutane c) 2,2',3,3'-tetramethylbutane c) 2,2',3,3'-tetramethylbutane has the highest metlign point due to its high symmetry giving it the ability to pack close together in the crystal lattice. 15) Draw 2-chloro-4-ethyl-3-methylheptane Cl Draw the most stable form of trans-1-bromo-3-ethylcyclohexane. H Br H H H H H H Br H H H H H H H H H H H H More stable H Using Newman projections, draw all the staggered conformations of 1-chloropropane, label the anti and gauche forms. 1 2 Cl