We provide information and advice to our customers
to the best of our knowledge and ability, but without
obligation or liability. Existing laws and regulations are
to be observed in all cases by our customers.
This also applies in respect to any rights of third parties.
Our information and advice do not relieve our customers
of their own responsibility for checking the suitability of
our products for the envisaged purpose.
Lab Tools
W.280111
060605
Lab Tools
Tables for laboratory use
Table for laboratory use
For any further information
please contact your local agent
Merck KGaA
64271 Darmstadt
Germany
Fax 0049 (0) 151 72-6080
E-Mail reagents@merck.de
Inernet www.merck-chemicals.com
Merck at a glance
Two major business sectors - Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
Approximately 33.000 employees in 60 countries
Total revenues in 2008: EUR 7.558 million
Headquarters: Darmstadt / Germany
The world´s oldest pharmaceutical and chemical company,
with roots dating back to 1668
Merck KGaA is listed on the Frankfurter Stock Exchange and
is a DAX® 30 company
Around 30% of the total capital is publicly trated. The Merck
family, indirectly holds around 70%
Merck invests in R&D: Pharmaceuticals business sector: 20%
of sale Chemicals business sector: 6.7% of sales
For more information, please visit our website
www.merck-chemicals.com
2
Chemicals
Performance & Life Science Chemicals
Focus on specialty chemicals solutions for cosmetic, pharmaceutical
and biopharmaceutical applications
Focus on effects pigments for cosmetics, coating, plastics and printing,
food and pharma
Laboratory supply
Liquid Crystals
Focus on innovation in disply technologies to sustain market leadership
Liquid Crystals, OLEDs, materials for solar cells
Pharmaceuticals
Merck Serono
Focus on specialist and innovative prescription drugs
Oncology, Neurodegenerative Diseases, Autoimmune and Inflammatory
Diseases, Fertility, Endocrinology, CardioMetabolic Care
Consumer Health Care
Focus on over-the-counter pharmaceutical products for four health
themes: Mobility, Everyday Health Protection, Woman´s and Children´s
Health, Cough and Cold
3
Content
Safety in the laboratory
Proper behaviour inside a laboratory
Hazard cautionary
Hazard symbols
Risk phrases
Safety phrases
Incompatible chemicals
page
08
10
16
18
24
30
Chemical and physical properties of elements
and inorganic compounds
Table of elements
Hardness scale according to MOHS
Electrochemical series of some nonmetals
Covalent single-bond radiuses
34
38
39
39
Solutions - aqueous systems
General mixing formulas for liquids
Conversion table for water hardness
Mixture rule
Preparation of dilute solutions
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water in relation to temperature
Solubility products of slightly soluble inorganic compounds
Sample preparation
Acids Sulfuric acid
Phosphoric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acid
Sodium hydroxide solution
Potassium hydroxide solution
Ammonia
Commercially available concentrations
of some acids and alkalis
42
43
44
44
45
54
57
58
60
60
62
63
65
68
69
Indicators and buffers
pH indicators
Buffer solutions
72
76
Chromatography
Analytical HPLC
Thin-layer Chromatography
Specification of column sorbents
LC Troubleshooting
Sample preparation
page
82
84
86
90
95
Organic solvents
Organic solvents - Properties and drying
Ethanol-water mixtures
Drying agents
Vapour pressure of water
LiChrosolv® - Solvents for chromatography
98
102
103
103
104
Physical Methods for the determination of elements
Flame photometry
Wavelength and wave number
Photometry: Transmission rate and absorbance
Calculation of the standard deviation
Direct-current polarography
Cathode ray polarography
108
108
108
108
109
109
Mass and weight
Energy dimensions - conversion factors
Pressure dimensions - conversion factors
Decimal multiples and parts of units
Concentration values
Basic units
Derived units
US and British measures units
112
112
113
113
113
114
118
Other useful tables
Physical constants
Establishment of constant humidity in closed vessels
Greek alphabet
Greek numerals / Roman numbers
Freezing mixtures
Extran®
Particle sizes
NMR: Carbon (13C) chemical shifts
NMR: Proton chemical shifts
Miscibility table
Stoichiometry formulary
122
123
124
125
126
126
128
130
132
134
136
Safety in the laboratory
Proper behaviour inside a laboratory 08
Hazard cautionary 10
Hazard symbols 16
Risk phrases 18
Safety phrases 24
Incompatible chemicals 30
Proper behaviour inside the laboratory
Chemistry is a fascinating thing for many beginners in related jobs.
Handling chemicals is not only fascinating, but also risky, especially if
processes are not performed adequately due to insufficient knowledge of the
properties of the used substances. Therefore it is absolutely necessary
to inform oneself prior to its first use about any possible hazards of a certain
chemical.
Each manufacturer of laboratory reagents is obliged to label reagents in
accordance with the Global Harmonized System (GHS) and provide the
respective material safety data sheets (MSDS).
Laboratory chemicals are neither intended nor approved for use in humans
or animals! Specifically tested pharmaceutical chemicals are available for such
purpose.
The handling of hazardous chemicals demands special know-how, carefulness
and adequate precautions. All use has to be performed in such a way that
hazardous gases, vapors or suspended particles are - as far as technically possible not released into the environment.
If necessary, appropriate measures have to be taken. When reaching the
specific occupational exposure limits, special safety measures become
necessary such as safe and practical personal protective equipment (PPE).
The following rules apply to provide safety during the working process:
1.When working in a laboratory or a warehouse wear safety glasses, special
working clothes or lab coat, suitable lab shoes and, where necessary,
suitable gloves.
2. In any case avoid contact with skin, eyes and mucous membranes.
3.In case of contact with a chemical, rinse off any splashes on the skin
with plenty of cold water; in the case of lipophilic substances rinse off
with polyglycol. Due to the danger of absorption, never use other
organic solvents. In doubt consult a physician as soon as possible.
4.Thoroughly rinse chemically burned eyes under a gentle stream of
water or with a special eye shower. Rinse with your eyes wide open
and roll your eyes in all directions. Subsequently, an eye examination
must be performed. It is absolutely necessary to inform the eye
specialist of the chemical used. It is also recommended to state its
hazardous properties in order to decide on adequate treatment.
5. Take off immediately any clothing contaminated with chemicals.
6.In case of accidents or if you feel unwell, consult a physician and state the
cause of accident including the name of the chemical involved.
7.Do not smoke, eat and drink in laboratory rooms or while working with
chemicals.
8
What is a hazardous material?
Safety in the laboratory
In accordance with OSHA a hazardous material is any item or agent (biological,
chemical, physical) which has the potential to cause harm to humans, animals, or
the environment, either by itself or through interaction with other factors including
materials which are carcinogens, toxic agents, irritants, corrosives, sensitizers; agents
which act on the hematopoietic system; agents which damage the lungs, skin, eyes,
or mucous membranes; chemicals which are combustible, explosive, flammable,
oxidizers, pyrophorics, unstable-reactive or water-reactive; and chemicals which in
the course of normal handling, use, or storage may produce or release dusts, gases,
fumes, vapors, mists or smoke which may have any of the previously mentioned
characteristics.
Acids in Safebreak bottles
Acids in glass bottles have hazard potential:
glass can break! Our solution is the Merck
Safebreak bottle - a PE-coated glass bottle.
In case of a breakage the acid and any
sherds are reliably held together and can be
disposed easily. The bottle protects the lab
staff from getting injured by the acid as well
as the glass splinters. Empty bottles can be
recycled as glass.
9
Hazard cautionary
H200
H201
H202
H203
H204
H205
H220
H221
H222
H223
H224
H225
H226
H228
H240
H241
H242
H250
H251
H252
H260
H261
H270
H271
H272
H280
H281
H290
H300
H301
H302
H304
H310
H311
H312
H314
H315
H317
H318
H319
H330
H331
H332
H334
H335
H336
H340
H341
H350
10
Unstable explosives.
Explosive; mass explosion hazard.
Explosive, severe projection hazard.
Explosive; fire, blast or projection hazard.
Fire or projection hazard.
May mass explode in fire.
Extremely flammable gas.
Flammable gas.
Extremely flammable aerosol.
Flammable aerosol.
Extremely flammable liquid and vapour.
Highly flammable liquid and vapour.
Flammable liquid and vapour.
Flammable solid.
Heating may cause an explosion.
Heating may cause a fire or explosion.
Heating may cause a fire.
Catches fire spontaneously if exposed to air.
Self-heating: may catch fire.
Self-heating in large quantities; may catch fire.
In contact with water releases flammable gases which may
ignite spontaneously.
In contact with water releases flammable gases.
May cause or intensify fire; oxidiser.
May cause fire or explosion; strong oxidiser.
May intensify fire; oxidiser.
Contains gas under pressure; may explode if heated.
Contains refrigerated gas; may cause cryogenic burns or injury.
May be corrosive to metals.
Fatal if swallowed.
Toxic if swallowed.
Harmful if swallowed.
May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways.
Fatal in contact with skin.
Toxic in contact with skin.
Harmful in contact with skin.
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Causes skin irritation.
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
Causes serious eye damage.
Causes serious eye irritation.
Fatal if inhaled.
Toxic if inhaled.
Harmful if inhaled.
May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties
if inhaled.
May cause respiratory irritation.
May cause drowsiness or dizziness.
May cause genetic defects state route of exposure if it is
conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the
hazard.
Suspected of causing genetic defects state route of exposure
if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause
the hazard.
May cause cancer state route of exposure if it is conclusively
proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard.
Suspected of causing cancer state route of exposure if it is
conclusively proven that no other routs of exposure cause
the hazard.
May damage fertility or the unborn child state specific effect
if known state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that
no other routes of exposure cause the hazard.
Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child state specific
effect if known state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven
that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard.
May cause harm to breast-fed children.
Causes damage to organs or state all organs affected, if known
state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other
routes of exposure cause the hazard.
May cause damage to organs or state all organs affected, if known
state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other
routes of exposure cause the hazard.
Causes damage to organs or state all organs affected, if known
through prolonged or repeated exposure state route of exposure if
it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause
the hazard.
May cause damage to organs or state all organs affected, if known
through prolonged or repeated exposure state route of exposure
if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the
hazard.
Very toxic to aquatic life.
Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life.
EU hazard cautionary
EUH001
EUH006
EUH014
EUH018
EUH019
EUH044
EUH029
EUH031
EUH032
EUH066
EUH070
EUH071
EUH059
EUH201
EUH201A
EUH202
EUH203
EUH204
EUH205
EUH206
Explosive when dry.
Explosive with or without contact with air.
Reacts violently with water.
In use may form flammable/explosive vapour-air mixture.
May form explosive peroxides.
Risk of explosion if heated under confinement.
Contact with water liberates toxic gas.
Contact with acids liberates toxic gas.
Contact with acids liberates very toxic gas.
Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking.
Toxic by eye contact.
Corrosive to the respiratory tract.
Hazardous to the ozone layer.
Contains lead. Should not be used on surfaces liable to be chewed
or sucked by children.
Warning! Contains lead.
Cyanoacrylate. Danger. Bonds skin and eyes in seconds. Keep out
of the reach of children.
Contains chromium (VI). May produce an allergic reaction.
Contains isocyanates. May produce an allergic reaction.
Contains epoxy constituents. May produce an allergic reaction.
Warning! Do not use together with other products.
May release dangerous gases (chlorine).
11
Safety in the laboratory
H351
H360
H361
H362
H370
H371
H372
H373
H400
H410
H411
H412
H413
EU hazard cautionary
EUH207
EUH208
EUH209
EUH209A
EUH210
EUH401
Warning! Contains cadmium. Dangerous fumes are formed during
use. See information supplied by the manufacturer. Comply with the
safety instructions.
Contains <name of sensitising substance>. May produce an
allergic reaction.
Can become highly flammable in use.
Can become flammable in use.
Safety data sheet available on request.
To avoid risks to human health and the environment, comply with
the instructions for use.
Precautionary
P101
P102
P103
P201
P202
P210
P211
P220
P221
P222
P223
P230
P231
P232
P233
P234
P235
P240
P241
P242
P243
P244
P250
P251
P260
P261
P262
P263
P264
P270
P271
P272
P273
P280
P281
P282
P283
P284
12
If medical advice is needed, have product container or label at hand.
Keep out of reach of children.
Read label before use.
Obtain special instructions before use.
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and
understood.
Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking.
Do not spray on an open flame or other ignition source.
Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials.
Take any precaution to avoid mixing with combustibles…
Do not allow contact with air.
Keep away from any possible contact with water, because of violent
reaction and possible flash fire.
Keep wetted with…
Handle under inert gas.
Protect from moisture.
Keep container tightly closed.
Keep only in original container.
Keep cool.
Ground/bond container and receiving equipment.
Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment.
Use only non-sparking tools.
Take precautionary measures against static discharge.
Keep reduction valves free from grease and oil.
Do not subject to grinding/shock/…/friction.
Pressurized container: Do not pierce or burn, even after use.
Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray.
Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray.
Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing.
Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing.
Wash … thoroughly after handling.
Do no eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the
workplace.
Avoid release to the environment.
Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face
protection.
Use personal protective equipment as required.
Wear cold insulating gloves/face shield/eye protection.
Wear fire/flame resistant/retardant clothing.
Wear respiratory protection.
In case of inadequate ventilation wear respiratory protection.
Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture.
Keep cool. Protect from sunlight.
IF SWALLOWED:
IF ON SKIN:
IF ON SKIN (or hair):
IF INHALED:
IF IN EYES:
IF ON CLOTHING:
IF exposed:
IF exposed or concerned:
IF exposed or if you feel unwell:
Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell.
Get medical advice/attention.
Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
Get immediate medical advice/attention.
Specific treatment is urgent (see … on this label).
Specific treatment (see … on this label).
Specific measures (see … on this label).
Rinse mouth.
Do NOT induce vomiting.
If skin irritation occurs:
If skin irritation or rash occurs:
Immerse in cool water/wrap in wet bandages.
Brush off loose particles from skin.
Thaw frosted parts with lukewarm water. Do no rub affected area.
If eye irritation persists:
Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable
for breathing.
If breathing is difficult, remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest
in a position comfortable for breathing.
If experiencing respiratory symptoms:
Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes.
Wash with plenty of soap and water.
Rinse skin with water/shower.
Rinse immediately contaminated clothing and skin with plenty of
water before removing clothes.
Remove/Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse.
Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
In case of fire:
In case of major fire and large quantities:
Explosion risk in case of fire.
DO NOT fight fire when fire reaches explosives.
Fight fire with normal precautions from a reasonable distance.
Fight fire remotely due to the risk of explosion.
Stop leak if safe to do so.
Leaking gas fire: Do not extinguish, unless leak can be stopped safely.
Use … for extinction.
Evacuate area.
Eliminate all ignition sources if safe to do so.
13
Safety in the laboratory
P285
P231/232
P235/410
P301
P302
P303
P304
P305
P306
P307
P308
P309
P310
P311
P312
P313
P314
P315
P320
P321
P322
P330
P331
P332
P333
P334
P335
P336
P337
P338
P340
P341
P342
P350
P351
P352
P353
P360
P361
P362
P363
P370
P371
P372
P373
P374
P375
P376
P377
P378
P380
P381
Precautionary
P390
P391
P301/310
P301/312
P301/330/331
P302/334
P303/350
P302/352
P303/361/353
P304/340
P304/341
P305/351/338
P306/360
P307/311
P308/313
P309/311
P332/313
P333/313
P335/334
P337/313
P342/311
P370/376
P370/378
P370/380
P370/380/375
P371/380/375
P401
P402
P403
P404
P405
P406
P407
P410
P411
P412
P413
P420
P422
P402/404
P403/233
P403/235
P410/403
14
Absorb spillage to prevent material damage.
Collect spillage.
IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or
doctor/physician.
IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you
feel unwell.
IF SWALLOWED: rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting.
IF ON SKIN: Immerse in cool water/wrap in wet bandages.
IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water.
IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off immediately all contaminated
clothing. Rinse skin with water/shower.
IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position
comfortable for breathing.
IF INHALED: If breathing is difficult, remove victim to fresh air and
keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove
contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
IF ON CLOTHING: rinse immediately contaminated clothing and skin
with plenty of water before removing clothes.
IF exposed: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
IF exposed or if you feel unwell: Call a POISON CENTER or
doctor/physician.
If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Brush off loose particles from skin. Immerse in cool water/wrap in a
wet bandages.
If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
If experiencing respiratory symptoms: Call a POISON CENTER or
doctor/physician.
In case of fire: Stop leak if safe to do so.
In case of fire: Use … for extinction.
In case of fire: Evacuate area.
In case of fire: Evacuate area. Fight fire remotely due to the risk
of explosion.
In case of major fire and large quantities: Evacuate area. Fight fire
remotely due to the risk of explosion.
Store …
Store in a dry place.
Store in a well-ventilated place.
Store in a closed container.
Store locked up.
Store in corrosive resistant/… container with a resistant inner liner.
Maintain air gap between stacks/pallets.
Protect from sunlight.
Store at temperatures not exceeding … °C/…°F.
Do not expose to temperatures exceeding 50 °C/122°F.
Store bulk masses greater than … kg/… lbs at temperatures not
exceeding … °C/…°F.
Store away from other materials.
Store contents under …
Store in a dry place. Store in a closed container.
Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool.
Protect from sunlight. Store in a well-ventilated place.
Protect from sunlight. Do no expose to temperatures exceeding
50 °C/122°F.
Store at temperatures not exceeding … °C/…°F. Keep cool.
Dispose of contents/container to …
Safety in the laboratory
P410/412
P411/235
P501
Chemizorb - absorbents for spilled liquids
Mishaps and accidents happen - every day and nearly in every lab!
With Chemizorb® you can remove spilled liquids quickly and safely.
Chemizorb® is capable of taking up 100 to 400 percent (depending
on the type) of their own weight in liquid material. Merck offers you
specific absorbents for each problem:
- the „allrounders“, Chemizorb® powder and granules,
- the „specialists“, Chemizorb® Alkalis, Acid, Hydrofluoric Acid, and also
- the „all-in-one“ Chemizorb® Mercury set
15
Hazard symbols
E: Explosive
Criteria: Chemicals and preparations which may react
exothermically without atmospheric oxygen and
which under defined test conditions detonate, quickly
deflagrate or upon heating explode when partially
confined.
Precaution: Avoid impact, knocks, friction, sparks, fire,
and heat.
O: Oxidizing.
Criteria: Organic peroxides which are combustible even
if not in contact with combustible materials.
Other chemicals and preparations which as a rule are not
combustible themselves, but which in contact with
combustible materials, mainly through oxygen evolution,
considerably increase the fire hazard and the intensity
of a fire.
Precaution: Avoid all contact with combustible substances.
Risk of ignition: The substance promotes fires once started
and impedes fire fighting.
F: Highly flammable.
Criteria: Liquids with a flash point below 21°C that are
not extremely flammable. Solid substances and preparations
which on brief exposure to a source of ignition may be
easily inflamed and then continue to burn and smoulder.
Precaution: Keep away from naked flames, sparks, and
sources of heat.
F+: Extremely flammable.
Criteria: Liquids with a flash point below 0 °C and
a boiling point of max. 35 °C. Gases and gas mixtures
which are flammable in air at normal pressure and
average temperatures.
Precaution: Keep away from naked flames, sparks, and
sources of heat.
T: Toxic.
Criteria: Inhalation, swallowing, or absorption through
the skin in small amounts can cause considerable damage
to health, and may sometimes be lethal. In the event of
serious evidence of severe, possiblyirreversible damage to
health by single, repeated, or prolonged absorption, especially
carcinogenic, mutagenic, and reproduction-toxic effects.
Precaution: All contact with the human body must be
avoided. If you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately.
Particular attention is drawn to the carcinogenic,
teratogenic, or mutagenic risks associated with certain
substances. Observe special regulations when handling
these substances!
16
C: Corrosive.
Criteria: Total damage to living tissues or when this result
can be predicted.
Precaution: Take special measures to protect eyes, skin, and
clothes. Do not inhale vapors! In case of accident or if you
feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately.
Xn: Harmful.
Criteria: Inhalation, swallowing, or absorption through the
skin can cause acute or chronic damage to health. In
the event of evidence of severe, possibly irreversible damage
to health by single, repeated, or prolonged absorption,
especially in suspected carcinogenic, mutagenic, and
reproduction-toxic effects. Risk of sensitization by inhalation
(classification with R42).
Precaution: All contact with the human body must be
avoided. Particular attention is drawn to substances which
are suspected to have a carcinogenic, mutagenic, or
reproduction-toxic effect.
Xi: Irritating.
Criteria: Without being corrosive, immediate, prolonged, or
epeated contact with skin or mucous membranes may
cause inflammations. Risk of sensitization by skin contact
(classification with R43).
Precaution: Avoid contact with eyes and skin, do not inhale
vapors.
N: Dangerous for the environment.
Criteria: Liberation into the aquatic and non-aquatic
environments can have an immediate or delayed detrimental
effect upon the ecosystem through alteration of the natural
balance. Some substances or their conversion products may
simultaneously affect various constituents of the ecosystem.
Precaution: Depending on the risk potential do not allow to
enter sewerage systems. Observe special disposal regulations!
17
Safety in the laboratory
T+: Very toxic.
Criteria: Inhalation, swallowing, or absorption through the
skin in very small amounts can cause considerable damage
to health, and may sometimes be lethal. In the event of
serious evidence of severe, possibly irreversible damage to
health by single, repeated, or prolonged absorption.
Criteria: All contact with the human body must be avoided.
If you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately.
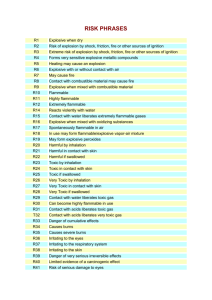
Risk (R) phrases
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
R9
R10
R11
R12
R14
R15
R16
R17
R18
R19
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
R27
R28
R29
R30
R31
R32
R33
R34
R35
R36
R37
R38
R39
R40
R41
R42
R43
R44
R45
R46
R48
R49
R50
R51
R52
R53
R54
R55
R56
18
Explosive when dry.
Risk of explosion by shock, friction, fire or other sources of ignition.
Extreme risk of explosion by shock, friction, fire or other sources
of ignition.
Forms very sensitive explosive metallic compounds.
Heating may cause an explosion.
Explosive with or without air contact.
May cause fire
Contact with combustible material may cause fire.
Explosive when mixed with combustible material.
Flammable.
Highly flammable.
Extremely flammable.
Reacts violently with water.
Contact with water liberates extremely flammable gases.
Explosive when mixed with oxidizing substances.
Spontaneously flammable in air.
In use, may form flammable/explosive vapour-air mixture.
May form explosive peroxides.
Harmful by inhalation.
Harmful in contact with skin.
Harmful if swallowed.
Toxic by inhalation.
Toxic in contact with skin.
Toxic if swallowed.
Very toxic by inhalation.
Very toxic in contact with skin.
Very toxic if swallowed.
Contact with water liberates toxic gas.
Can become highly flammable in use.
Contact with acids liberates toxic gas.
Contact with acids liberates very toxic gas.
Danger of cumulative effects.
Causes burns.
Causes severe burns.
Irritating to eyes.
Irritating to respiratory system.
Irritating to skin.
Danger of very serious irreversible effects.
Possible risk of irreversible effects.
Risk of serious damage to eyes.
May cause sensitization by inhalation.
May cause sensitization by skin contact.
Risk of explosion if heated under confinement.
May cause cancer.
May cause heritable genetic damage.
Danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure.
May cause cancer by inhalation.
Very toxic to aquatic organisms.
Toxic to aquatic organisms.
Harmful to aquatic organisms.
May cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
Toxic to flora.
Toxic to fauna.
Toxic to soil organisms.
R57
R58
R59
R60
R61
R62
R63
R64
R65
R66
R67
R68
Toxic to bees.
May cause long-term adverse effects in the environment.
Dangerous for the ozone layer.
May impair fertility.
May cause harm to the unborn child.
Possible risk of impaired fertility.
Possible risk of harm to the unborn child.
May cause harm to breastfed babies.
Harmful: May cause lung damage if swallowed.
Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness and dizziness.
Vapours may cause tiredness and lightheadedness.
Possible risks of irreversible effects.
R14/15
R15/29
R20/21
R20/21/22
R20/22
R21/22
R23/24
R23/24/25
R23/25
R24/25
R26/27
R26/27/28 R26/28
R27/28
R36/37
R36/37/38
R36/38
R68/20
R68/20/21
R68/20/21/22
R68/20/22
R68/21
R68/21/22
R68/22
Safety in the laboratory
Combination of risk phrases
Reacts violently with water, liberating extremely flammable gases.
Contact with water liberates toxic, highly flammable gas.
Harmful by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed.
Harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin
and if swallowed.
Toxic by inhalation and if swallowed.
Toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Very toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Very toxic by inhalation and if swallowed.
Very toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Irritating to eyes and respiratory system.
Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
Irritating to eyes and skin.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation
and in contact with skin.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation,
in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation
and if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin
and if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects if swallowed.
19
Risk (R) phrases
R37/38
R39/23
R39/23/24
R39/23/25
R39/23/
24/25
Irritating to respiratory system and skin.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation
and in contact with skin.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation
and if swallowed.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation
in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R39/24
R39/24/25
R39/25
R39/26
R39/26/27
R39/26/
27/28
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin
and if swallowed.
Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if swallowed.
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation.
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation and in contact with skin.
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R39/26/28
R39/27
R39/27/28
R39/28
R40/20
R40/20/21
R40/20/
21/22
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects
through inhalation and if swallowed.
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects
in contact with skin.
Very toxic: danger of very serious effects in contact with skin and
if swallowed.
Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation and
in contact with skin.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation,
in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R40/20/22
R40/21
R40/21/22
R40/22
R42/43
R48/20
R48/20/21
R48/20/
21/22
R 48/20/22
R 48/21
R 48/21/22
R 48/22
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation and
if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin and
if swallowed.
Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects if swallowed.
May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation and in contact with skin.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by
prolonged exposure through inhalation and if swallowed.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by
prolonged exposure in contact with skin.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to
health by prolonged exposure in contact with
skin and if swallowed.
Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by
prolonged exposure if swallowed.
20
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation and in contact with skin.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin and if
swallowed.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
through inhalation and if swallowed.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
in contact with skin.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure
if swallowed.
Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse
effects in the aquatic environment.
Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects
in the aquatic environment.
Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse
effects in the aquatic environment.
Safety in the laboratory
R 48/23
R 48/23/24
R 48/23/
24/25
R 48/23/25
R 48/24
R 48/24/25
R 48/25
R 50/53
R 51/53
R 52/53
Risk phrases with supplements
R E20
R E20/21
R E20/21/22
R E20/22
R E21
R E21/22
R E22
R E23
R E23/24
R E23/24/25
Also harmful by inhalation.
Also harmful by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin
and if swallowed.
Also harmful by inhalation and if swallowed.
Also harmful in contact with skin.
Also harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also harmful if swallowed.
Also toxic by inhalation.
Also toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
21
Risk (R) phrases
R E23/25
R E24
R E24/25
R E25
R E26
R E26/27
R E26/27/28
R E26/28
R E27
R E27/28
R E28
R E39/23
R E39/23/24
R E39/23/
24/25
Also toxic by inhalation and if swallowed.
Also toxic in contact with skin.
Also toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also toxic if swallowed.
Also very toxic by inhalation.
Also very toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also very toxic by inhalation and if swallowed.
Also very toxic in contact with skin.
Also very toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also very toxic if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R E39/23/25
R E39/24
R E39/24/25
R E39/25
R E39/26
R E39/26/27
R E39/26/
27/28
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation and if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact
with skin.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact
with skin and if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if swallowed.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R E39/26/28
R E39/27
R E39/27/28
R E39/28
R E40/20/21
R E40/20/
21/22
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through
inhalation and if swallowed.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact
with skin.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact
with skin and if swallowed.
Also very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if
swallowed.
Also harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation
and in contact with skin.
Also harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation,
in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R E40/20/22
R E40/21
R E40/21/22
R E40/22
R E42/43
R E48/20
Also harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation
and if swallowed.
Also harmful: possible risk of very serious irreversible effects in
contact with skin.
Also harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin
and if swallowed.
Also harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects if swallowed.
May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation.
22
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by
prolonged exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin and
if swallowed.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation and if swallowed.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure in contact with skin.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation.
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation and in contact with skin.
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
R E48/23/25
R E48/24
R E48/24/25
R E48/25
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure through inhalation and if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure in contact with skin.
Also harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Also toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged
exposure if swallowed
Safety in the laboratory
R E48/20/21
R E48/20/
21/22
R E48/20/22
R E48/21
R E48/21/22
R E48/22
R E48/23
R E48/23/24
R E48/23/
24/25
Acid in Safebreak bottle
23
Safety (S) phrases
S 1
Keep locked up.
S 2
Keep out of reach of children.
S 3
Keep in a cool place.
S 4
Keep away from living quarters.
S 5Keep contents under ... (appropriate liquid to be specified by the
manufactures)
S 6
Keep contents under ... (inert gas to be specified by the
manufacturer).
S 6.1
Keep under nitrogen.
S 7
Keep container tightly closed.
S 8
Keep container dry.
S 9
Keep container in a well-ventilated place.
S 12
Do not keep the container sealed.
S 13
Keep away from food, drink and animal feeding stuffs.
S 14Keep away from ... (incompatible materials to be indicated by the
manufactures)
S 14.1
Keep away from reducing agents, heavy metal compounds, acids
and alkalis.
S 14.10
Keep away from acids, reducing agents and flammable material.
S 14.11
Keep away from flammable material.
S 14.2
Keep away from oxidizing and acidic substances as well as heavy
metal compounds.
S 14.3
Keep away from iron.
S 14.4
Keep away from water and alkalis.
S 14.5
Keep away from acids.
S 14.6
Keep away from alkalis.
S 14.7
Keep away from metals.
S 14.8
Keep away from oxidizing and acidic substances.
S 14.9
Keep away from flammable organic substances.
S 15
Keep away from heat.
S 16
Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking.
S 17
Keep away from combustible material.
S 18
Handle and open container with care.
S 20
When using do not eat or drink.
S 21 When using do not smoke.
S 22 Do not breathe dust.
S 23 Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapour/spray
S 23.1
Do not breathe gas.
S 23.2
Do not breathe vapour.
S 23.3
Do not breathe spray.
S 23.4
Do not breathe fumes.
S 23.5
Do not breathe fumes/spray.
S 24
Avoid contact with skin.
S 25
Avoid contact with eyes.
S 26
In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of
water and seek medical advice.
S 27
Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
S 28After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of... (to be
specified by the manufactures)
S 28.1
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water.
S 28.2
After contact with skin, wash immediately with
plenty of soap and water.
S 28.3
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap
and water, if possible also with polyethylene glycol 400.
24
Safety in the laboratory
S 28.4After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of
polyethylene glycol 300 and ethanol (2:1) followed by plenty of
soap and water.
S 28.5
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of
polyethylene glycol 400.
S 28.6
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of
polyethylene glycol 400, then rinse with plenty of water.
S 28.7
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water
and acidic soap.
S 29
Do not empty into drains.
S 30
Never add water to this product.
S 33
Take precautionary measures against static discharges.
S 35
This material and its container must be disposed of in a safe way.
S 36
Wear suitable protective clothing.
S 37
Wear suitable gloves.
S 38
In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory
equipment.
S 39
Wear eye/face protection.
S 40
To clean the floor and all objects contaminated by this material
use... (to be specified by the manufacturer).
S 41
In case of fire and/or explosion do not breathe fumes.
S 42
During fumigation/spraying with wear suitable respiratory
equipment.
S 43
In case of fire, use ... (indicate the precise type of fire-fighting
equipment. If water increases risk, add -‘Never use water‘.
S 43.1
In case of fire, use water.
S 43.2
In case of fire, use water or powder extinguisher.
S 43.3
In case of fire, use powder extinguisher. Never use water.
S 43.4
In case of fire, use CO2 - never use water.
S 43.6
In case of fire, use sand - never use water.
S 43.7
In case of fire, use metal fire powder - never use water.
S 43.8
In case of fire, use sand, CO2 or powder extinguisher,
never use water.
S 45
In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice
immediately (show the label where possible).
S 46
If swallowed, seek medical advice immediately and show this
container or label.
S 47
Keep at temperature no exceeding ...°C (to be specified by the
manufacturer).
S 47.1
Keep at temperature no exceeding 20°C.
25
Safety (S) phrases
S 48
S 49
S 50
S 50.1
S 50.2
S 50.3
S 51
S 52
S 53
S 56
S 57
S 59
S 60
S 61
S 62
S 63
S 64
Keep wet with ... (appropriate material to be specified by the
manufacturer).
Keep only in the original container.
Do not mix with ... (to be specified by the manufacturer).
Do not mix with acids.
Do not mix with alkalis.
Do not mix with strong acids, strong bases, non-ferrous metals or
their salts.
Use only in well-ventilated areas.
Not recommended for interior use on large surface areas.
Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.
Restricted to professional users.
Dispose of this material and its container at hazardous or special
waste collection point.
Use appropriate container to avoid environmental contamination!
Refer to manufacturer/supplier for information on recovery/recycling.
This material and its container must be disposed of as hazardous
waste.
Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions /
Safety data sheet.
If swallowed, do not induce vomiting. Seek medical advice
immediately and show this container or label.
In case of accident through inhalation: remove casually to fresh air
and kept at rest.
In case of swallowed, rinse mouth with water (only if the person is
conscious).
Combination of safety phrases
S 1/2
S 3/7
S 3/9
S 3/9/14
S 3/9/14.1
S 3/9/14.2
S 3/9/14.3
S 3/9/14.4
S 3/9/14.5
S 3/9/14.6
S 3/9/14.7
S 3/9/14.8
S 3/9/14/49
S 3/9/14.1/49
S 3/9/14.2/49
26
Keep locked up and out of the reach of children.
Keep container tightly closed in a cool place.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from ....
(incompatible substances are to be specified by the manufacturer).
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from reducing agents,
heavy metal compounds, acids and alkalis.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from oxidizing agents and
acidic substances as well as heavy metal compounds.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from iron.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from water and alkalis.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from acids.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from alkalis.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from metals.
Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from oxidizing and acidic
substances.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from ... (incompatible materials to be indicated by the
manufacturer).
Keep in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place away
from reducing agents, heavy metal compounds, acids and alkalis.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from oxidizing and acidic substances as well as heavy metal
compounds.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from iron.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from water and alkalis.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from acids.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from alkalis.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from metals.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place
away from oxidizing and acidic substances.
Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place.
Keep in a cool place away from ... (incompatible materials to be
indicated by the manufacturer).
Keep in a cool place away from reducing agents, heavy metal
compounds, acids and alkalis.
Keep in a cool place away from oxidizing and acidic substances as
well as heavy metal compounds.
Keep in a cool place away from iron.
Keep in a cool place away from water and alkalis.
Keep in a cool place away from acids.
Keep in a cool place away from alkalis.
Keep in a cool place away from metals.
Keep in a cool place away from oxidizing and acidic substances.
Safety in the laboratory
S 3/9/14.3/49
S 3/9/14.4/49
S 3/9/14.5/49
S 3/9/14.6/49
S 3/9/14.7/49
S 3/9/14.8/49
S 3/9/49
S 3/14 S 3/14.1 S 3/14.2
S 3/14.3
S 3/14.4
S 3/14.5 S 3/14.6
S 3/14.7
S 3/14.8
27
Safety (S) phrases
S 7/8
S 7/9
S 7/47
S 20/21
S 24/25
S 27/28
S 29/56
S 36/37
S 36/37/39
S 36/39
S 37/39
S 47/49
Keep container tightly closed and dry.
Keep container tightly closed and in a well-ventilated place.
Keep container tightly closed and at temperature no exceeding ...°C
(to be specified by the manufacturer).
When using do not eat, drink or smoke.
Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
After contact with skin, take off immediately all contaminated
clothing and wash skin with plenty of ... (to be specified by the
manufacturer).
Do not empty into drains; dispose of this material and its container
at hazardous or special waste collection point.
Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
Wear suitable protective clothing and eye/face protection.
Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection.
Keep only in the original container at temperature no exceeding ...°C
(to be specified by the manufacturer).
Copyright © 1999 [Merck KGaA]. All rights reserved. Last update: 10.11.2009
28
GHS – the first-ever globally uniform basis
Safety in the laboratory
GHS stands for the Globally Harmonised System of Classification and Labelling
of Chemicals. In December 2002, the United Nations published the GHS
in the so-called “Purple Book“ with a description of harmonised classification
and labelling criteria. The goal of GHS is to harmonise the various existing
classification and labelling systems all over the world. Because of the various
evaluation criteria, it has long been the case that one and the same
substance can be classified as poisonous, harmful to health, or even not harmful.
This leads to different levels of protection in terms of occupational health
and safety, consumer protection, and environmental protection. GHS offers the
first-ever globally uniform basis for the evaluation of substance properties.
GHS establishes the requirement for a globally high protection level for human
health and the environment.
The resulting harmonised hazard communication includes criteria for classification
and labelling as well as hazardous substance labelling and requirements for the
creation of Safety Data Sheets.
for more information visit
www.merck-chemicals.com/ghs
29
Incompatible chemicals
The chemicals listed below may react violently with one another. They must be kept
apart and must never come into contact with one another. The objective of this list
is to give information on how to avoid accidents in the laboratory.
Due to the great number of hazardous materials, this list includes only the most
important examples.
Substance
Incompatible with
Acetylenehalogen, copper, silver, mercury, air, oxidant, oxygen,
silver compound, mercury compound, copper compound
and heavy metal salts
Acetic acidchromium (VI) oxide, nitric acid, alcohols, ethylene
glycol, perchloric acid, peroxides, permanganates, alkali,
base, cyanide
Activated carboncalcium hypochlorite, oxidizing agents, alcohols, acids,
organic nitro compound and oxidant
Alkali metals
water, carbon tetrachloride and other halogenated
alkanes, carbon dioxide, halogens
Aluminum alkyls
water, alcohols, oxidant and acids
Ammonia (laboratory
mercury (e.g. in pressure gauges), calcium hypochlo
gas or solutions)
rite, hydrogen fluoride, halogen, acids, air and oxygen
Ammonium nitrate
acids, powdered metals, flammable liquids, chlorates,
sulfur, fine-particulate organic or combustible
materials, alkali metals, base, oils, reducing agent, potassium dichromate
Anilinenitric acid, hydrogen peroxide Oxidationsmittel, Säure
Bromine
see chlorine
Chlorine
ammonia, acetylene, butadiene, butane, methane,
propane, hydrogen, petroleum benzine, benzene,
powdered metals, phosphor
Chloratesammonium salts, acids, powdered metals, sulfur,
fine-particulate organic or combustible substances, azide,
picrate and picric acid
Chromium (VI) oxideacetic acid, naphthalene, camphor, glycerol, petroleum
benzine, alcohols, flammable liquids
Copper
acetylene, hydrogen peroxide
Cumene hydroperoxide
acids, both organic and inorganic
Cyanides
acids
Flammable liquidsammonium nitrate, chromium (VI) oxide, hydrogen
peroxide, nitric acid, sodium peroxide, halogens, oxidant
Fluorine
extremely aggressive; store separately!
Hydrocarbonfluorine, chlorine, bromine, (butane, propane, chromium
(VI) oxide, sodium peroxide benzene etc.)
Hydrogen fluoride
ammonia (laboratory gas or solutions), alkali metals, base
Hydrogen peroxidecopper, chromium, iron, metals and metal salts, alcohols,
acetone, organic substances, aniline, nitro-methane,
combustible substances (solid or liquid), manganese
dioxid, permanganate, ether
Hydrogen sulfide
fuming nitric acid, oxidizing gases, oxygen
30
Iodineacetylene, ammonia (laboratory gas or solutions), alkali
metals and ammonium compound
Mercury
acetylene, ammonia, aluminium
Nitric acidacetic acid, aniline, chromium (VI) oxide,prussic acid,
(concentrated) hydrogen sulfide, flammable liquids and
gases, flammable substances, dichloromethane, organic
solvents
silver, mercury, oxidant, alkalis
Perchloric acidacetic anhydride, bismuth and its alloys, alcohols,
paper, wood, flammable and organic substances, dichloromethane and organic solvents
Phosphorussulfur, compounds containing oxygen, e.g. chlorates,
oxidant and chlorate
Potassium
see alkali metals
Potassium chlorate
see chlorate
Potassium perchlorate
see chlorate
Potassium
glycerol, ethylene glycol, benzaldehyde, sulfuric acid
permanganate
Silver
acetylene, oxalic acid, tartaric acid, ammonium
compounds, acetylide and azide
Sodium
see alkali metals
Sodium peroxidemethanol, ethanol, glacial acetic acid, acetic
anhydride, benzaldehyde, carbon disulfide, glycerol,
ethylene glycol, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate,
furfural, flammable substances, metals in powder form
and acids
Sulfuric acidchorate, perchlorate, potassium permangangate, cyanide,
permanganate, alkali metals, alkali compounds and base
31
Safety in the laboratory
Oxalic acid
Chemical and physical properties
of elements and
inorganic compounds
Table of elements 34
Hardness scale according to MOHS 38
Electrochemical series of some nonmetals 39
Covalent single-bond radiuses 39
* Gases in [g/ l] at °C and normal pressure
** longest-lived isotope in brackets
*** Earth's crust
Table of elements
Element
name
Symbol
Ordinalnumber
Actinium
Aluminium
Americium
Antimony
Argon
Arsenic
Astatine
Barium
Berkelium
Beryllium
Bismuth
Boron
Bromine
Cadmium
Cesium
Calcium
Californium
Carbon
Cerium
Chlorine
Chromium
Cobalt
Copper
Curium
Dysprosium
Einsteinium
Erbium
Europium
Fermium
Fluorine
Francium
Gadolinium
Gallium
Germanium
Gold
Hafnium
Helium
Holmium
Hydrogen
Indium
Iod
Iridium
Iron
Krypton
Lanthanum
Lawrencium
Lead
Lithium
Lutetium
Magnesium
Manganese
Ac
Al
Am
Sb
Ar
As
At
Ba
Bk
Be
Bi
B
Br
Cd
Cs
Ca
Cf
C
Ce
Cl
Cr
Co
Cu
Cm
Dy
Es
Er
Eu
Fm
F
Fr
Gd
Ga
Ge
Au
Hf
He
Ho
H
In
I
Ir
Fe
Kr
La
Lr
Pb
Li
Lu
Mg
Mn
89
13
95
51
18
33
85
56
97
4
83
5
35
48
55
20
98
6
58
17
24
27
29
96
66
99
68
63
100
9
87
64
31
32
79
72
2
67
1
49
53
77
26
36
57
103
82
3
71
12
25
34
Atomic
mass**
227.028
26.98154
(243)
121.76
39.948
74.9216
(210)
137.33
(247)
9.01218
208.9804
10.81
79.904
112.41
132.9054
40.078
(251)
12.011
140.115
35.4527
51.996
58. 9332
63.546
(247)
162.50
(254)
167.26
151.96
(257)
18.9984
(223)
157.25
69.723
72.61
196.966
178.49
4.00260
164.93
1.00794
114.82
126.9045
192.22
55.847
83.80
138.9055
(260)
207.2
6.941
174.967
24.305
54.93805
Density
20°
4°
10.1
2.70
11.7
6.68
*1.784
5.73
–
3.7
–
1.86
9.80
2.34
3.14
8.64
1.90
1.55
–
2.25
6.8
*3.214
7.19
8.83
8.93
–
8.54
–
9.05
5.26
–
*1.70
–
7.90
6.0
5.36
19.3
13.3
*0.178
8.80
*0.0899
7.31
4.94
22.6
7.86
*3.708
6.1
–
11.4
0.53
9.84
1.74
7.3
Meltingpoint [°C]
1050
660.37
994 ± 4
630.74
–189.2
817 (28 bar)
302
725
–
1278 ± 5
271.3
2300
–7.2
320.9
28.40 ± 0.01
839 ± 2
–
~ 3550
798 ± 3
–100.98
1857 ± 20
1495
1083.4 ± 0.2
1340 ± 40
1409
–
1522
822 ± 5
–
–219.62
(27)
1311 ± 1
29.78
937.4
1064.4
2227 ± 20
–272.2
1470
– 259.14
156.61
113.5
2410
1535
–156.6
920 ± 5
–
327.5
180.54
1656 ± 5
648.8 ± 0,5
1244 ± 3
3200 ± 300
2467
2607
1750
-185.7
613 (sub.)
337
1640
–
2970 (5 mm)
1560 ± 5
2550 (sub.)
58.78
765
678.4
1484
–
4827
3257
–34.6
2672
2870
2567
–
2335
–
2510
1597
–
–188.14
(677)
3233
2403
2830
2807
4602
–268.934
2720
–252.87
2080
184.35
4130
2750
–152(3)
3454
–
1740
1347
3315
1090
1962
Occurrence of
the elements***
[%]
–
8.1
–
0.0001
–
0.0005
–
0.025
–
0.0006
0.00002
0.0003
0.00016
0.000015
0.0007
3.6
–
0.03
0.0046
0.031
0.02
0.0023
0.007
–
0.00045
–
0.00025
0.00011
–
0.03
–
0.00064
0.0015
0.0007
0.00000005
0.00045
0.00000003
0.00012
0.14
0.00001
0.00003
0.00000001
5.0
–
0.0018
–
0.0016
0.0065
0.00008
0.21
0.1
Atomic
radiuses
[pm]
–
143
–
145
191
125
–
217
–
112
155
97
119
149
262
196
–
77
182
107
125
125
128
–
–
–
–
–
–
71
–
–
–
–
144
–
145
–
46
–
136
–
124
–
–
–
175
152
–
160
118
Ionic radiuses
[pm]
Electronegativity
118 (III)
51 (III)
107 (III), 92 (IV)
76 (III), 62 (V)
–
58 (III), 46 (V)
62 (VII)
134 (II)
–
35 (II)
96 (III), 74 (V)
23 (III)
196 (–I), 47 (V), 39 (VII)
97 (II)
167 (I)
99 (II)
–
16 (IV)
107 (III), 94 (IV)
181 (–I), 34 (V), 27 (VII)
63 (III), 52 (VI)
72 (II), 63 (III)
96 (I), 72 (II)
–
92 (III)
–
89 (III)
124 (II), 98 (III)
–
133 (–I), 8 (VII)
180 (I)
97 (III)
62 (III)
73 (II), 53 (IV)
137 (I), 85 (III)
78 (IV)
–
91 (III)
154 (–I)
81 (III)
220 (–), 62 (V), 50 (VII)
68 (IV)
74 (II), 64 (III)
–
114 (III)
–
215 (–II), 120 (II), 84 (IV)
68 (I)
85 (III)
66 (II)
80 (II), 66 (III), 60 (IV), 46 (VII)
1.00
1.47
~ 1.2
1.82
–
2.20
1.96
0.97
~ 1.2
1.47
1.67
2.01
2.74
1.46
0.86
1.04
~ 1.2
2.50
1.06
2.83
1.56
1.70
1.75
~ 1.2
1.10
~ 1.2
1.11
1.01
~ 1.2
4.10
0.86
1.11
1.82
2.02
1.42
1.23
–
1.10
2.20
1.49
2.21
1.55
1.64
–
1.08
–
1.55
0.97
1.14
1.23
1.60
35
Chemical and physical properties of elements and inorganic compounds
Boilingpoint [°C]
* Gases in [g/ l] at °C and normal pressure
** longest-lived isotope in brackets
*** Earth's crust
Table of elements
Element
name
Symbol
Ordinalnumber
Atomic
mass**
Mendelevium
Mercury
Molybdenum
Neodymium
Neon
Neptunium
Nickel
Niobium
Nitrogen
Nobelium
Osmium
Oxygen
Palladium
Phosphorous, white
Platinum
Plutonium
Polonium
Potassium
Praseodymium
Promethium
Protactinium
Radium
Radon
Rhenium
Rhodium
Rubidium
Ruthenium
Samarium
Scandium
Selenium
Silver
Silicium
Sodium
Strontium
Sulphur
Tantalum
Technetium
Tellurium
Terbium
Thallium
Thorium
Thulium
Tin
Titanium
Tungston
Uranium
Vanadium
Xenon
Ytterbium
Yttrium
Zinc
Zirkonium
Md
Hg
Mo
Nd
Ne
Np
Ni
Nb
N
No
Os
O
Pd
P
Pt
Pu
Po
K
Pr
Pm
Pa
Ra
Rn
Re
Rh
Rb
Ru
Sm
Sc
Se
Ag
Si
Na
Sr
S
Ta
Tc
Te
Tb
Tl
Th
Tm
Sn
Ti
W
U
V
Xe
Yb
Y
Zn
Zr
101
80
42
60
10
93
28
41
7
102
76
8
46
15
78
94
84
19
59
61
91
88
86
75
45
37
44
62
21
34
47
14
11
38
16
73
43
52
65
81
90
69
50
22
74
92
23
54
70
39
30
40
(258)
200.59
95.94
144.24
20.1797
237.0482
58.69
92.9064
14.0067
(259)
190.23
15.9994
106.42
30.97376
195.08
(244)
(209)
39.0983
140.908
(145)
231.036
226.0254
(222)
186.207
102.905
85.4678
101.07
150.36
44.9559
78.96
107.8682
28.0855
22.98977
87.62
32.066
180.9479
(97)
127.60
158.92534
204.3833
232.0381
168.9342
118.71
47.88
183.84
238.029
50.9415
131.29
173.04
88.90585
65.39
91.224
36
Density
20°
4°
–
13.55
10.2
7.0
*0.90
19.5
8.90
8.5
*1.251
–
22.5
*1.429
12.0
1.83
21.45
19.7
9.32
0.86
6.7
–
–
~6
*9.96
20.9
12.4
1.53
12.4
7.5
3.0
4.8
10.5
2.4
0.97
2.6
2.0
16.7
11.5
6.2
8.3
11.85
11.7
9.33
7.3
4.51
19.30
19.1
6.1
*5.89
6.5
4.5
7.2
6.5
Meltingpoint [°C]
–
– 38.87
2617
1010
– 248.7
640±1
1453
2468 ± 10
– 209.86
–
3045 ± 30
– 218.4
1552
44.1
1.772
641
254
63.65
931 ± 4
~ 1080
< 1600
700
– 71
3180
1966 ± 3
38.89
2310
1072 ± 5
1539
217
961.93
1410
97.81± 0.03
769
112.8
2996
2172
449.5 ± 0.3
1360 ± 4
303.5
1750
1545 ± 15
231.9681
1660 ± 10
3410 ± 20
1132.3±0.8
1890 ± 10
– 111.9
824 ± 5
1523 ± 8
419.58
1852 ± 2
Occurrence of
the elements***
Atomic
radiuses
[%]
Ionic radiuses
[pm]
Electronegativity
–
356.58
4612
3127
– 246.05
3902
2732
4742
– 195.8
–
5027±100
– 182.962
3140
280
3827
3232
962
774
3212
–
–
1140
– 61.8
–
3727±100
688
3000
1778
2832
684.9±1.0
2212
2355
882.9
1384
444.674
5425±100
4877
989.8±3.8
3041
1457±10
ca. 4790
1727
2270
3287
5660
3818
3380
– 107.1±3
1193
3337
907
4377
0.00005
0.0015
0.0024
–
–
0.008
0.0024
0.0046
–
0.00000001
46.6
0.0000001
1.2
0.00000005
–
–
2.6
0.00055
–
–
–
–
0.00000001
0.00000001
0.03
0.00000001
0.00065
0.0005
0.000009
0.00001
27.7
2.8
0.03
0.05
0.00021
–
0.00000002
0.00009
0.00006
0.0012
0.00002
0.004
0.45
0.007
0.0004
0.015
–
0.00027
0.0028
0.013
0.022
150
–
–
–
–
124
–
71
–
–
65
–
–
138
–
–
231
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
243
–
–
–
–
144
117
186
–
104
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
140
–
136
138
–
–
–
–
133
–
110 (II)
70 (IV), 62 (VI)
104 (III)
–
110 (III), 95 (IV), 71 (VII)
69 (II)
74 (IV), 69 (VI)
16 (III), 13 (V)
–
67 (IV), 69 (VI)
132 (–II), 10 (VI)
80 (II), 65 (IV)
44 (III), 35 (V)
80 (II), 65 (IV)
108 (III), 93 (IV)
–
133 (I)
106 (III), 92 (IV)
106 (III)
113 (III), 98 (IV), 89 (V)
143 (II)
–
72 (IV), 56 (VII)
68 (III)
147 (I)
67 (IV)
100 (III)
81 (III)
191 (–II), 83 (III), 50 (IV), 42 (VI)
126 (I), 89 (II)
221 (–IV), 42 (IV)
97 (I)
112 (II)
174 (–II), 37 (IV), 30 (VI)
68 (V)
56 (VII)
211 (–II), 70 (IV), 56 (VI)
93 (III), 89 (IV)
147 (I), 95 (III)
102 (IV)
87 (III)
294 (–IV), 93 (II), 71 (IV)
80 (II), 76 (III), 68 (IV)
70 (IV), 62 (VI)
97 (IV), 80 (VI)
88 (II), 74 (III), 63 (IV), 59 (V)
–
86 (III)
92 (III)
74 (II)
79 (IV)
~ 1.2
1.44
1.30
1.07
–
1.22
1.75
1.23
3.07
–
1.52
3.50
1.35
2.06
1.44
1.22
1.76
0.91
1.07
1.07
1.14
0.97
–
1.46
1.45
0.89
1.42
1.07
1.20
2.48
1.42
1.74
1.01
0.99
2.44
1.33
1.36
2.01
1.10
1.44
1.11
1.11
1.72
1.32
1.40
1.22
1.45
–
1.06
1.11
1.66
1.22
37
Chemical and physical properties of elements and inorganic compounds
Boilingpoint [°C]
Hardness scale acc. to MOHS
Hardness
Mineral
Formula
1
Talcum
Mg3 [(OH)2 / Si4O10]
2
Gypsum
CaSO4 · 2H2O
3
Calcite
CaCO3
4
Fluorspar
CaF2
5
Apatite
Ca5 [(F, CI, OH) / (PO4)3]
6
Feldspar
KAISi3O8
7
Quartz
SiO2
8
Topaz
AI2 [F2 / SiO4]
9
Corundum
AI2O3
10
Diamond
C
Infotext zu Element
Infotext zu Element
38
Chemical and physical properties of elements and inorganic compounds
Electrochemical series of some nonmetals (alkaline solution)
Red ⇄® Ox + e
e° (Volt)
Red ⇄® Ox + e
Te2– ⇄ Te + 2e
– 1.14
2 I–⇄ I2 + 2e
e° (Volt)
+ 0.54
Se2– ⇄ Se + 2e
– 0.92
2 Br–⇄ Br2 + 2e
+ 1.07
S2– ⇄ S + 2e
– 0.48
2 CI–⇄ Cl2 + 2e
+ 1.36
2 F–⇄ F2 + 2e
+ 2.87
Covalent single-bond radiuses (in PM)
H*
28
O
66
C
77
S
104
Si
117
Se
117
Ge
122
Te
137
Sn
140
F
64
N
70
CI
99
P
110
Br
114
As
121
I
133
Sb
141
* Determined from H-X bond distances
Infotext zu Element
39
Solutions - aqueous systems
General mixing formulas for liquids
Conversion table for water hardness
Mixture rule
Preparation of dilute solutions
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water
in relation to temperature
Solubility products of slightly soluble inorganic compounds
Sample preparation
Acids Sulfuric acid
Phosphoric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acid
Sodium hydroxide solution
Potassium hydroxide solution
Ammonia
Commercially available concentrations
of some acids and alkalis
42
43
44
45
46
54
57
58
60
60
62
63
65
68
69
General formulas for mixing liquids
C (a – c)
B (a – b)
A = c – b
B=
C=
a – b
a–c
With:
A = weight of the original liquid
B = weight of the diluent
C = weight of the prepared mixture For water as diluent: b = 0
a = its content in % by weight
b = its content in % by weight
c = its content in % by weight
Example
10 l of battery sulfuric acid with a density of
D20°
4° = 1.28. 1.28 is required. Available: concentrated
sulfuric acid with a density of D20°
4° = 1.84 (= 97.5 weight %).
How much sulfuric acid and how much water are needed to
prepare 10 l (= 12.8 kg) of battery sulfuric acid?
Calculation
In the table 'Sulfuric acid‘ on page 52 we find:
D20°
4° = 1.28 equivalent to 37.36 weight%.
C (a – c) 12.80 (97.50 – 37.36) B
= a – b
=
97.50 – 0= 7.895 kg diluent
(water)
Consequently, 4.905 kg (= 2.666 l) of concentrated sulfuric acid with a
density of D20°
4° = 1.84 must be added to 7.895 kg (= l) of water to yield
10 l of battery acid with a density of D20° = 1.28.
4°
42
Alkaline
earth ions
mmol/l
Alkaline
earth ions
mval/l
German
degree
°d
ppm
CaCO3
English
degree
°e
French
degree
°f
1 mmol/l
Alkaline earth ions
1.00
2.00
5.60
100.00
7.02
10.00
1 mval/l
Alkaline earth ions
0.50
1.00
2.80
50.00
3.51
5.00
1 German degree
0.18
0.357
1.00
17.80
1.25
1.78
1 ppm CaCO3
0.01
0.020
0.056
1.00
0.0702
0.10
1 English degree
0.14
0.285
0.798
14.30
1.00
1.43
1 French degree
0.10
0.200
0.560
10.00
0.702
1.00
With Merckoquant® Total Hardness strips you can
easily and quickly check the water hardness in the
following ranges:
< 3 – 21°d
< 5 – 25°d
soft – medium - hard
43
Solutions - aqueous systems
Convention table for water hardness units
Mixture rules
Example
Sulfuric acid with a density of D20°
4° = 1.520 is to be prepared
from sulfuric acid with a density of D20°
4° = 1.435 and sulfuric
20°
acid of D 4° = 1.824.
1.435 ↖
1.824
↙
1.520
Calculation
The table 'Sulfuric acid' (p. 56) informs that sulfuric acid with a density
of D20° = 1.435 = 54.00 weight% H2SO4 contains sulfuric acid with
4°
a density of D20° = 1.824 = 92.00 weight% H2SO4 and that of
4°
D20° = 1.520 = 62.00 weight% H2SO4.
4°
From this, form the mixing cross:
54 ↖
92
↙
62
↗ 30
↘
8
i.e. 30 parts by weight of 54.00 % sulfuric acid must be mixed with 8 parts by
weight of 92.00 % sulfuric acid to yield sulfuric acid of 62.00 weight% H2SO4,
equivalent to D 20° = 1.520.
4°
44
Preparation of dilute solutions
Slowly stir the stated quantity of concentrated solution or solid KOH or NaOH,
respectively, into water.
Solutions - aqueous systems
Caution! Strong development of heat may occur! Cool to room temperature,
then make up to 1 liter with water. Store alkaline solutions in polyethylene bottles,
because they attack glass. As a rule of thumb, more concentrated solutions can
be prepared by taking a multiple of the stated quantity.
Example
6 mol/l HNO3 from 6/2 x 140 ml = 420 ml 65 % HNO3.
Solution to be prepared
Original quantity to prepare
1 l of dilute solution
Weight%
Density
mol/l
Weight%
ml
Acetic acid
12
1.01
2
100
115
Nitric acid
12
1.07
2
65
140
7
1.03
2
36
165
Hydrochloric
acid
Sulfuric acid
9.5
1.06
1
96
56
Ammonia
3.5
0.98
1
30
115
Potassium
hydroxide
solution
10.5
1.09
2
113 g solid KOH
(85%)
Sodium
hydroxide
solution
7.5
1.08
2
80 g solid NaOH
(100%)
45
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water
A
B
C
I
46
Name
Cat. No.
Formula
Aluminum ammonium sulfate dodecahydrate
101031
AINH4(SO4)2 · 12H2O
Aluminum chloride hexahydrate
Aluminum nitrate nonahydrate
Aluminum potassium sulfate dodecahydrate
101084
101063
101047
AICI3 · 6H2O
AI(NO3)3 · 9H2O
AIK(SO4)2 · 12H2O
Aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate
Ammonium bromide
Ammonium chloride
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate
di-Ammonium hydrogen phosphate
101102
101125
101145
101126
101131
101207
AI2(SO4)3 · 18H2O
NH4Br
NH4CI
NH4H2PO4
NH4HCO3
(NH4)2HPO4
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate hexahydrate
Ammonium monovanadate
Ammonium nitrate
Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium thiocyanate
Antimony(III) chloride
Barium acetate
Barium chloride dihydrate
Barium hydroxide octahydrate
Barium nitrate
di-Boron trioxide
Boric acid
Cadmium sulfate hydrate
Calcium acetate
Calcium chloride dihydrate
Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate
Calcium sulfate dihydrate
Cesium chloride
Cesium nitrate
Chromium(VI) oxide
103792
101226
101188
101217
101213
107838
101704
101719
101737
101729
100163
100165
102027
109325
102382
102121
102161
102038
102856
100229
(NH4)2Fe(SO4)2 · 6H2O
NH4VO3
NH4NO3
(NH4)2SO4
NH4SCN
SbCI3
Ba(CH3COO)2
BaCI2 · 2H2O
Ba(OH)2 · 8H2O
Ba(NO3)2
B2O3
H3BO3
3CdSO4 · 8H2O
Ca(CH3COO)2
CaCI2 · 2H2O
Ca(NO3)2 · 4H2O
CaSO4 · 2H2O
CsCI
CsNO3
CrO3
Cobalt chloride
Cobalt chloride hexahydrate
Cobalt nitrate hexahydrate
Cobalt sulfate heptahydrate
Copper(I) chloride
802540
102539
102536
102556
102739
CoCI2
CoCl2 · 6H2O
Co(NO3)2 · 6H2O
CoSO4 · 7H2O
CuCl
Copper(II) chloride dihydrate
Copper(II) nitrate trihydrate
Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
Copper sulfate
Iron(III) chloride
Iron(III) chloride hexahydrate
102733
102753
102790
102791
803945
103943
CuCl2 · 2H2O
Cu(NO3)2 · 3H2O
CuSO4 · 5H2O
CuSO4
FeCl3
FeCl3 · 6H2O
in relation to temperature
0
20
40
60
80
100
2.6
6.6
12.4
21.1
35.2
44.9
61.0
2.96
45.6
75.4
6.01
46.3
89.0
13.6
47.7
108.0
33.3
47.7
–
31.2
60.6
29.7
22.7
11.9
57.5
36.4
75.5
37.6
36.8
21.2
68.6
45.6
91.1
46.0
56.7
36.6
81.8
58.0
107.8
55.3
82.9
59.2
97.6
73.0
126.7
65.6
120.7
109.2
(115.5)
109.2
(95 °C)
–
–
109.0
(90 °C)
89.0
145.6
77.3
174.0
355.0
–
53.4
–
415.0
87.4
347.0
4531.0
74.0
46.4
21.0
20.3
6.2
14.8
82.0
32.7
136.8
–
0.20
230.0
83.8
176.0
72.0
–
–
–
610.0
1000.0
94.1
102.0
–
–
–
–
74.0
74.0
52.5
58.7
–
–
27.2
34.2
9.5
15.7
23.6
39.7
84.6
–
33.5
29.7
147.0
159.0
–
–
0.19
0.16
250.0
271.0
134.0
197.0
189.0
199.0
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
525.1
–
–
–
–
537.0
–
–
83.8
160.0
29.0
48.0
49.9
126.0
91.2
179.0
39.1
60.0
–
169.5
99.2
208.0
53.6
70.0
–
–
107.9
(257.0)
73.6
83.0
–
–
17.8
–
118.5
70.4
115.0
601.6
58.0
30.7
1.5
5.0
1.1
2.7
75.5
37.4
–
101.0
0.18
161.0
9.3
163.0
26.9
38.5
4.8
13.2
187.7
283.0
75.4
81.2
163.0
235.0
931.5 1368.0
72.0
79.0
35.7
40.8
3.5
8.2
9.1
14.4
2.2
4.0
5.04
8.7
76.7
79.3
34.7
33.2
–
128.1
129.4
196.0
0.20
0.21
187.0
208.0
23.0
47.2
166.7
171.0
74.5
–
–
91.9
62.35
–
41.9
–
70.65
–
14.8
25.5
25.5
83.5
53.6
1.5
(25 °C)
77.0
–
20.8
36.2
36.3
100.0
–
68.6
–
69.5
78.3
72.0
Content of
the total
solution at
20 °C. in %
6.2
31.3
43.0
5.67
26.7
43.9
27.3
26.9
17.5
40.70
21.2
–
65.0
43.0
62.0
90.3
–
26.3
3.4
8.3
2.15
4.8
43.4
–
–
56.4
0.20
–
–
62.50
47.9
38.4
–
34.9
1.497
(25 °C)
43.5
–
17.2
–
26.6
50.0
Density of
the total
solution at
20 °C. in %
1.0459
(15.5 °C)
–
–
1.053
1.308
–
1.075
–
1.07
1.3436
(14.5 °C)
1.18
–
1.308
1.247
–
–
–
1.28
1.04
1.069
–
1.015
1.616
–
–
–
1.001
–
–
1.7100
(16.5 °C)
1.52
1.49
–
–
–
Solutions - aqueous systems
Solubility in g/100 g H2O at °C
1. 55
–
1.1965
–
–
–
47
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water
Name
I
L
M
N
P
48
Cat. No.
Formula
Iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate
103861
FeCl2 · 4H2O
Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate
Iron(II) sulfate monohydrate
Lead chloride
Lead nitrate
Lithium bromide
Lithium carbonate
Lithium chloride monohydrate
Lithium iodide
Lithium nitrate
Lithium sulfate monohydrate
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
Magnesium nitrate hexahydrate
103965
103967
807383
107398
105669
105680
105677
818287
112230
105694
105833
105853
FeSO4 · 7H2O
FeSO4 · H2O
PbCI2
Pb(NO3)2
LiBr
Li2CO3
LiCl · H2O
Lil
LiNO3
LiSO4 · H2O
MgCl2 · 6H2O
Mg(NO3)2 · 6H2O
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate
Manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate
105886
105927
MgSO4 · 7H2O
MnCl2 · 4H2O
Manganese(II) chloride dihydrate
Manganese(II) sulfate monohydrate
Mercury(II) bromide
105934
105941
104421
MnCl2· 2H2O
MnSO4 · H2O
HgBr2
Mercury(II) chloride
Nickel chloride hexahydrate
Nickel nitrate hexahydrate
Nickel sulfate hexahydrate
Potassium acetate
Potassium bromate
Potassium bromide
Potassium carbonate
Potassium chlorate
Potassium chloride
Potassium chromate
Potassium cyanide
104419
106717
106721
106727
104820
104912
104905
104928
104944
104936
104952
104967
HgCl2
NiCl2 · 6H2O
Ni(NO3)2 · 6H2O
Ni2SO4 · 6H2O
KCH3COO
KBrO3
KBr
K2CO3
KClO3
KCl
K2CrO4
KCN
Potassium dichromate
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
Potassium disulfite
Potassium hexachloroplatinate(IV)
Potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) trihydrate
Potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
Potassium hydrogen carbonate
di-Potassium hydrogen phosphate trihydrate
104864
104873
105057
119238
104984
104973
104854
105099
K2Cr2O7
KH2PO4
K2S2O5
K2 [Pt(Cl)6]
K4 [Fe(CN)6] · 3H2O
K3 [Fe(CN)6]
KHCO3
K2HPO4 · 3H2O
di-Potassium hydrogen phosphate
Potassium hydrogen sulfate
Potassium hydroxide monohydrate
105104
104885
105002
K2HPO4
KHSO4
KOH · H2O
in relation to temperature
0
–
20
–
15.6
40
–
26.6
40.3
–
–
–
0.67
36.4
143.0
–
–
151.0
48.0
36.2
52.8
63.9
0.99
52.2
177.0
1.3
82.8
165.0
76.0
34.8
54.6
70.1
1.45
69.4
205.0
–
90.4
180.0
–
33.5
57.5
81.8
35.6
73.6
45.4
88.7
–
63.6
–
–
–
–
–
4.29
51.7
79.2
–
217.0
3.1
54.0
106.0
3.3
28.2
59.0
(63.0)
4.7
14.3
27.5
0.74
15.0
29.9
22.6
–
–
0.62
(25 °C)
6.6
55.3
94.1
–
256.0
6.8
65.8
110.0
7.3
34.2
63.7
71.6
(25 °C)
12.5
22.7
44.9
1.1
28.9
46.0
33.3
159.0
–
36.3
–
–
9.6
–
118.8
–
323.0
13.1
76.1
117.0
14.5
40.3
67.0
–
26.3
33.9
63.9
1.7
42.7
59.5
45.3
212.5
–
51.4
–
60.0
(0.96)
67.3
136.4
60
(90.5)
(56 °C)
47.6
–
1.98
88.0
224.0
–
100.0
–
–
32.3
60.7
93.7
–
(106.0)
(58.1°C)
–
58.6
1.7
80
107.5
–
43.8
2.6
107.5
245.0
–
113.0
–
–
31.5
65.9
–
–
(31.6)
3.3
127.3
266.0
–
(127.5)
480.0
227.0
31.0
72.7
–
–
–
–
–
110.5
45.5
2.8
115.0
35.5
4.9
13.9
–
–
57.0
350.0
22.0
85.9
127.0
25.9
45.6
70.9
81.0
(50 °C)
45.6
48.6
85.0
2.6
56.0
70.9
60.0
–
(50 °C)
266.0
–
147.0
100
100.0
24.2
–
–
–
–
33.9
95.3
140.0
39.7
51.0
75.1
(95.0)
(75 °C)
73.0
68.0
108.0
3.8
68.9
81.8
–
–
(75 °C)
–
–
160.0
54.1
–
–
–
380.0
49.7
104.9
156.0
56.2
56.2
79.2
122.0
(103.3 °C)
103.0
–
133.0
5.2
(82.7)
91.6
–
–
–
121.6
178.0
Content of
the total
solution at
20 °C. in %
–
–
21.0
–
0.98
34.3
–
1.31
45.3
–
–
25.6
35.3
41.2
26.25
42.4
–
–
0.62
(25 °C)
6.2
35.6
48.5
–
–
6.4
39.7
–
6.8
25.5
38.9
41.73
(25 °C)
11.1
18.5
30.99
–
22.4
31.5
24.98
61.4
–
33.95
–
Density of
the total
solution at
20 °C. in %
1.225
–
1.007
1.40
–
–
1.29
–
–
1.23
1.331
1.388
(25 °C)
1.31
1.499
Solutions - aqueous systems
Solubility in g/100 g H2O at °C
–
–
–
1.052
1.46
–
–
–
1.048
1.370
–
1.042
1.174
1.378
–
1.077
–
–
–
1.16
1.18
1.18
–
–
–
–
49
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water
P
S
50
Name
Cat. No.
Formula
Potassium iodate
Potassium iodide
Potassium nitrate
di-Potassium oxalate monohydrate
Potassium perchlorate
Potassium permanganate
Potassium peroxodisulfate
Potassium sulfate
Potassium thiocyanate
Rubidium chloride
Sodium acetate trihydrate
105051
105043
105063
105073
105076
105082
105091
105153
105125
107615
106267
KlO3
Kl
KNO3
K2C2O4 · H2O
KClO4
KMnO4
K2S2O8
K2SO4
KSCN
RbCl
NaCH3COO · 3H2O
Sodium bromide
Sodium carbonate decahydrate
Sodium carbonate monohydrate
Sodium carbonate
Sodium chlorate
Sodium chloride
Sodium dichromate dihydrate
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate
tetra-Sodium diphosphate decahydrate
Sodium disulfite
Sodium fluoride
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate
Sodium hydroxide monohydrate
Sodium hydroxide
Sodium iodate
Sodium iodide
Sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrite
Sodium perchlorate monohydrate
tri-Sodium phosphate dodecahydrate
Sodium sulfate decahydrate
Sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfite
di-Sodium tetraborate
Sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate
Silver nitrate
Silver sulfate
106363
106391
106386
106392
106420
106404
106336
106342
106370
106591
106528
106449
106329
106579
106575
106580
106586
106466
106498
106525
106523
106537
106549
106564
106578
106648
106649
106657
106310
106516
101512
101509
NaBr
Na2CO3 · 10H2O
Na2CO3 · H2O
Na2CO3
NaClO3
NaCl
Na2Cr2O´7 · 2H2O
NaH2PO4 · 2H2O
NaH2PO4
Na4P2O7 · 10H2O
Na2S2O5
NaF
NaHCO3
Na2HPO4 · 12H2O
Na2HPO4 · 7H2O
Na2HPO4 · 2H2O
Na2HPO4
NaOH · H2O
NaOH
NalO3
Nal
NaNO3
NaNO2
NaClO4 · H2O
Na3PO4 · 12H2O
Na2SO4 · 10H2O
Na2SO4
Na2SO3
Na2B4O7
Na2S2O3 · 5H2O
AgNO3
Ag2SO4
in relation to temperature
20
40
4.7
127.8
13.3
–
0.76
2.8
0.18
7.3
177.0
70.6
36.3
0
8.1
144.5
31.7
35.9
1.7
6.4
0.5
11.1
218.0
83.6
46.4
12.9
161.0
63.9
–
3.6
12.6
1.1
14.8
–
–
65.4
–
–
–
–
6.86
–
21.7
–
7.1
80.5
–
163.2
57.7
–
2.7
–
(3.6)
6.89
1.63
–
–
–
–
–
2.5
–
70.7
73.0
167.0
1.5
4.56
–
–
1.2
52.5
115.0
0.57
21.4
98.8
35.9
180.2
85.2
–
5.5
65.3
4.1
9.6
7.7
–
–
–
109.2
–
9.1
–
88.3
84.5
181.0
12.1
19.2
–
–
2.7
70.1
219.2
0.79
48.9
48.5
115.2
36.4
220.5
138.2
–
12.5
71.1
–
12.7
–
55.0
–
–
126.0
–
–
–
104.9
95.7
243.0
31.0
–
48.1
37.0
6.0
102.6
334.8
0.98
60
80
18.5
176.2
109.9
–
7.2
22.4
–
18.2
–
–
138.0
(58°C)
118.0
–
46.2
46.5
(138.0)
37.1
283.0
–
179.3
21.9
79.9
–
16.0
–
–
83.0
–
178.0
–
23.0
–
124.7
112.3
–
55.0
–
45.3
33.2
20.3
–
471.0
1.15
24.8
191.5
169.0
–
13.4
–
–
21.3
–
–
–
65.9
118.3
–
44.5
45.8
(167.0)
38.1
385.0
–
207.3
30.0
88.7
–
19.7
–
–
92.4
–
–
313.7
27.0
295.0
148.0
135.5
–
81.0
–
43.1
29.0
31.5
–
652.0
1.3
100
32.3
208.0
245.2
–
22.2
–
–
24.1
–
128.0
–
72.7
121.2
–
44.5
45.5
204.0
39.2
–
–
284.4
40.3
(100.0)
–
23.6
–
–
–
104.1
–
341.0
32.8
303.0
176.0
163.0
–
108.0
–
42.3
26.6
52.5
–
1024.0
1.5
Content of
the total
solution at
20 °C in %
7.5
59.1
24.1
26.4
1.7
6.0
0.468
10.0
68.55
–
31.7
35.3
–
17.8
–
–
49.7
26.4
64.3
46.0
–
5.2
39.5
3.94
8.76
7.2
–
–
–
52.2
–
–
–
46.8
45.8
64.4
10.8
16.1
–
–
–
41.2
68.6
0.75
Density of
the total
solution at
20 °C in %
1.064
1.71
1.16
–
1.008
1.04
–
1.0807
1.42
–
1.17
1.331
–
1.1941
–
–
–
1.201
–
–
–
1.05
–
1.04
1.08
1.08
–
–
–
1.55
–
–
–
1.38
1.33
1.757
1.106
1.150
–
–
–
1.39
2.18
–
Solutions - aqueous systems
Solubility in g/100 g H2O at °C
51
Solubility of inorganic compounds in water
S
T
Z
Name
Cat. No.
Formula
Strontiumchlorid-Hexahydrat
Strontiumhydroxid-Octahydrat
Strontiumnitrat
Tin(II) chloride
107865
107876
107872
818150
SrCl2 · 6H2O
Sr(OH)2 · 8H2O
Sr(NO3)2
SnCl2
Zinc bromide
Zinc chloride
Zinc nitrate tetrahydrate
Zinc sulfate heptahydrate
Zinc sulfate monohydrate
818631
108816
108833
108883
108882
ZnBr2
ZnCl2
Zn(NO3)2 · 4H2O
ZnSO4 · 7H2O
ZnSO4 · H2O
Our range of Inorganic Salts EMSURE® contains
a wide assortment of inorganic salts for analytical
use in the qualitative and quantitative analysis
of various substances and substance mixtures in
the analytical laboratory.
Inorganic Salts EMSURE® are manufactured
under strictly controlled conditions at Merck KGaA
in Darmstadt, Germany.
The key feature of these salts is their analytical
purity (their assay and trace element content are
precisely known).
52
in relation to temperature
0
44.1
0.35
–
83.9
390.0
–
–
41.6
–
20
40
60
53.9
0.7
66.6
1.5
91.2
85.2
3.1
94.2
–
269.8
(15°C)
440.0
–
–
53.8
–
80
–
7.0
97.2
100
Content of
the total
solution at
20 °C in %
–
–
–
–
24.2
101.2
–
–
453.0
211.5
–
–
620.0
488.0
–
–
76.5
640.0
541.0
–
–
66.7
670.0
–
–
–
60.5
35.0
0.69
–
72.96
(15°C)
–
–
–
35.0
–
Density of
the total
solution at
20 °C in %
1.39
–
–
2.07
–
–
–
1.47
–
Solutions - aqueous systems
Solubility in g/100 g H2O at °C
53
Solubility products of slightly
Soluble inorganic compounds
Solubility product
at given
temperature, in [mol/l]
Substance
Formula
A
Aluminum hydroxide
Al(OH)3
4.00 x 10–13
1.50 x 10–15
3.70 x 10–15
(15°)
(18°)
(25°)
B
Arsenic(III) sulfide
Barium carbonate
As2S3
BaCO3
Barium chromate
BaCrO4
Barium fluoride
BaF2
Barium oxalate
BaC2O4 · 2H2O
4.00 x 10–29
7.00 x 10–9
8.10 x 10–9
1.60 x 10–10
2.40 x 10–10
1.60 x 10–6
1.70 x 10–6
1.20 x 10–7
(18°)
(16°)
(25°)
(18°)
(28°)
(10°)
(18°)
(18°)
Barium sulfate
BaSO4
8.70 x 10–11
1.08 x 10–10
1.98 x 10–10
(18°)
(25°)
(50°)
Beryllium hydroxide
Bismuth hydroxide
Bismuth oxide chloride
Bismuth sulfide
Cadmium carbonate
Cadmium oxalate
Cadmium sulfide
Calcium carbonate
Calcium fluoride
Be(OH)2
Bi(OH)3
BiOCl
Bi2S3
CdCO3
CdC2O4 · 3H2O
CdS
CaCO3
CaF2
Calcium hydroxide
Calcium oxalate
Ca(OH)2
CaC2O4 · H2O
Calcium phosphate
Calcium sulfate
Ca3(PO4)2
CaSO4
Calcium tartrate
Cobalt(II) carbonate
Cobalt(II) sulfide
Copper(I) bromide
Copper(II) carbonate
Copper(I) chloride
Copper(II) hydroxide
Copper(I) iodide
Copper(I) sulfide
Copper(II) sulfide
Copper(I) thiocyanate
Iron(II) carbonate
Iron(II) hydroxide
Iron(III) hydroxide
Lanthanum hydroxide
Lead bromide
Lead carbonate
CaC4H4O6 · 2H2O
CoCO3
CoS
CuBr
CuCO3
CuCI
Cu(OH)2
Cul
Cu2S
CuS
CuSCN
FeCO3
Fe(OH)2
Fe(OH)3
La(OH)3
PbBr2
PbCO3
2.70 x 10–19
4.30 x 10–31
1.60 x 10–31
1.60 x 10–72
2.50 x 10–14
1.53 x 10–8
3.60 x 10–29
4.80 x 10–9
3.40 x 10–11
3.95 x 10–11
5.47 x 10–6
1.78 x 10–9
2.57 x 10–9
1.00 x 10–25
6.10 x 10–5
2.45 x 10–5
7.70 x 10–7
1.00 x 10–12
1.90 x 10–27
4.15 x 10–8
1.37 x 10–10
1.02 x 10–6
5.60 x 10–20
5.06 x 10–12
2.00 x 10–47
8.00 x 10–45
1.60 x 10–11
2.50 x 10–11
1.64 x 10–14
1.10 x 10–36
~
10–20
3.90 x 10–5
3.30 x 10–14
(25°)
(18°)
(25°)
(18°)
(25°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(18°)
(26°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
(10°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(20°)
(18–20°)
(25°)
(18–20°)
(25°)
(18–20°)
(18°)
(18°)
(18°)
(20°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
(18°)
C
I
L
54
Solubility products of slightly
Soluble inorganic compounds
M
M
N
P
S
Formula
Lead chloride
Lead chromate
Lead fluoride
PbCl2
PbCrO4
PbF2
Lead iodate
Pb(IO3)2
Lead iodide
Pbl2
Lead oxalate
Lead sulfate
Lead sulfide
Lithium carbonate
Magnesium ammonium
phosphate
Magnesium carbonate
Magnesium fluoride
Magnesium hydroxide
Manganese carbonate
Manganese sulfide
Mercury(I) bromide
Mercury(I) chloride
Mercury(I) chromate
Mercury(I) cyanide
Mercury(I) iodide
Mercury(II) iodide
Mercury(I) oxide
Mercury(II) oxide
Mercury(I) sulfide
Mercury(II) sulfide
Nickel(II) carbonate
Nickel(II) hydroxide
Nickel(II) sulfide
Potassium
hexachloroplatinate (IV)
Potassium hydrogen
tartrate
Potassium perchlorate
Silver arsenate
Silver bromide
Silver chloride
AgCl
Solubility product
at given
temperature, in [mol/l]
2.12 x 10–5
1.77 x 10–14
2.70 x 10–8
3.20 x 10–8
5.30 x 10–14
1.20 x 10–13
2.60 x 10–13
(25°)
(25°)
(9°)
(18°)
(9.2°)
(18°)
(25.8°)
PbC2O4
PbSO4
PbS
Li2CO3
MgNH4PO4
7.50 x 10–9
1.40 x 10–9
2.74 x 10–11
1.06 x 10–8
3.40 x 10–28
1.70 x 10–3
2.50 x 10–13
(15°)
(25°)
(18°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
MgCO3
MgF2
Mg(OH)2
MnCO3
MnS
Hg2Br2
Hg2Cl2
Hg2CrO4
Hg2(CN)2
Hg2I2
HgI2
Hg2O
HgO
Hg2S
HgS
NiCO3
Ni(OH)2
NiS
K2PtCl6
2.60 x 10–5
7.10 x 10–9
1.20 x 10–11
8.80 x 10–10
7.00 x 10–16
1.30 x 10–21
2.00 x 10–18
2.00 x 10–9
5.00 x 10–40
1.20 x 10–28
3.20 x 10–29
1.60 x 10–23
1.70 x 10–26
1.00 x 10–47
3.00 x 10–54
1.35 x 10–7
1.60 x 10–14
1.00 x 10–26
1.10 x 10–5
(12°)
(18°)
(18°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
(20°)
(18°)
KHC4H4O6
3.80 x 10–4
(18°)
KCIO4
Ag3AsO4
AgBr
1.07 x 10–2
1.00 x 10–19
4.10 x 10–13
7.70 x 10–13
0.21 x 10–10
0.37 x 10–10
1.56 x 10–10
13.2 x 10–10
215 x 10–10
(25°)
(25°)
(18°)
(25°)
(4.7°)
(9.7°)
(25°)
(50°)
(100°)
Solutions - aqueous systems
L
Substance
55
Solubility products of slightly
Soluble inorganic compounds
T
Z
56
Substance
Formula
Silver chromate
Ag2CrO4
Silver iodide
Agl
Silver sulfide
Silver thiocyanate
Ag2S
AgSCN
Strontium carbonate
Strontium fluoride
Strontium oxalate
Strontium sulfate
SrCO3
SrF2
SrC2O4
SrSO4
Thallium(I) bromide
Thallium(I) chloride
Thallium(I) iodide
Thallium(III) hydroxide
Thallium(II) sulfide
Thallium(I) thiocyanate
Zinc carbonate
Zinc hydroxide
Zinc sulfide, alpha
Zinc sulfide, beta
TlBr
TlCl
Tll
Tl(OH)3
Tl2S
TlSCN
ZnCO3
Zn(OH)2
ZnS
ZnS
Solubility product
at given
temperature, in [mol/l]
1.20 x 10–12
9.00 x 10–12
0.32 x 10–16
1.50 x 10–16
1.60 x 10–49
0.49 x 10–12
1.16 x 10–12
1.60 x 10–9
2.80 x 10–9
5.60 x 10–8
2.80 x 10–7
3.80 x 10–7
3.90 x 10–6
1.90 x 10–4
5.80 x 10–8
1.40 x 10–53
9.00 x 10–23
2.30 x 10–4
6.00 x 10–11
1.00 x 10–17
6.90 x 10–26
1.10 x 10–24
(14.8°)
(25°)
(13°)
(25°)
(18°)
(18°)
(25°)
(25°)
(18°)
(18°)
(2.9°)
(17.4°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(25°)
(20°)
(25°)
Sample prepartation
The more complicated the matrix, the more important the sample preparation!
The better the sample preparation, the simpler the subsequent chromatographic
separation!
The consequence of these two statements is:
Sample preparation is a must!
Best performance with Merck products:
Solutions - aqueous systems
Digestion systems and ultrapure digestion media for more 'difficult'
dissolutions or processes to be performed in accordance with DIN*
standards
An extensive range of different reagents and solvents for improved
precipitation, distribution and extraction
The Extrelut® product range – a porous kieselguhr – and corresponding prepacked columns provide not only quicker but also better results
than the conventional liquid-liquid extraction of aqueous matrices in
the separation funnel
LiChroLut® extraction columns for rapid, convenient and efficient
extractions, enrichments and selective elutions
L iChroCART® range of precolumns, which are an excellent alternative
for online sample preparation for HPLC
Inorganic membrane filters avoiding clogging of your HPLC columns
by particles
Derivatization substances for gas chromatography, i.e. for samples which are
volatile by definition
Sample preparation with Merck for reliable performance!
*DIN = Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. (German Institute of Standardization)
57
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4 , M = 98.08 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.200
1.205
1.210
1.215
1.220
1.225
1.230
1.235
1.240
58
H2SO4 content
weight%
0.2609
0.9855
1.731
2.485
3.242
4.000
4.746
5.493
6.237
6.956
7.704
8.415
9.129
9.843
10.56
11.26
11.96
12.66
13.36
14.04
14.73
15.41
16.08
16.76
17.43
18.09
18.76
19.42
20.08
20.73
21.38
22.03
22.67
23.31
23.95
24.58
25.21
25.84
26.47
27.10
27.72
28.33
28.95
29.57
30.18
30.79
31.40
32.01
32.61
mol/l
0.0266
0.101
0.1783
0.2595
0.3372
0.4180
0.4983
0.5796
0.6613
0.7411
0.8250
0.9054
0.9865
1.066
1.152
1.235
1.317
1.401
1.484
1.567
1.652
1.735
1.820
1.905
1.990
2.075
2.161
2.247
2.334
2.420
2.507
2.594
2.681
2.768
2.857
2.945
3.033
3.122
3.211
3.302
3.302
3.481
3.572
3.663
3.754
3.846
3.938
4.031
4.123
Density
d 20°
4°
1.245
1.250
1.255
1.260
1.265
1.270
1.275
1.280
1.285
1.290
1.295
1.300
1.305
1.310
1.315
1.320
1.325
1.330
1.335
1.340
1.345
1.350
1.355
1.360
1.365
1.370
1.375
1.380
1.385
1.390
1.395
1.400
1.405
1.410
1.415
1.420
1.425
1.430
1.435
1.440
1.445
1.450
1.455
1.460
1.465
1.470
1.475
1.480
1.485
H2SO4 content
weight%
33.22
33.82
34.42
35.01
35.60
36.19
36.78
37.36
37.95
38.53
39.10
39.68
40.25
40.82
41.39
41.95
42.51
43.07
43.62
44.17
44.72
45.26
45.80
46.33
46.86
47.39
47.92
48.45
48.97
49.48
49.99
50.50
51.01
51.52
52.02
52.51
53.01
53.50
54.00
54.49
54.97
55.45
55.93
56.41
56.89
57.36
57.84
58.31
58.78
mol/l
4.216
4.310
4.404
4.498
4.592
4.686
4.781
4.876
4.972
5.068
5.163
5.259
5.356
5.452
5.549
5.646
5.743
5.840
5.938
6.035
6.132
6.229
6.327
6.424
6.522
6.620
6.718
6.817
6.915
7.012
7.110
7.208
7.307
7.406
7.505
7.603
7.702
7.801
7.901
8.000
8.099
8.198
8.297
8.397
8.497
8.598
8.699
8.799
8.899
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4 , M = 98.08 g/mol
H2SO4 content
weight%
59.24
59.70
60.17
60.62
61.08
61.54
62.00
62.45
62.91
63.36
63.81
64.26
64.71
65.15
65.59
66.03
66.47
66.91
67.35
67.79
68.23
68.66
69.09
69.53
69.96
70.39
70.82
71.25
71.67
72.09
72.52
72.95
73.37
73.80
74.22
74.64
75.07
75.49
75.92
76.34
76.77
77.20
77.63
78.06
78.49
78.93
79.37
79.81
80.25
mol/l
9.000
9.100
9.202
9.303
9.404
9.506
9.608
9.711
9.8136
9.916
10.02
10.12
10.23
10.33
10.43
10.54
10.64
10.74
10.85
10.96
11.06
11.16
11.27
11.38
11.48
11.59
11.70
11.80
11.91
12.02
12.13
12.24
12.43
12.45
12.56
12.67
12.78
12.89
13.00
13.12
13.23
13.34
13.46
13.57
13.69
13.80
13.92
14.04
14.16
Density
d 20°
4°
1.735
1.740
1.745
1.750
1.755
1.760
1.765
1.770
1.775
1.780
1.785
1.790
1.795
1.800
1.805
1.810
1.815
1.820
1.821
1.822
1.823
1.824
1.825
1.826
1.827
1.828
1.829
1.830
1.831
1.832
1.833
H2SO4 content
weight%
80.70
81.16
81.62
82.09
82.57
83.06
83.57
84.08
84.61
85.16
85.74
86.35
86.99
87.69
88.43
89.23
90.12
91.11
91.33
91.56
91.78
92.00
92.25
92.51
92.77
93.03
93.33
93.64
93.94
94.32
94.72
mol/l
14.28
14.40
14.52
14.65
14.78
14.90
15.04
15.17
15.31
15.46
15.61
15.76
15.92
16.09
16.27
16.47
16.68
16.91
16.96
17.01
17.06
17.11
17.17
17.22
17.28
17.34
17.40
17.47
17.54
17.62
17.70
Solutions - aqueous systems
Density
d 20°
4°
1.490
1.495
1.500
1.505
1.510
1.515
1.520
1.525
1.530
1.535
1.540
1.545
1.550
1.555
1.560
1.565
1.570
1.575
1.580
1.585
1.590
1.595
1.600
1.605
1.610
1.615
1.620
1.625
1.630
1.635
1.640
1.645
1.650
1.655
1.660
1.665
1.670
1.675
1.680
1.685
1.690
1.695
1.700
1.705
1.710
1.715
1.720
1.725
1.730
59
Hydrochloric acid
HCl , M = 36.47 g/mol
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4 , M = 97.99 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.0038
1.0092
1.0146
1.0200
1.0255
1.0309
1.0365
1.0420
1.0476
1.0532
1.0590
1.0647
1.0705
1.0764
1.0824
1.0884
1.0946
1.1008
1.1071
1.1134
1.1199
1.1263
1.1329
1.1395
1.1462
1.1529
1.1597
1.1665
1.1735
1.1805
1.216
1.254
1.293
1.335
1.379
1.426
1.476
1.526
1.579
1.633
1.689
1.746
1.770
1.794
1.819
1.844
1.870
60
H3PO4 content
weight%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
92
94
96
98
100
mol/l
0.102
0.206
0.312
0.416
0.523
0.631
0.740
0.851
0.962
1.074
1.189
1.304
1.420
1.538
1.657
1.777
1.899
2.021
2.147
2.272
2.400
2.529
2.659
2.791
2.924
3.059
3.195
3.333
3.473
3.614
4.333
5.118
5.938
6.811
7.740
8.731
9.784
10.90
12.08
13.33
14.65
16.03
16.61
17.20
17.82
18.44
19.08
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.198
HCl content
weight%
0.3600
1.360
2.364
3.374
4.388
5.408
6.433
7.464
8.490
9.510
10.52
11.52
12.51
13.50
14.495
15.485
16.47
17.45
18.43
19.41
20.39
21.36
22.33
23.29
24.25
25.22
26.20
27.18
28.18
29.17
30.14
31.14
32.14
33.16
34.18
35.20
36.23
37.27
38.32
39.37
40.00
mol/l
0.09872
0.3748
0.6547
0.9391
1.227
1.520
1.817
2.118
2.421
2.725
3.029
3.333
3.638
3.944
4.253
4.565
4.878
5.192
5.5095
5.829
6.150
6.472
6.796
7.122
7.449
7.782
8.118
8.459
8.809
9.159
9.505
9.863
10.225
10.595
10.97
11.34
11.73
12.11
12.50
12.90
13.14
Acids for analysis EMSURE®
Solutions - aqueous systems
Merck’s acids for analysis EMSURE®
are delivered to you with the
highest possible quality standard
and with the greatest safety.
Our products underlie strict quality
checks in ultra-modern laboratories
using the latest and most sensitive
analytic instruments.
Take advantage of our outstanding,
application-oriented quality and
of reliable and reproducible results
of your analysis.
61
Nitric acid
HNO3 , M = 63.02 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.200
1.205
1.210
1.215
1.220
1.225
1.230
1.235
1.240
1.245
1.250
1.255
62
HNO3 content
weight%
0.3333
1.255
2.164
3.073
3.982
4.883
5.784
6.661
7.530
8.398
9.259
10.12
10.97
11.81
12.65
13.48
14.31
15.13
15.95
16.76
17.58
18.39
19.19
20.00
20.79
21.59
22.38
23.16
23.94
24.71
25.48
26.24
27.00
27.76
28.51
29.25
30.00
30.74
31.47
32.21
32.94
33.68
34.41
35.16
35.93
36.70
37.48
38.25
39.02
39.80
40.58
41.36
mol/l
0.05231
0.2001
0.3468
0.4950
0.6445
0.7943
0.9454
1.094
1.243
1.393
1.543
1.694
1.845
1.997
2.148
2.301
2.453
2.605
2.759
2.913
3.068
3.224
3.381
3.539
3.696
3.854
4.012
4.171
4.330
4.489
4.649
4.810
4.970
5.132
5.293
5.455
5.618
5.780
5.943
6.107
6.273
6.440
6.607
6.778
6.956
7.135
7.315
7.497
7.679
7.863
8.049
8.237
Density
d 20°
4°
1.260
1.265
1.270
1.275
1.280
1.285
1.290
1.295
1.300
1.305
1.310
1.315
1.320
1.325
1.330
1.335
1.340
1.345
1.350
1.355
1.360
1.365
1.370
1.375
1.380
1.385
1.390
1.395
1.400
1.405
1.410
1.415
1.420
1.425
1.430
1.435
1.440
1.445
1.450
1.455
1.460
1.465
1.470
1.475
1.480
1.485
1.490
1.495
1.500
1.501
1.502
1.503
HNO3 content
weight%
42.14
42.92
43.70
44.48
45.27
46.06
46.85
47.63
48.42
49.21
50.00
50.85
51.71
52.56
53.41
54.27
55.13
56.04
56.95
57.87
58.78
59.69
60.67
61.69
62.70
63.72
64.74
65.84
66.97
68.10
69.23
70.39
71.63
72.86
74.09
75.35
76.71
78.07
79.43
80.88
82.39
83.91
85.50
87.29
89.07
91.13
93.49
95.46
96.73
96.98
97.23
97.49
mol/l
8.426
8.616
8.808
9.001
9.195
9.394
9.590
9.789
9.990
10.19
10.39
10.61
10.83
11.05
11.27
11.49
11.72
11.96
12.20
12.44
12.68
12.93
13.19
13.46
13.73
14.01
14.29
14.57
14.88
15.18
15.49
15.81
16.14
16.47
16.81
17.16
17.53
17.90
18.28
18.68
19.09
19.51
19.95
20.43
20.92
21.48
22.11
22.65
23.02
23.10
23.18
23.25
Sodium hydroxide solution
NaOH , M = 40.01 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.504
1.505
1.506
1.507
1.508
1.509
1.510
1.511
1.512
1.513
HNO3 content
weight%
97.74
97.99
98.25
98.50
98.76
99.01
99.26
99.52
99.77
100.0
mol/l
23.33
23.40
23.48
23.56
23.63
23.71
23.79
23.86
23.94
24.01
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.200
1.205
H2SO4 content
weight%
0.159
0.602
1.0455
1.49
1.94
2.39
2.84
3.29
3.745
4.20
4.655
5.11
5.56
6.02
6.47
6.93
7.38
7.83
8.28
8.74
9.19
9.64
10.10
10.55
11.01
11.46
11.92
12.37
12.83
13.28
13.73
14.18
14.64
15.09
15.54
15.99
16.44
16.89
17.34
17.80
18.25
18.71
mol/l
0.0398
0.151
0.264
0.378
0.494
0.611
0.731
0.851
0.971
1.097
1.222
1.347
1.474
1.602
1.731
1.862
1.992
2.123
2.257
2.391
2.527
2.664
2.802
2.942
3.082
3.224
3.367
3.510
3.655
3.801
3.947
4.095
4.244
4.395
4.545
4.697
4.850
5.004
5.160
5.317
5.476
5.636
Solutions - aqueous systems
Nitric acid
HNO3 , M = 63.02 g/mol
Acids in Safebreak bottles
Acids in glass bottles have hazard potential:
glass can break!
63
Sodium hydroxide solution
NaOH , M = 40.01 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.210
1.215
1.220
1.225
1.230
1.235
1.240
1.245
1.250
1.255
1.260
1.265
1.270
1.275
1.280
1.285
1.290
1.295
1.300
1.305
1.310
1.315
1.320
1.325
1.330
1.335
1.340
1.345
1.350
1.355
1.360
1.365
64
NaOH content
weight%
19.16
19.62
20.07
20.53
20.98
21.44
21.90
22.36
22.82
23.275
23.73
24.19
24.645
25.10
25.56
26.02
26.48
26.94
27.41
27.87
28.33
28.80
29.26
29.73
30.20
30.67
31.14
31.62
32.10
32.58
33.06
33.54
mol/l
5.796
5.958
6.122
6.286
6.451
6.619
6.788
6.958
7.129
7.302
7.475
7.650
7.824
8.000
8.178
8.357
8.539
8.722
8.906
9.092
9.278
9.466
9.656
9.875
10.04
10.23
10.43
10.63
10.83
11.03
11.24
11.45
Density
d 20°
4°
1.370
1.375
1.380
1.385
1.390
1.395
1.400
1.405
1.410
1.415
1.420
1.425
1.430
1.435
1.440
1.445
1.450
1.455
1.460
1.465
1.470
1.475
1.480
1.485
1.490
1.495
1.500
1.505
1.510
1.515
1.520
1.525
1.530
NaOH content
weight%
34.03
34.52
35.01
35.505
36.00
36.495
36.99
37.49
37.99
38.49
38.99
39.495
40.00
40.515
41.03
41.55
42.07
42.59
43.12
43.64
44.17
44.695
45.22
45.75
46.27
46.80
47.33
47.85
48.38
48.905
49.44
49.97
50.50
mol/l
11.65
11.86
12.08
12.29
12.51
12.73
12.95
13.17
13.39
13.61
13.84
14.07
14.30
14.53
14.77
15.01
15.25
15.49
15.74
15.98
16.23
16.48
16.73
16.98
17.23
17.49
17.75
18.00
18.26
18.52
18.78
19.05
19.31
Potassium hydroxide solution
KOH , M = 56.11 g/mol
KOH content
weight%
0.197
0.743
1.295
1.84
2.38
2.93
3.48
4.03
4.58
5.12
5.66
6.20
6.74
7.28
7.82
8.36
8.89
9.43
9.96
10.49
11.03
11.56
12.08
12.61
13.14
13.66
14.19
14.705
15.22
15.74
16.26
16.78
mol/l
0.0351
0.133
0.233
0.333
0.4355
0.536
0.6395
0.774
0.848
0.954
1.06
1.17
1.27
1.38
1.49
1.60
1.71
1.82
1.94
2.05
2.16
2.28
2.39
2.51
2.62
2.74
2.86
2.975
3.09
3.21
3.33
3.45
Density
d 20°
4°
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.200
1.205
1.210
1.215
1.220
1.225
1.230
1.235
1.240
1.245
1.250
1.255
1.260
1.265
1.270
1.275
1.280
1.285
1.290
1.295
1.300
1.305
1.310
1.315
KOH content
weight%
17.29
17.81
18.32
18.84
19.35
19.86
20.37
20.88
21.38
21.88
22.38
22.88
23.38
23.87
24.37
24.86
25.36
25.85
26.34
26.83
27.32
27.80
28.29
28.77
29.25
29.73
30.21
30.68
31.15
31.62
32.09
32.56
mol/l
3.58
3.70
3.82
3.945
4.07
4.195
4.32
4.45
4.57
4.70
4.83
4.955
5.08
5.21
5.34
5.47
5.60
5.74
5.87
6.00
6.135
6.27
6.40
6.54
6.67
6.81
6.95
7.08
7.22
7.36
7.49
7.63
Solutions - aqueous systems
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
65
Potassium hydroxide solution
KOH , M = 56.11 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
1.000
1.005
1.010
1.015
1.020
1.025
1.030
1.035
1.040
1.045
1.050
1.055
1.060
1.065
1.070
1.075
1.080
1.085
1.090
1.095
1.100
1.105
1.110
1.115
1.120
1.125
1.130
66
KOH content
weight%
0.197
0.743
1.295
1.84
2.38
2.93
3.48
4.03
4.58
5.12
5.66
6.20
6.74
7.28
7.82
8.36
8.89
9.43
9.96
10.49
11.03
11.56
12.08
12.61
13.14
13.66
14.19
mol/l
0.0351
0.133
0.233
0.333
0.4355
0.536
0.6395
0.774
0.848
0.954
1.06
1.17
1.27
1.38
1.49
1.60
1.71
1.82
1.94
2.05
2.16
2.28
2.39
2.51
2.62
2.74
2.86
Density
d 20°
4°
1.135
1.140
1.145
1.150
1.155
1.160
1.165
1.170
1.175
1.180
1.185
1.190
1.195
1.200
1.205
1.210
1.215
1.220
1.225
1.230
1.235
1.240
1.245
1.250
1.255
1.260
1.265
KOH content
weight%
14.705
15.22
15.74
16.26
16.78
17.29
17.81
18.32
18.84
19.35
19.86
20.37
20.88
21.38
21.88
22.38
22.88
23.38
23.87
24.37
24.86
25.36
25.85
26.34
26.83
27.32
27.80
mol/l
2.975
3.09
3.21
3.33
3.45
3.58
3.70
3.82
3.945
4.07
4.195
4.32
4.45
4.57
4.70
4.83
4.955
5.08
5.21
5.34
5.47
5.60
5.74
5.87
6.00
6.135
6.27
Potassium hydroxide solution
KOH , M = 56.11 g/mol
KOH content
weight%
28.29
28.77
29.25
29.73
30.21
30.68
31.15
31.62
32.09
32.56
33.03
33.50
33.97
34.43
34.90
35.36
35.82
36.28
36.735
37.19
37.65
38.105
38.56
39.01
39.46
39.92
40.37
mol/l
6.40
6.54
6.67
6.81
6.95
7.08
7.22
7.36
7.49
7.63
7.77
7.91
8.05
8.19
8.335
8.48
8.62
8.76
8.905
9.05
9.19
9.34
9.48
9.63
9.78
9.93
10.07
Density
d 20°
4°
1.405
1.410
1.415
1.420
1.425
1.430
1.435
1.440
1.445
1.450
1.455
1.460
1.465
1.470
1.475
1.480
1.485
1.490
1.495
1.500
1.505
1.510
1.515
1.520
1.525
1.530
KOH content
weight%
40.82
41.26
41.71
42.155
42.60
43.04
43.48
43.92
44.36
44.79
45.23
45.66
46.095
46.53
46.96
47.39
47.82
48.25
48.675
49.10
49.53
49.95
50.38
50.80
51.22
51.64
mol/l
10.22
10.37
10.52
10.67
10.82
10.97
11.12
11.28
11.42
11.58
11.73
11.88
12.04
12.19
12.35
12.50
12.66
12.82
12.97
13.13
13.29
13.45
13.60
13.76
13.92
14.08
Solutions - aqueous systems
Density
d 20°
4°
1.270
1.275
1.280
1.285
1.290
1.295
1.300
1.305
1.310
1.315
1.320
1.325
1.330
1.335
1.340
1.345
1.350
1.355
1.360
1.365
1.370
1.375
1.380
1.385
1.390
1.395
1.400
67
Ammonia
NH3 , M = 17.03 g/mol
Density
d 20°
4°
0.998
0.996
0.994
0.992
0.990
0.988
0.986
0.984
0.982
0.980
0.978
0.976
0.974
0.972
0.970
0.968
0.966
0.964
0.962
0.960
0.958
0.956
0.954
0.952
0.950
0.948
0.946
0.944
0.942
0.940
0.938
0.936
0.934
68
NH3 content
weight%
0.0465
0.512
0.977
1.43
1.89
2.35
2.82
3.30
3.78
4.27
4.76
5.25
5.75
6.25
6.75
7.26
7.77
8.29
8.82
9.34
9.87
10.405
10.95
11.49
12.03
12.58
13.14
13.71
14.29
14.88
15.47
16.06
16.65
mol/l
0.0273
0.299
0.570
0.834
1.10
1.365
1.635
1.91
2.18
2.46
2.73
3.01
3.29
3.57
3.84
4.12
4.41
4.69
4.98
5.27
5.55
5.84
6.13
6.42
6.71
7.00
7.29
7.60
7.91
8.21
8.52
8.83
9.13
Density
d 20°
4°
0.932
0.930
0.928
0.926
0.924
0.922
0.920
0.918
0.916
0.914
0.912
0.910
0.908
0.906
0.904
0.902
0.900
0.898
0.896
0.894
0.892
0.890
0.888
0.886
0.884
0.882
0.880
NH3 content
weight%
17.24
17.85
18.45
19.06
19.67
20.27
20.88
21.50
22.125
22.75
23.39
24.03
24.68
25.33
26.00
26.67
27.33
28.00
28.67
29.33
30.00
30.685
31.37
32.09
32.84
33.595
34.35
mol/l
9.44
9.75
10.06
10.37
10.67
10.97
11.28
11.59
11.90
12.21
12.52
12.84
13.16
13.48
13.80
14.12
14.44
14.76
15.08
15.40
15.71
16.04
16.36
16.69
17.05
17.40
17.75
Commercially available concentrations
of some acids and alkalis
weight%
Acetic acid
Acetic acid (glacial acetic acid)
Acetic acid, dilute
Ammonia solution
Ammonia solution
Ammonia solution
Formic acid
Hydriodic acid
Hydrobromic acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, concentration (1.16)
Hydrochloric acid, concentration (1.18)
Hydrochloric acid, fuming
Hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid
Nitric acid, concentration
Nitric acid, fuming
Perchloric acid
Perchloric acid
Phosphoric acid, concentration (1.71)
Phosphoric acid, concentration (1.75)
Potassium hydroxide solution
Potassium hydroxide solution
Sodium hydroxide solution
Sulfuric acid, concentration
Sulfuric acid, dilute
96
99 – 100
30
35
30
25
98 – 100
57
40
25
32
36
37
48
40
65
100
70
60
85
89
47
30
33
95 – 97
25
Density
d 20°
4°
1.06
1.06
1.04
0.88
0.88
0.91
1.22
1.7
1.38
1.12
1.16
1.18
1.19
1.16
1.13
1.40
1.52
1.67
1.53
1.71
1.75
1.5
1.3
1.36
1.84
1.18
Density
(mol/l*)
17
18
5
18
15.5
13.5
26
7.5
7
8
10
12
12.5
28
23
14
21
12
9
15
16
12.5
7
11
18
3
Solutions - aqueous systems
Name
*rounded off
Baumé degrees (°Bé) and density
°Bé = 145 - 145
density
Example
Sodium hydroxide solution 40 % with a density of 1.430 g/cm3
145 - 145 = 43.60 °Bé
density
69
Indicators and buffers
pH indicators
Buffer solutions
72
76
pH-indicators
0
Malachite green oxalate
1
2
3
green
green-blue
Brilliant green
yellow
green
Eosin Y
yellow
Erythrosin B
orange
Methyl green
yellow
Methyl violet
yellow
Cresol red
green flourescence
red
blue
violet
yellow
red
Crystal violet
4
yellow
blue-violet
Cresol purple
red
yellow
Thymol blue
red
yellow
2,2',2'',4,4' Pentamethoxytriphenylcarbinol
red
colorless
Eosin B
colorless
Quinaldine red
colorless
2.4-Dinitrophenol
4-(Dimethylamino) azobenzenel
pink flourescence
pink
colorless
red
yellow
Bromochlorophenol blue
yellow
bl
Bromophenol blue
yellow
bl
green yellow
bl
Bromphenol blue sodium salt
Congo red
blue
Methyl orange
red
Methyl orange solution
red
Bromocresol green
Bromocresol green sodium salt
2.5-Dinitrophenol
Mixed indicator 4.5 acc. to Mortimer
Alizarin sulfonic acid sodium salt
Methyl red
Methyl red sodium salt
yello
yello
yellow
yellow
colorless
red
yellow
red
red
Mixed indicator 5
red-viole
Chlorophenol red
yell
Bromocresol purpley
Bromophenol red
The pH ranges and color shades shown are approximations
For more information please visit www.merck-chemicals.com/labtools
than choose “pH-Indicator Selector”
72
yello
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
blue
orange
13
14 pH
colorless
purple
purple
yellow
blue
Indicators and buffers
yellow
yellow
w-orange
lue-violet
lue-violet
lue-violet
yellow-orange
ow-orange
ow-orange
blue
blue
yellow
blue
violett
yellow-orange
d
yellow-orange
d
et
green
low
yellow
ow-orange
purple
purple
purple
73
pH-indicators
0
1
2
3
4
4-Nitrophenol
col
Bromoxylenol blue
Alizarin
Bromothymol blue sodium salt
Bromothymol blue
Phenol red
Phenol red sodium salt
3-Nitrophenol
Neutral red
1-Naphtholphthalein
Phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein solution (1% in ethanol)
Phenolphthalein solution (0.375 % in methanol)
Thymolphthalein
Alkali blue
Alizarin yellow GG
Indigo carmine
Epsilon blue
Titan yellow
The pH ranges and color shades shown are approximations
74
The broad pH test range offers
you an optimal solution for
each application area. You can
easily and quickly measure
the pH without using instruments.
5
6
7
8
lorless
9
10
11
12
13
14 pH
yellow
yellow
blue
red
yellow
red
purple
blue
yellow
blue
yellow
violet-red
yellow
violet-red
colorless
yellow-orange
yellow-orange
blue-red
brown
blue-green
colorless
red-violet
colorless
red-violet
red-violet
colorless
colorless
blue
violet
pink
light yellow
brownish-yellow
blue
orange
yellow
yellow
violet
red
75
Indicators and buffers
yellow
Buffer solutions
Prepare stock and buffer solutions with distilled, boiled, CO2-free water.
Buffersolution
No.
1
2
3
4
Stock solutions and their content of buffer substance
A
Glycine 0.1 mol/l + NaCI 0.1 mol/l
[Glycine: 7.507 g/l + NaCI: 5.844 g/l]
di-Sodium citrate 0.1 mol/l
[Citric acid monohydrate:
21.014 g/l + 200 ml NaOH 1 mol/l]
Potassium hydrogen phthalate l
0.1 mol/[C8H5KO4: 20.42 g/l
As No. 3
HCI 0.1 mol/l
HCI 0.1 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
50 ml A + x ml B
make up to 100 ml*
50 ml A + x ml B,
5
As No. 2
NaOH 0.1 mol/l
make up to 100 ml*
NaOH 0.1 mol/l
6
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
1/15 mol/l [KH2PO4: 9.073 g/l]
[Na2HPO4 · 2 H2O: 11.87 g/l]
di-Sodium hydrogen
phosphate 1/15
mol/l
7
5.5-Diethylbarbituric acid
sodium salt 0.1 mol/l
[Barbital-Na: 20.62 g/l]
HCI 0.1 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
8
Borax solution 0.05 mol/l
[H3BO3:
12.37 g/l + 100 ml NaOH 1 mol/l]
HCI 0.1 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
9
As No. 1
NaOH 0.1 mol/l
10
Citric acid 0.1 mol/l
[Citric acid monohydrate: 21.014 g/l]
[Na2HPO4 · 2 H2O: 35.60 g/l]
di-Sodium hydrogen
phosphate 0.2 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
11
Sodium acetate 0.1 mol/l
[C2H3O2Na: 8.204 g/l or
C2H3O2Na · 3 H2O: 13.61 g/l]
Acetic acid 0.1 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
12
Imidazole 0.2 mol/l
[C3H4N2: 13.62 g/l]
Triethanolamine 0.5 mol/l +
Titriplex® III
[C6H15NO3: 74.60 g/l +
Titriplex® III: 20 g/l]
HCI 0.1 mol/l
25 ml A + x ml B,
make up to 100 ml*
10 ml A + x ml B,
make up to 100 ml*
13
14
15
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
0.2 mol/l [TRIS: 24.23 g/l]
Sodium carbonate 0.1 mol/l (10.60 g/l)
[Na2CO3: 10.60 g/l]
[NaHCO3: 8.401 g/l]
*fill up with dissolution
76
B
HCI 0.1 mol/l
Composition
of buffer
solution
HCI 0.05 mol/l
HCI 0.1 mol/l
Sodium hydrogen
carbonate 0.1 mol/l
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
25 ml A + x ml B,
make up to 100 ml*
x parts A +
(100-x) parts B
Indicators and buffers
CertiPUR-Buffer Sachets for
calibration of pH instruments!
77
pKa values of selected
biological buffers
Buffer
ACES
pKa (4°C)
7.22
pKa (20°C)
pKa (25°C)
pKa (37°C)
△pKa/°C
6.90
6.80
6.56
-0.020
ADA
6.80
6.62
6.56
6.43
-0.011
BES
7.41
7.15
7.07
6.88
-0.016
BICIN
8.64
8.35
8.26
8.04
-0.018
BIS-TRIS
6.88
6.56
6.46
6.22
-0.020
-0.011
CHES
9.73
9.55
9.50
9.36
Citrat pKa2
4.79
4.77
4.76
4.74
-0.0016
Glycin pKa2
10.32
9.91
9.78
9.47
-0.026
Gly-Gly
8.85
8.40
8.26
7.92
-0.028
HEPES
7.77
7.55
7.48
7.32
-0.014
HEPPS
8.18
8.00
7.95
7.82
-0.011
Imidazole
7.37
7.05
6.95
6.71
-0.020
MES
6.33
6.15
6.10
5.97
-0.011
MOPS
7.41
7.20
7.14
6.98
-0.013
-0.0085
PIPES
6.94
6.80
6.76
6.66
Phosphate pKa2
7.26
7.21
7.20
7.17
-0.0028
TAPS
8.02
8.31
8.40
8.62
+0.018
TES
7.82
7.50
7.40
7.16
-0.020
TRICIN
8.49
8.15
8.05
7.79
-0.021
TRIS
8.75
8.30
8.08
7.82
-0.028
78
Buffer ranges
Buffer
Glycine/HCI
Citric acid / Na-citrate
Acetic acid / Na-acetate
KH2PO4 / Na2HPO4
MES
BIS-TRIS
ADA
ACES
PIPES
Imidazole / HCL
Indicators and buffers
BES
MOPS
HEPES
TES
TRIS/HCI
HEPPS
TRICIN
Gly-Gly
BICIN
Na-borate / HCI
Glycine / NaOH
CHES
AMP / HCL
Na2CO3 / NaHCO3
Na-borate / NaOH
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
79
Chromatography
Analytical HPLC
Thin-layer Chromatography
Specification of column sorbents
LC Troubleshooting
Sample preparation
82
84
86
90
95
Chromatography
Analytical HPLC
Analytical HPLC has taken on a position of central importance in research
and development, in pharmaceutical quality control and in environmental analysis.
Merck is among the major suppliers of HPLC products worldwide.
Our extensive portfolio comprises products for analytical and preparative HPLC. With
our series of very widely used HPLC sorbents, which includes LiChrosorb®, LiChrospher®, Superspher®, Purospher® and ZIC-HILIC, we offer you the most
suitable products for your application. With Chromolith® – an HPLC column based on
monolithic technology – we have established and maintained technology leadership
in chromatography to ideally fulfill your requirements.
Chromolith® HPLC columns provide excellent separations in a fraction of the
time that a standard particulate column will take - typically four
times faster, because they are made from highly porous monolithic rods of silica
with a bimodal pore structure. The column is no longer packed
with small particles but instead consists of a single piece of high-purity silica
gel. Longer lifetime and lower matrix sensitivity with biological samples are
additional advantages of Chromolith® columns. Multiple Chromolith® columns
coupled together provide separation efficiencies of 100,000 plates/column at
normal pressure.
82
P urospher® HPLC columns are based upon a high-purity silica for excellent
separations with very good peak symmetry. The base material for Purospher®
high-purity HPLC columns consists of tetra-alkoxysilane.
Due to the absence of heavy metals in the silica matrix and in combination
with a complete coverage of the silica surface, this stationary phase enables
tailing-free chromatography of acidic, basic and chelating compounds. This
is of particular advantage for method development.
Chromatography
L iChrospher® is a reliable and versatile traditionally produced spherical silica
carrier with a particle size of 5 µm or 10 µm, providing well balanced
pressure / separation performance ratio. A broad range of modi-fications on
LiChrospher® are very widely used by HPLC-users all over the world for
a broad range of applications. LiChrospher® sorbents are available as reversed
phase derivatives (RP-8, RP-18 endcapped, RP-18, RP-18 endcapped
and RP-select B), medium polar (NH2, CN, DIOL) and polar derivatives (Si 60).
Furthermore LiChrospher® PAH is highly efficient and selective for the
separation of PAH; LiChrospher® WP is very well suited for the separation of
peptides and low molecular weight proteins.
IC
RPLC
Fig.1
Schematic illustration demonstrating
how ZIC®-HILIC complements other
areas of chromatography and extends
the separation capabilities.
ZIC ®-HILIC
NPLC
ZIC®-HILIC HPLC columns are suitable for separation of strongly polar and
hydrophilic compounds, which often have little or no retention on
reversed phase columns. Merck´s unique ZIC®-HILIC technology is based on
a stationary phase with a covalently bonded, highly polar zwitterionic
functional group that provides higher stability and more robust HILIC separations than conventional silica or amino phases.
83
Thin Layer Chromatography
Thin Layer Chromatography is a simple, fast and
highly versatile separation tool for both
qualitative and quantitative analysis. The field
of application covers virtually all classes of
substances including pesticides, steroids, alkaloids,
lipids, nucleotides, glycosides, carbohydrates, fatty
acids and many others.
Cheap separation method without the need for sophisticated instruments
No cumbersome sample preparation step needed because plates are
disposable
Sample components are stored on the plate allowing to repeat the analysis
several times
Multiple samples (up to 72) can be run simultaneously under identical
conditions
Easy 2 dimensional separation by using two distinct mobile phases in
different directions
Thin Layer Chromatography can be a manual method as in classical TLC,
or automated as in instrumented high-performance thin layer chromatography
(HPTLC). Furthermore, it can be easily extended to preparative scale for PLC.
Unmodified silica gel covers more than 80% of thin layer chromatography
applications for both adsorption- and partition thin layer chromatography. It
allows separating a large range of different substances such as aflatoxins,
alkaloids, anabolics, benzodiazepins, carbohydrates, fatty acids, glycosides, lipids,
mycotoxins, nucleotides, peptides, pesticides, steroids, sulfonamids, surfactants,
tetracyclines and many others making it suitable for:
In-process control in drugs
Purity checks of synthesis steps
Identity testing of pharmaceutical compounds
HPTLC Premium Purity plate is designed for high performance,
completely contamination free separations especially in demanding
pharmacopoeia applications.
Highly pure, exhibiting minimal background even with middle-polar
solvent systems
Identical separation performance as the related HPTLC plate product
Especially suited for pharmacopoeia applications
84
Bild wird in besserer
Auflösung benötigt!
Chromatography
Fig.XX
Guercin exer si. To dolor suscil euis ad dolobore
veliquat, commodignis amet nit ex eugait
em vent incidui blan henim vulputat irillummy
nim elit eu feugue dignibt.
Fig.3
Comparison of the separation of dansyl
amino acids on a
(A) classical TLC silica gel 60 plate or
(B) HPTLC silica gel 60 plate under
identical conditions. The comparison
clearly demonstrates that the HPTLC
plate delivers sharper zones with
shorter migration distances and hence
running times. In addition the HPTLC
plate allows the separation of twice
the number of samples simultaneously.
Compounds:
1. N-alpha-dansyl-L-arginine
2. alpha-dansyl-L-arginine
3. Dansyl-L-cysteic acid
4. N-Dansyl-glycine
5. Dansyl-glycine
6. N-N-Didansyl-L-tyrosine
Sample volume:
TLC 4 µl; HPTLC 0,3 µl
Mobil phase:Ethyl acetat/methanol/
propionic acid (22/10/3)
Migration distance: TLC 10 cm; HPTLC 5 cm
Analysis time:TLC 42 min;
HPTLC 13 min 45 sec
Detection:
UV 366
85
Specifications of column sorbents
Polar stationary phases (normal phase chromatography)
(shipping eluent: n-Heptane/Dioxane (99/1))
Designation
Sorbent Characteristics
Particle
Size
LiChrosorb® Si 60
irregular particles of silica
5, 7, 10 μm
LiChrosorb® Si 100
irregular particles of silica
5, 7, 10 μm
LiChrospher® Si 60
spherical particles of silica
5, 10 μm
LiChrospher® Si 100
spherical particles of silica
5, 10 μm
LiChrospher® Si 300
spherical particles of silica
10 μm
LiChrospher® Si 1000
spherical particles of silica
10 μm
LiChrospher® Si 4000
spherical particles of silica
10 μm
Aluspher® AL
spherical particles of aluminia oxide
5 μm
Superspher® Si 60
spherical particles of silica
4 μm
Purospher® STAR Si
spherical particles of high purity silica
5 μm
Chromolith® Si
Monolithic high purity silica
2 μm
Specifications of column sorbents
Mediaum solar stationary phases
(shipping eluent: n-Heptane/Dioxane (99/1))
Designation
Sorbent Characteristics
LiChrosorb® CN
irregular particles of silica
with γ-Cyanopropyl function
irregular particles of silica
with γ-Aminopropyl function
spherical particles of silica
with DIOL function on carbonchains
spherical particles of silica
with γ-Cyanopropyl function
spherical particles of silica
with γ-Aminopropyl function
spherical particles of silica
with DIOL function on carbonchains
spherical particles of high purity silica
with γ-Aminopropyl function
LiChrosorb® NH2
LiChrosorb® DIOL
LiChrospher® CN
LiChrospher® NH2
LiChrospher® DIOL
Purospher® STAR NH2
86
Particle
Size
5, 7, 10 μm
5, 7, 10 μm
5, 7, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5 μm
Pore
volume
Spec. surface area
60 Å
0.75 ml/g
500 m2/g
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m /g
60 Å
0.85 ml/g
700 m2/g
400 m /g
Efficiency
55 000 N/m
15 000 N/m
2
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
300 Å
0.78 ml/g
60 m2/g
1000 Å
0.78 ml/g
30 m2/g
15 000 N/m
4000 Å
0.78 ml/g
10 m2/g
15 000 N/m
100 Å
60 Å
120
130
2
Chromatography
Pore
Size
170 m2/g
0.85 ml/g
700 m2/g
100 000 N/m
1.1
330
50 000
1 ml/g
300
Pore
Size
Pore
volume
Spec.
surface
%C
Surface
coverage
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m2/g
6.1 %
3.82 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m2/g
3.5 %
3.54 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m2/g
7.1 %
3.91 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
6.6 %
3.52 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
4.6 %
41 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
8.0 %
3.87 μmol/m2
120
1.1
330
3.5
3
Efficiency
40 000 N/m
15 000 N/m
25 000 N/m
10 000 N/m
40 000 N/m
15 000 N/m
40 000 N/m
15 000 N/m
25 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
50 000
87
Specifications of column sorbents
Non-polar stationary phases (reversed phase chromatography)
(shipping eluent: acetronitrile/water)
Designation
Sorbent Characteristics
Particle
Size
LiChrosorb® RP-8
irregular particles of silica with
octyl derivative
irregular particles of silica with
octyl derivative
irregular particles of silica with
octyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative endcapped
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative endcapped
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative endcapped
spherical particles of silica with
octyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of silica with
octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of high purity silica
with octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of high purity silica
with octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of high purity silica
with octyl derivative
spherical particles of high purity silica
with octadecyl derivative
spherical particles of high purity silica
with octadecyl derivative
Monolithic high purity silica with
octyl derivative
Monolithic high purity silica with
octadecyl derivative
5, 7, 10 μm
LiChrosorb® RP-select B
LiChrosorb® RP-18
LiChrospher® RP-8
LiChrospher® RP-8 endcapped
LiChrospher® RP-select B
LiChrospher® RP-18
LiChrospher® RP-18 endcapped
LiChrospher® WP 300 RP-18
LiChrospher® PAH
Superspher® RP-8
Superspher® RP-8 endcapped
Superspher® RP-select B
Superspher® RP-18
Superspher® RP-18 endcapped
Purospher® RP-18
Purospher® RP-18 endcapped
Purospher® STAR RP-8 endcapped
Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped
Purospher® HC
Chromolith® RP-8 endcapped
Chromolith® Rp-18 endcapped
88
5, 7, 10 μm
5, 7, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 10 μm
5, 12, 15 μm
5 μm
4 μm
4 μm
4 μm
4 μm
4 μm
5 μm
5 μm
3,5 μm
3,5 μm
5 μm
2 μm
2 μm
Pore
volume
Spec.
surface
%C
Surface
coverage
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m2/g
9.5 %
3.4 μmol/m2
Efficiency
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
55 000 N/m
20 000 N/m
n.a.
60 Å
0.75 ml/g
300 m /g
11.4 %
4.21 μmol/m
100 Å
1.0 ml/g
300 m2/g
16.2 %
3.0 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
12.5 %
4.04 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m /g
13.0 %
4.44 μmol/m2
60 Å
0.9 ml/g
360 m2/g
11.5 %
3.55 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m /g
21.0 %
3.61 μmol/m2
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
21.6 %
4.09 μmol/m2
300 Å
1.0
80 m /g
n.a.
n.a.
150 Å
n.a.
200 m2/g
20 %
4.04 μmol/m2
80 000 N/m
2
2
2
2
2
2
60 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m /g
12.5 %
4.44 μmol/m
100 000 N/m
60 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
13.0 %
3.55 μmol/m2
100 000 N/m
2
2
60 Å
0.9 ml/g
360 m /g
11.5 %
3.61 μmol/m
100 000 N/m
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
21.0 %
4.09 μmol/m2
100 000 N/m
100 Å
1.25 ml/g
350 m2/g
21.6 %
100 000 N/m
90 Å
1.05 ml/g
480 m /g
17.0 %
80 000 N/m
90 Å
1.05 ml/g
480 m2/g
18.0 %
80 000 N/m
120 Å
1.1 ml/g
330 m /g
11.2 %
120 Å
1.1 ml/g
330 m2/g
17.0 %
90 Å
1.05 ml/g
470 m2/g
18.0 %
130
1
300
11.0 %
130
1
300
18.0 %
2
2
2
3 μmol/m2
Chromatography
Pore
Size
130 000 N/m
80 000 N/m
130 000 N/m
80 000 N/m
89
LC Troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
High pressure
Precolumn blocked
Column head blocked
No peaks; changing peakhight
Noise or drift problems
Capillary blocked
No flow; leak
Sample injection is not reproducible
Column is not in equilibrium
Impurities elute slowly from the column
Enrichment of impurities
Differentces in temperature
(column or detector)
Air bubbles
Detector lamp
Electrical interferences
Ghost peaks
Peaks from previous injection
Unknown sample compunds
Column contamination
Peaks with shoulders; Fronting
Solvent impurities
Mixing problems of mobile phase
Oxidation of TFA (peptinde mapping)
Precolumn defective or soiled
Cavity at column head (dead-volume) or
channels in column packing
Sample dissolved in wrong solvents
Interfering compounds; Impurities
Peaks are broad
90
Column overload
Extra column effects
Precolumn or column defective or soiled
Column overload; injection volume too large
Sample dissolved in wrong solvent
Too weak buffer
Extra column effects
Solution
Change precolumn
Change filter of column head; flush column;
change column
Change capillary
Checkpump; check frit; check mobil phase
composition; fix leak
Check sample injection system
Flush column
Flush colum with strong eluent
Flush column; improve sample cleanup;
use HPLC-grade solvents
Use column thermostat
Chromatography
Degas mobile phase; use back-pressure regulator
Replace UV lamp (expected life time: 1000 h)
Use voltage stabilizer; check for local
interference sources
Use longer run-time; flush column with strong
solvent after each run; improve sample cleanup;
use gradient elution
Improve sample cleanup
Flush column with strong solvent after each run;
improve sample cleanup
Use HPLC-grade solvents
Dissolve sample in mobil phase
Prepare fresh daily; use antioxidant
Change precolumn
Change column
Dissolve sample in mobil phase or (if not possible)
inject very small sample volume (1 μl)
Improve sample cleanup; check column with test
mixture; use HPLC-grade solvents
Dilute sample
Check capillary connections
Change precolumn or column
Reduce sample volume; dilute sample
Dissolve sample in mobile phase
Use higher concentration or different buffer
Check capillary connections
91
LC Troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
Peaks are broad
Leak between column and detector;
large detector cell
Too low column temperature; high mobile
phase viscosity
Too low column temperature; high mobile
phase viscosity
Too long capillary connections
Peak tailing
Poor column efficiency
Column overload
Interfering peaks; Impurities
Silanol interactions
Peak doubling or splitting
Blocked column frit
Extra column effects; dead-volume
Column void or channeling
Sample volume too large; column overload
Sample dissolved in wrong solvent
Increasing retention times
Column void or channeling
Blocked column frit
Unswept injector flowpath
Flow rate is decreasing
Active sites on silica packing
Loss of bonded stationary phase
Mobile phase composition changing
Decreasing retention times
Temperature decreasing
Flow rate is increasing
Column overload
Loss of bonded stationary phase
Mobile phase composition changing
Temperature increasing
Column ageing
92
Solution
Fix leak; use smaller cell
Increase column temperature
Increase column temperature
Chromatography
Use shorter capillaries with smaller i.D.;
check for dead volume
Use column with smaller particles
Decrease sample size; increase column diameter;
use higher capacity stationary phase
Improve sample cleanup; adjust mobile phase;
check column with test mixture; use HPLC-grade solvents
Use modifier (triethylamine); increase buffer or salt
concentration (ion-pair-chromatography); lower mobil
phase pH; use base deactivated column
Replace frit; add in-line filter; filter samples
Check capillary connections
Replace column; use less aggressive conditions
Reduce sample volume; dilute sample; inject
sample prepared in mobil phase
Dissolve sample in mobile phase or (if not possible)
inject very small sample volume (1 μl)
Replace column; use less aggressive conditions
Replace frit; add in-line filter; filter samples
Replace injecto rotor
Fix leaks; replace pump seals; remove bubbles;
check for cavitation
Use mobile phase modifier; add triethylamine;
use base-deactivated column
Keep mobile phase pH between 2 and 7.5
Check pump; check frit; avoid evaporation or
degradation of mobile phase
Use column thermostat
Check pump; check flow
Decrease sample size
Keep mobile phase pH between 2 and 7.5
Check pump; check frit; avoid evaporation or
degradation of mobile phase
Use column thermostat
Replace column; use guard column
93
LC Troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
Retention times changing
Flow rate varying
Insufficient column equilibration
Insufficient buffer capacity
Mobile phase composition changing;
poor mixing
Column temperature varying
Contamination build up
Change in column activation
Differences in selectivity
Different in mobile phase composition
Too weak solvent
Sample dissolved in wrong solvent
Decreasing column life; contamination
Temperature varying
Column to column reproducibility
Bildmaterial wird
benötigt!
94
Solution
Fix leaks; replace pump seals; remove bubbles;
check for phase
Equilibrate with at least 10 column volume of
mobile phase
Use buffer concentration >20 mM and <50mM
Check pump; check frit; avoid evaporation or
degradation of mobile phase
Use solumn thermostat
Flush column
Condition column with initial injection of
concentrated of mobile
Check pump; check frit; avoid evaporation or degradation of mobile
Chromatography
Use buffer or ion-pair system
Dissolve sample in mobile phase or (if not possible) inject very small
sample volume (1 μl)
Replace column; improve sample cleanup;
check column with test mixture;
use HPLC-grade solvent
Use column thermostat
Replace column; check with manufacturer
Sample preparation
Routine laboratory work involves purifying, enriching or separating for
subsequent analysis. Solid, liquid and gaseous substances also have
to be purified for pro-duction-scale processes. Various chemical and physical
methods can be used for this purpose: absorption, adsorption, chromatography, distillation, extraction, ion exchange, filtration, complex formation,
crystallization, drying and many more. Merck offers a wide range of
products with absorptive, adsorptive, filtration and clarification properties.
These products can be used for purification but also as reaction and
filtration aids, as fillers, additives or as carriers of active ingredients. In addition
we offer reagents for the preparation of gases, cooling mixtures or
adjusting relative humidity as well as classical laboratory auxiliaries. Products
avail-able for Sample preparation are:
LiChrolut® for solid-phase extraction
Extrelut® NT for liquid-liquid extraction
LiChrospher® ADS for LC-integrated solid-phase extraction
95
Organic solvents
Organic solvents - Properties and drying 98
Ethanol-water mixtures
102
Drying agents
103
Vapour pressure of water
103
LiChrosolv® - Solvents for chromatography
104
Organic solvents
Organic solvents
properties and drying
Solvent
Acetone
Acetic acid
Acetic anhydride
Acetonitrile
Aniline
Anisole
Benzene
1-Butanol
2-Butanol
tert-Butanol
n-Butyl acetate
Carbon disulfide
Carbon tetrachloride
Chlorobenzene
Chloroform
Cyclohexane
Decahydronaphthalene
(Dekalin)
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
Diethyl carbonate
Diethylene
Diethylene
Diethylene glycol
dimethyl ether
Diethyl ether
Diisopropyl ether
Dimethyl formamide
Dimethyl sulfoxide
98
point
[°C]
20°
4°
D
20°
D
n
MAC (2)
Flash
point
[°C]
56
0.791
1.359
– 18
ppm
500
118
136
82
1.049
1.082
0.782
1.372
1.390
1.344
+ 40
+ 49
+6
10
5
40
184
154
80
1.022
0.995
0.879
1.586
1.518
1.501
+ 76
+ 51
– 10
117
100
82
127
46
77
0.810
0.808
0.786
0.882
1.263
1.594
1.399
1.398
1.384
1.394
1.626
1.460
+ 29
+ 24
+ 11
+ 33
– 30
132
62
1.106
1.486
1.525
1.448
non
flammable
+ 29
non
flammable
mg/m3
1200
25
20
69
8
H.A
Drying agent (1)
K2CO3 Molecular sieve
0.3 nm
P2O5; CuSO4
CaCl2
CaCl2; P2O5; K2CO3
Molecular sieve 0.3 nm
KOH; BaO
CaCl2; distillation; Na
distillation
CaCl2; Na; Pb/Na
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
100
100
100
100
H5
H 10
B
310
310
310
480
16
65
K2CO3; distillation
K2CO3; distillation
CaO; freezing
MgSO4
CaCl2; P2O5
Distillation;
CaCl2; P2O5; Pb/Na;
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
10
B.10
47
50
CaCl2; distillation;
CaCl2; P2O5; Pb/Na
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Na; Na/Pb; LiAIH4
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
CaCl2; Na; Pb/Na
81
0.779
1.426
– 17
200
700
189/
191
40
0.886
1.48
< 54
–
–
1.325
1.424
non
flammable
B.100
350
126
255
0.975
0.885
1.384
1.423
+ 25
+ 118
–
–
–
–
188
0.906
1.412
+ 82.5
–
–
155
165
34
0.945
1.407
+ 70
–
–
0.714
1.353
– 40
400
1200
CaCl2; Na; Pb/Na;
LiAIH4
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
68
0.726
1.368
– 23
500
2100
CaCl2; Na
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Distillation
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Distillation
Molecular sieve 0.3 nm
153
0.950
1.430
+ 62
H. 10
30
189
1.101
1.478
+ 95
–
–
Organic solvents
Boiling
CaCl2; Pb/Na
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
K2CO3; Na2SO4
CaCl2; Na
glycoldibutyl ether
CaCl2; Na
glycoldiethyl ether
CaCl2; Na
99
Organic solvents
properties and drying
Solvent
Boiling
point
[°C]
20°
4°
D
20°
n
D
Flash
point
[°C]
MAC (2)
Drying agent (1)
101
1.034
1.422
+ 11.8
ppm
H.B20
mg/m
73
Ethanol
79
0.791
1.361
+ 12
1000
1900
CaO; Mg; MgO.
Molecular sieve 0.3 nm
Ethyl acetate
77
0.901
1.372
–4
400
1500
K2CO3; P2O5; Na2SO4.
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol
monoethyl ether
197
135
1.109
0.930
1.432
1.408
+ 111
+ 41
–
H5
–
20
Distillation; Na2SO4
Distillation
Ethylene glycol
monomethyl
125
0.965
1.402
+ 52
H5
15
Distillation
Ethyl formate
Formamide
Glycerol
Hexafluoroacetone
(sesqui-hydrate)
54
211
290
0.924
1.134
1.260
1.685
1.360
1.447
1.475
– 20
155
+ 176
100
–
300
–
MgSO4; Na2SO4
Na2SO4; CaO
Distillation
1.4-Dioxane
n-Hexane
Isobutanol
Isobutyl
methyl ketone
Methanol
3
CaCl2; Na
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
non
flammable
69
0.659
1.375
– 23
50
180
Na; Pb/Na; LiAIH4.
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
108
117
0.803
0.801
1.396
1.396
+ 28
+ 15.5
100
20
300
83
K2CO3; CaO; Mg; Ca
K2CO3
65
0.792
1.329
+ 11
H 200
270
Mg; CaO.
Molecular sieve 0.3 nm
Methyl acetate
1-Methyl-2pyrrolidone
57
202
0.933
1.0260
1.362
1.4684
– 10
+ 95
5
20
20
80
K2CO3; CaO
Distillation; Na2SO4;
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Methyl ethyl ketone
Nitrobenzene
80
211
0.806
1.204
1.379
1.556
– 4.4
+ 92
200
H1
600
5
36
97
82
0.626
0.804
0.785
1.358
1.385
1.378
– 49
+ 15
+ 12
1000
–
200
3000
–
500
Na; Pb/Na
CaO; Mg
CaO; Mg;
Molecular sieve 0.3 nm
Pyridine
116
0.982
1.510
+ 20
5
15
KOH; BaO;
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydronaphthalene (Tetralin)
66
208
0.887
0.973
1.405
1.541
– 17.5
+ 78
50
–
150
–
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
CaCl2; Na
Toluene
111
0.867
1.496
+4
50
190
Distillation; Ca; CaCl2;
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Trichloroethylene
87
1.462
1.477
non
flammable
B. –
–
137/
140
˜ 0.86
˜ 1.50
+ 25
100
440
n-Pentane
1-Propanol
2-Propanol
Xylene
(isomeric mixture)
100
K2CO3
CaCl2; P2O5;
Distillation
Distillation;
Na2SO4; K2CO3
Distillation; Na; CaCl2;
Molecular sieve 0.4 nm
Organic solvents
properties and drying
S = Danger of absorption through the skin
A =This substance is definitely known to be a carcinogenic;
no MAC values can be quoted.
B =There are grounds to suppose that this substance has
carcinogenic potential.
Substances for which no MAC value is given have not been classified by the German
Senate Commission on hazardous materials, though this fact is not to be construed
as meaning that the substances carry no risk.
Chemical Characteristics (Safety)
Forms explosive peroxides on
contact with air, if they become
concentrated, these peroxides
may present an explosion hazard.
Hazardous polymerization will
not occur.
101
Organic solvents
(1)For details of drying methods please refer to the brochure
"Drying in the laboratory and pilot plant"
(2) MAC values
Ethanol-water mixtures
Density
D 20º
20º
%
by weight
ethanol
%
by volume
ethanol
Density
D 20º
20º
%
by weight
ethanol
%
by volume
ethanol
1.00000
0.99813
0.99629
0.99451
0.99279
0.99113
0.98955
0.98802
0.98653
0.98505
0.98361
0.98221
0.98084
0.97948
0.97560
0.97687
0.97687
0.97431
0.97301
0.97169
0.97036
0.96901
0.96763
0.96624
0.96483
0.96339
0.96190
0.96037
0.95880
0.95717
0.95551
0.95381
0.95207
0.95028
0.94847
0.94662
0.94432
0.94281
0.94086
0.93886
0.93648
0.93479
0.93272
0.93062
0.92849
0.92636
0.92421
0.92204
0.91986
0.91766
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
0
1.3
2.5
3.8
5.0
6.2
7.5
8.7
10.0
11.2
12.4
13.6
14.8
16.1
17.3
18.5
19.7
20.9
22.1
23.3
24.5
25.7
26.9
28.1
29.2
30.4
31.6
32.7
33.9
35.1
36.2
37.4
38.5
39.6
40.7
41.9
43.0
44.1
45.2
46.3
47.4
48.43
49.51
50.6
51.6
52.6
53.7
54.7
55.8
56.8
0.91546
0.91322
0.91097
0.90872
0.90645
0.90418
0.90191
0.89962
0.89733
0.89502
0.89271
0.89040
0.88807
0.88574
0.88339
0.88104
0.87869
0.87632
0.87396
0.87158
0.86920
0.86680
0.86440
0.86200
0.85958
0.85716
0.85473
0.85230
0.84985
0.84740
0.84494
0.84245
0.83997
0.83747
0.83496
0.83242
0.82987
0.82729
0.82469
0.82207
0.81942
0.81674
0.81401
0.81127
0.80848
0.80567
0.80280
0.79988
0.79688
0.79383
0.79074
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
57.8
58.8
59.8
60.8
61.8
62.8
63.8
64.8
65.8
66.8
67.7
68.6
69.9
70.5
71.5
72.4
73.3
74.2
75.1
76.0
76.9
77.8
78.6
79.5
80.4
81.2
82.1
83.0
83.8
84.6
85.4
86.2
87.1
87.9
88.7
89.5
90.2
91.0
91.8
92.5
93.2
94.0
94.7
95.4
96.1
96.7
97.4
98.1
98.7
99.3
100.0
102
Drying agents
Formula
Water content of
air in equilibrium,
in mg/l (at 25 °C)
Aluminium oxide
Calcium chloride
Calcium hydride
Calcium oxide
Calcium sulfate
Copper sulfate
Dessicant sachets
Magnesium oxide
Magnesium perchlorate
Magnesium sulfate
Molecular sieves
Phosphorus pentoxide
Potassium hydroxide
Sicacide®
Sicapent®
Silica gel, blue gel
Silica gel, orange gel
Sodium hydroxide
Sodium sulfate
Sulfuric acid
Al2O3
CaCl2
CaH2
CaO
CaSO4
CuSO4
SiO2
MgO
Mg(ClO4)2
MgSO4
–
P2O5
KOH
H2SO4*
P2O5*
(SiO2)x
SiO2
NaOH
Na2SO4
H2SO4
0.003
< 0.00001
0.14
0.003
0.004 – 0.07
1.4
0.003
0.008
0.0005 – 0.002
1.0
0.0001 – 0.5
0.00002
0.002
0.003 – 0.3
< 0.000025
0.003
0.003
0.002
1.0
0.005 – 0.3
Organic solvents
Name
*on siliceous supporting material
Vapour pressure of water over
H2SO4 (AT 20 °C)
% H2SO4
p [mbar]
% H2SO4
p [mbar]
10
22,9
65
2,1
20
20,5
70
1,1
30
17,6
75
0,4
40
13,0
80
0,1
50
8,2
85
0,04
55
5,9
90
0,007
60
3,7
103
LiChrosolv®
Solvents for chromatography
Elutopic
series
n-Heptane
n-Hexane
Cyclohexane
Isooctane
Toluene
Chloroform
Dichloroethane
Dichlormethane
1-Butanol
Acetonitrile
2--Propanol
Ethyl acetate
Acetone
Ethanol
1.4-Dioxane
Tetrahydrofuran
Methanol
Water
(1)
Cat. No.
104390
104391
102827
104717
108327
102444
113713
106044
101988
100030
101040
100868
100020
111727
103132
108101
106007
115333
Polarity
index
acc. to
Snyder
(1)
0.2
0.0
0.0
0.4
2.3
4.4
3.7
3.4
3.9
6.2
4.3
4.3
5.4
5.2
4.8
4.2
6.6
9.0
Formula
Molar
mass
[g/mol]
C7H16
C6H14
C6H12
C8H18
C6H5CH3
CHCl3
ClCH2CH2Cl
CH2Cl2
CH3(CH2)3OH
CH3CN
CH3CH(OH)CH3
CH3COOC2H5
CH3COCH3
C2H5OH
C4H8O2
C4H8O
CH3OH
H2O
100.21
86.18
84.16
114.23
92.14
119.38
98.97
84.93
74.12
41.05
60.10
88.10
58.08
46.07
88.11
72.11
32.04
18.01
acc. to L. R. Snyder, Journal of Chromatography 92, 233, (1974)
(2)Detailed solvent tables acc. to H. Halpaap can be found in:
Einführung in HPDC,
ed. R. E. Kaiser, IfC-Verlag Bad Dürkheim 1976, p. 232–233; HPTLC,
ed. A. Zlatkis, R. E. Kaiser Elsevier and IfC 1977, p. 126–127.
(3)A = This substance is definitely known to be a carcinogenic;
no MAC values can be quoted.
104
Refractive
index
20°
D
n
1.388
1.375
1.427
1.392
1.496
1.946
1.445
1.424
1.399
1.344
1.378
1.372
1.359
1.361
1.422
1.405
1.329
1.333
Boiling
point
[°C]
98.4
68.9
80.7
99.2
110.6
61.7
83.4
40.0
117.2
81.6
82.4
77.1
56.2
78.5
101.0
66.0
65.0
100.0
[mbar]
(20°C)
48
160
104
51
29
210
87
453
6.7
97
43
97
233
59
41
200
128
23
Dynamic
viscosity
Surface
tension
against
air or
vapor
MAC
value
1998
mg
Dielectric
constant
[mPa · s]
(22°C)
(40°C)
[mN/m]
(20°C)
[ml/m3]
or
[ppm]
DK
(20 or
25°C)
0.40
0.31
0.94
0.51
0.58
0.56
0.80
0.43
2.95
0.39
2.27
0.44
0.32
1.20
1.21
0.47
0.52
0.95
20.4
18.4
25.5
–
28.5
27.1
24.2
26.5
24.6
29.3
21.7
23.9
23.7
22.8
33.7
–
22.6
72.8
500
50
200
500
50
10
A(3)
100
100
40
200
400
500
1000
20
50
200
–
1.9
1.9
2.0
1.9
2.4
4.8
10.6
9.1
17.8
37.5
18.3
6.0
20.7
24.3
2.2
7.4
32.6
80.2
0.33
0.26
0.71
0.50
0.47
0.47
0.65
0.36
1.78
–
1.35
0.36
0.27
0.83
0.92
0.38
0.45
0.65
Dipole
moment
acc.
to
Debye
ε°
against
AL2O3
(1)
acc. to
Snyder
0
0
0
0
0.36
1.01
1.75
1.60
1.66
3.44
1.66
1.78
2.70
1.70
0.40
1.63
1.70
1.85
0.01
–
0.04
0.01
0.29
0.40
0.44
0.42
–
0.65
0.82
0.58
0.56
0.88
0.56
0.57
0.95
–
Flow coefficient x
[mm2/s] DC-(silica
gel 60 precoated
plate) 22°C
migration distance
[mm]
50
70
100
9.2
12.5
5.4
7.9
8.3
9.0
7.6
10.1
–
12.6
2.1
9.2
12.7
3.4
5.2
10.9
5.6
5.1
10.6
13.9
6.3
8.3
9.8
10.5
8.4
11.8
–
14.0
2.3
10.9
14.7
3.9
6.0
11.9
6.5
5.7
11.4
14.6
6.7
8.7
11.0
11.6
8.9
13.2
–
15.4
2.5
12.1
16.2
4.2
6.5
12.6
7.1
5.8
105
Organic solvents
Vapor
pressure
Physical methods for
the determination of elements
Flame photometry
Wavelength and wave number
Photometry: Transmission rate and absorbance
Calculation of the standard deviation
Direct-current polarography
Cathode ray polarography
108
108
108
108
109
109
Flame photometry
Important emission lines in the flame spectra of some elements
Element
Wavelength l [nm]
Ag
Ba
B
Ca
Co
Cr
Cs
Cu
Fe
K
Li
Mg
Mn
Na
Ni
Pb
Rb
Sr
Ti
328.1
553.6
452
422.7
346.6
360.5
455.5
324.8
373.7
404.7
670.8
285.2
403.3
330.3
341.5
368.4
420.2
460.7
377.6
(B)
(G)
(G)
(D)
(G)
(D)
(G)
(D)
338.3
744
548
554
353.0
427.5
852.1
327.4
386.0
766.5
460.3
371
543.3
589.3
352.5
405.8
780.0
821
535.0
(B)
(B)
(B)
(G)
(G)
(D)
(B)
(D)
(G)
(B)
(B) = Band of the oxide
(D) = Dual line, the center point between the two lines is given
(G) = Group of lines in the region of the stated wavelength
Wavelength and wave number
Wavelength l [nm] and wave number n [cm-1]
v = 1 ;
λ
400 nm ⩠ 25000 cm-1
Photometry - transmission rate and absorbance
A = - IgT
(e.g. A = 23.6% = 0,236 → T = 0.627)
Calculation of the standard deviation
A = √∑ F2
108
873
345
622
387.4
425.5
894.3
520
385.6
344.6
323.3
383
279.5
818.3
385.8
261.4
794.8
407.8
276.8
(B)
(B)
(B)
(B)
(G)
(D)
(B)
(D)
(G)
(D)
Direct-current polarography
Half-wave potentials of some important metals
Half-wave potential [V]
Support electrolyte / concentration
Cu2+
Pb2+
Cd2+
Ni2+
Zn2+
Co2+
Fe2+
Mn2+
Cu2+
– 0.42
– 0.48
– 0.64
– 1.00
– 1.06
– 1.30
– 1.41
–1.55
– 0.32
Pb2+
Co2+
Zn2+
Mn2+
– 0.52
– 0.86
– 1.08
– 1.40
NH4 CH3 COO 0.85 mol/l
KSCN 0.0025 mol/l
“
“
“
“
“
“
Saturated CaCl2 solution
about 10–12 mol/l
“
“
“
“
Physical methods for the determination of elements
Metal
Cathode ray polarography
Peak potentials of some important metals (1)
Metal
Peak potential [V]
Support electrolyte / concentration
Interference by
Zn2+
Cd2+
Cu2+
Pb2+
Ni2+
Bi3+
Co2+
Sb3+
Sn2+
Cr6+
Cr3+
– 1.03
– 0.63
– 0.15
– 0.40
– 0.80
– 0.08
– 1.05
– 0.13
– 0.50
– 0.75
– 1.10
Pyridine hydrochloride
HCI
HCI
HCI
Pyridine hydrochloride
HCI
Pyridine hydrochloride
HCI
HCI
LiOH
LiCI
Co2+
0.1 mol/l
0.2 mol/l
0.2 mol/l
0.2 mol/l
0.1 mol/l
0.5 mol/l
0.1 mol/l
0.5 mol/l
5 mol/l
0.5 mol/l
0.5 mol/l
Sb3+
Sn2+
Cu2+
Zn2+
Cu2+
Pb2+, TI+
Zn2+
(1) measured against a silver/silver chloride reference electrode
109
Mass and weight
Energy dimensions - conversion factors
Pressure dimensions - conversion factors
Decimal multiples and parts of units
Concentration values
Basic units
Derived units
US and British measures units
112
112
113
113
113
114
118
Energy dimensions — conversion factors
Given
dimension
Unit
1J
(1)
1 kWh (1)
1 MeV (1)
1 mkp
1 kcal15°
1 erg
Required dimension with conversion factor (2)
J
kWh
MeV
mkp
kcal15°
erg
1
3600000
1.602·10–13
9.80665
4185.5
10–7
2.77778·10–7
1
4.45·10–20
2.72407·10–6
1.16264·10–3
2.77778·10–14
6.242·1012
2.247·1019
1
6.124·1013
2.613·1016
6.242·105
0.1019716
367097.8
1.634·10–14
1
426.80
0.1019716·10–7
2.38920·10–4
860.11
3.827·10–17
2.34301·10–3
1
2.38920·10–11
107
3.6·1013
1.602·10–6
9.80665·107
4.1855·1010
1
Torr
(mm HG)
Ibs/sq.in.
(psi)
(1) Legal measurement units
(2) Examples: 1 J = 2.38920·10–4 kcal 1 MeV = 1.602·10 –13J
Pressure dimensions — conversion factors
Given
dimension
Unit
1 N·m
1 Pa
(1)
1 bar (1)
1 atm
1 kp·m2
1 Torr
(1 mm Hg)
-2
10 Ibs/sq.in. (psi)
Required dimension with conversion factor (2)
N · m-2
(Pa)
bar
atm
1
10
9.8692·10
105
101325
9.80665
133.3224
1
101325
9.80665·10–5
1.333224·10–3
68948
0.68948
–5
kp·m-2
1.019710·10
–3
7.50062 ·10
1.45038·10-4
9.8692
1
9.67841·10-5
1.31579·10-3
10197.16
10332.27
1
13.5951
750.062
759.9988
7.35559·10–2
1
14.5038
14.6960
1.42234·10-3
1.93368·10-2
0.68046
7030.68
517.148
10
-6
(1) Legal measurement units
(2) Examples: 1 Pa = 7.50062·10–3 Torr 10 psi = 0.68046 atm
112
-1
Decimal units multiples and subdivisions
Prefix
1018
1015
1012
109
106
103
102
10
Symbol
Exa
Peta
Tera
Giga
Mega
Kilo
Hecto
Deca
Prefix
E
P
T
G
M
k
h
da
10–1
10–2
10–3
10–6
10–9
10–12
10–15
10–18
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
0.000 1
0.000 01
0.000 001
0.000 000 1
g/kg
mg/g
µg/mg
10
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
0.000 1
0.000 01
0.000 001
Symbol
Deci
Centi
Milli
Micro
Nano
Piko
Femto
Atto
d
c
m
µ
n
p
f
a
Proportion
1 : 100
1 : 1 000
1 : 10 000
1 : 100 000
1 : 1million
1 : 10 million
1 : 100 Millionen
1 : 1 Milliarde
1 : 10 Milliarden
1 : 100 Milliarden
1 : 1 Billion
Potency %
1 x 10–2
1 x 10–3
1 x 10–4
1 x 10–5
1 x 10–6
1 x 10–7
1 x 10–8
1 x 10–9
1 x 10–10
1 x 10–11
1 x 10–12
ppm
ppb
ppt
mg/kg
µg/g
ng/mg
10 000
1 000
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
µg/kg
ng/g
pg/mg
ng/kg
pg/g
fg/mg
1 000
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
1 000
100
10
1
The tables on pages 96 to 101 were reprinted with permission of the Deutsches
Institut für Normung e.V. (DIN, German Institute of Standardization).
They contain excerpts from DIN 1301. Always use the most current version of
the norm to be obtained from Beuth Verlag GmbH, Burggrafenstraße 4–10,
10772 Berlin, Germany.
Basic units
Dimension
Length
Mass
Time
Electric current
Temperature
Luminous intensity
Amount of substance
Basic unit
Name
Meter
Kilogram
Second
Ampere
Kelvin
Candela
Mole
Symbol
m
kg
s
A
K
cd
mol
113
Mass and weight
Concentrations
Derived units
with conversion of previous units
Size
SI unit
Name
Symbol
Further units
Relationship
Name
Symbol
Liter
l
1 l = 10–3 m3
t
1 t = 103 kg
1 u = 1,66053
·10–27 kg
Length, surface, volume
Length
Surface
Volume
Meter
Square meter
Cubic meter
m
m2
m3
Kilogram
kg
Mass
Mass
Density
Specific
volume
Kilogram
per
cubic meter
Cubic meter
per
kilogram
Metric
ton
Atomic
mass unit
u
kg·m–3
m3·kg–1
Amount of substance
Amount of
substance
Molar
mass
Concentration
of a substance
Molality
Mole
Mass
per amount
of substance
Amount of
substance
in given
volume
of solvent
Amount of
substance
per mass
of solvent
mol
Kelvin
K
kg·mol–1
g·mol–1
mol·m–3
mol·l–1
mol·kg–1
mol·g–1
Temperature
Temperature
114
Degree
centigrade
°C
Derived units
with conversion of previous units
Size
SI unit
Name
Symbol
Time
Time interval
second
s
Frequency
Velocity
Hertz
Meter
per
second
Further units
Relationship
Name
Symbol
minute
hour
day
min
h
d
1 min = 60 s
1 h = 60 min
1 d = 24 h
1 Hz = 1 s-1
Kilometer
per
hour
km·h-1
1 km·h-1
= 1 m·s-1
3.6
Poise
P
Centipoise
cP
Stokes
St
Centistoke
cSt
Time
Hz
Viscosity
Dynamic
viscosity
Kinematic
viscosity
Pascalsecond
Square
meters
per
second
Pa·s
m2·s-1
1 Pa·s = 1 N·s·m-2
= 1 kg·m-1·s-1
1P
= 0.1 Pa·s
1 cP
= 0.01 Pa·s
= 0.001 Pa·s
= mPa·s
1 St
= 1 cm2·s-1
1 cSt
= 1 mm2·s-1
115
Mass and weight
m·s–1
Derived units
with conversion of previous units
Size
SI unit
Name
Symbol
Force
Newton
N
Pressure
Newton
per
square
meter
Pascal
N·m-2
Pa
Joule
J
Further units
Name
Relationship
Symbol
Force, energy, power
Energy, work
heat quantity
Power
Watt
W
Electric
current
Electric
potential
Electric
conductance
Electric
resistance
Ampere
A
Volt
V
Siemens
S
Ohm
V
Electric
charge
Coulomb
C
1N
= 1 kg·m·s-2
Bar
bar
Kilowatthour
kW·h
1 Pa
= 1 N·m-2
1 bar
= 105 Pa
1J
= 1 N·m
= 1 W·s
= 1 kg·m2·s-2
1 kW·h
= 3,6 MJ
1W
= 1 J·s-1
= 1 N·ms-1
= 1 VA
Electrical measures
Amperehour
Electric
capacitance
Farad
F
Candela
Lumen
Lux
cd
lm
lx
Axh
1S
= 1 A·V-1
1V
= 1 V·A-1
= 1 S-1
1C
= 1 A·s
1 A·h
= 3600 A·s
1F
= 1 C·V-1
Luminous intensity
Luminous intensity
Luminous flux
Illuminance
116
1 lm = 1 cd·sr
1 lx = 1 lm·m-2
1 cd·sr·m-2
Derived units
with conversion of previous units
Size
SI unit
Name
Symbol
Becquerel
Bq
Further units
Relationship
Name
Symbol
Curie
Ci
Ionizing radiation
Activity
1 Bq = 1 s-1
1 Ci = 37 G Bq
Enzymatic
activity
Katal
kat
Enzyme
unit
U
1 kat
= 1 mol·s-1
= 60 mol·min-1
1U
= 1 mol·s-1
= 1 μkat
60
= 16.67 nkat
117
Mass and weight
Enzymatic activity
US and British measuring units
Conversion to metric units
Volume
Liters
US gallons
Imperial gallons
Imperial gallons
US gallons
Cubic meters
Cubic feet
Cubic meters
US gallons
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
0.2642
3.785
1.201
4.546
0.8327
35.31
0.0283
264.2
0.00379
= US gallons
= Liters
= US gallons
= Liters
= Imperial gallons
= Cubic feet
= Cubic meters
= US gallons
= Cubic meters
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
3.281
0.3048
39.37
0.0254
0.3937
2.540
0.0394
25.4
= Feet
= Meters
= Inches
= Meters
= Inches
= Centimeters
= Inches
= Millimeters
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
2.2046
0.4536
1016.05
2240
1000
2204.6
907.185
2000
15.432653
0.0647989
0.0352740
28.349527
31.1035
= Pounds
= Kilograms
= Kilograms
= Pounds
= Kilograms
= Pounds
= Kilograms
= Pounds
= Grains
= Grams
= Ounces (US)
= Grams
= Grams
Length
Meters
Feet
Meters
Inches
Centimeters
Inches
Millimeters
Inches
Weight
Kilograms
Pounds
Tons (long)
Tons (long)
Tonnes (metr.)
Tonnes (metr.)
Tons (short)
Tons (short)
Grams
Grains
Grams
Ounces (US)
Ounces (troy)
118
US and British measuring units
Conversion to metric units
Temperatur
°Centigrade
a° Centigrade
required in
°Réaumur
a·8
10
–
b · 10
8
(c - 32) · 10
18
b° Réaumur
c° Fahrenheit
°C
°F
°C
°F
– 40
– 35
– 30
– 25
– 20
– 15
– 10
–5
0
– 40
– 31
– 22
– 13
–4
+5
14
23
32
+5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
41
50
59
68
77
86
95
104
113
°C
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
°Fahrenheit
a · 8 + 32
10
b · 10 + 32
8
–
(c - 32) · 8
18
–
°F
°C
°F
°C
°F
°C
°F
122
131
140
149
158
167
176
185
194
95
100
105
110
115
120
125
130
135
203
212
221
230
239
248
257
266
275
140
145
150
155
160
165
170
175
180
284
293
302
311
320
329
338
347
356
185
190
195
200
210
365
374
383
392
410
119
Mass and weight
given in
Other useful tables
Physical constants
Establishment of constant humidity in closed vessels
Greek alphabet
Greek numerals / Roman numbers
Freezing mixtures
Extran®
Particle sizes
NMR: Carbon (13C) chemical shifts
NMR: Proton chemical shifts
Miscibility table
Stoichiometry formulary
122
123
124
125
126
126
128
130
132
134
136
Physical constants
Constant
Symbol
Value
Atomic mass unit
Avogadro constant
Bohr magneton
Bohr radius
Boltzmann constant
Compton wavelength (e)
Compton wavelength (n)
Compton wavelength (p)
Electric field
constant in vacuo
Electron radius
Elementary charge
Faraday constant
Fine structure constant
Gas constant
Gravitation constant
Intrinsic impedance
Light velocity
in vacuo
Loschmidt constant
Magnetic field
constant in vacuo
Molar volume of ideal
gases 298 K, 101.325 kPa
Normal acceleration of fall
Planck constant
Rest mass of the electron
Rest mass of the neutron
Rest mass of the proton
Rotational quantum
ydberg constant
mU
NA
μB
αO
kB
λCe
λCn
λCp
εO
1.660540
6.022137
9.274015
5.291771
1.380662
2.426311
1.319591
1.321410
8.854188
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
10–27
1023
10–24
10–11
10–23
10–12
10–15
10–15
10–12
kg
mol–1
JT–1
m
JK–1
m
m
m
Fm–1
r
e
F
α
R
f
Γ
c
2.817941
1.602177
9.648531
7.297353
8.31451
6.672590
3.767301
2.997924
·
·
·
·
10–15
10–19
104
10–3
m
C
Cmol–1
·
·
·
10–11
102
108
J mol–1K–1
Nm2kg–2
V
ms–1
NL
2.686763
·
1025
m–3
μO
nm
1.256637
2.445294
·
·
10
10–2
Hm–1
m3mol–1
g
h
me
mn
mp
h/(2π)
R∞
9.80665
6.626075
9.109390
1.674929
1.672623
1.054588
1.097373
·
·
·
·
·
·
10–34
10–31
10–27
10–27
10–34
107
ms–2
Js
kg
kg
kg
Js
m–1
122
τ e
–7
Creation constant air humidity in closed vessels
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate
Sodium carbonate
Zinc sulfate
Potassium chloride
Ammonium sulfate
Sodium chloride
Sodium nitrite
Ammonium nitrate
Calcium nitrate
Potassium carbonate
Zinc nitrate
Calcium chloride
Lithium chloride
% relative air humidity
above the solution
(at 20 °C)
Na2HPO4 · 12 H2O
Na2CO3 · 10 H2O
ZnSO4 · 7 H2O
KCl
(NH4)2SO4
NaCl
NaNO2
NH4NO3
Ca (NO3)2 · 4 H2O
K2CO3
Zn (NO3)2 · 6 H2O
CaCl2 · 6 H2O
LiCl · H2O
95
92
90
86
80
76
65
63
55
45
42
32
15
Other useful tables
Saturated aqueous
solution with
considerable precipitates
123
Greek alphabet
Letter
A
B
Γ
Δ
E
Z
H
Θ
I
K
Λ
M
N
Ξ
O
Π
P
Σ
Τ
Υ
Φ
Χ
Ψ
Ω
α
β
γ
δ
ε
ζ
η
θ
ι
κ
λ
μ
ν
ξ
ο
π
ρ
σ1, ς2
τ
υ
φ
χ
ψ
ω
Name
Pronunciation
álpha
béta
gámma
délta
épsilon
zéta
éta
théta
ióta
káppa
lámbda
mü
nü
xi
ómicron
pi
rho
sigma
tau
ýpsilon
phi
chi
psi
ómega
a
b
g
d
e (short)
z
e (long)
th
i
k
l
m
n
x
o (short)
p
r
s
t
y
ph
ch
ps
o (long)
1 At the beginning and in the middle of a word
2 At the end of a word
124
Greek numbers / Roman numbers
hemi –
mono –
sesqui –
di –, bi –
hemipenta –
tri –
tetra –
penta –
hexa –
hepta –
octa –
nona –, ennea –
deca –
hendeca –, undeca
dodeca –
trideca
tetradeca –
pentadeca –
hexadeca –
heptadeca –
octadeca –
nonadeca –
eicosa –
tetraconta –
pentaconta –
hexaconta –
nonaconta –
hecta –
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
VIII
IX
X
XI
XII
XIII
XIV
XV
XVI
XVII
XVIII
XIX
XX
XL
L
LX
XC
IC
C
CC
CD
D
DC
CM
XM
M
Other useful tables
1
⁄2
1
11⁄2
2
21⁄2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
50
60
90
99
100
200
400
500
600
900
990
1000
125
Freezing mixtures
The numbers represent weight proportions
4 water
1 water
1 water
3 ice ground
1,2 ice ground
1,2 ice ground
1,4 ice ground
Methanol or acetone
Diethyl ether
+ 1 potassium chloride
+ 1 ammonium nitrate
+ 1 sodium nitrate + 1 ammonium chloride
+ 1 sodium chloride
+ 1 magnesium chloride (MgCl2 · 7 H2O)
+ 2 calcium chloride (CaCl2 · 6 H2O)
+ 2 calcium chloride (CaCl2 · 6 H2O)
+ dry ice
+ dry ice
Lowering
temperature
from [°C] to
+ 10
+ 10
+ 8
0
0
0
0
+ 15
+ 15
– 12
– 15
– 24
– 21
– 34
– 39
– 55
– 77
– 100
Extran® laboratory cleaning agents
Name
Cat. No.
Notes on use
Extran® MA 01
alkaline / liquid
107555
Universal cleaning agent for heavy contamination.
For hard water even up to 40° d. For cleaning tables,
tiles, and floors in the laboratory.
Suitable for ultrasonic cleaning.
Extran® MA 02
neutral / liquid
107553
Special cleaner for precision instruments of glass,
quartz and sensitive metals. Suitable for ultrasonic
cleaning.
Extran® MA 03
phosphate-free
liquid
107550
Universal cleaning agent for heavy contamination.
With very hard water also usable without restrictions.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate.
Suitable for ultrasonic cleaning.
Extran® MA 05
liquid / alkaline
/ phosphatefree
concentrate
140000
Universal cleaning agent for heavy contamination. With
very hard water also usable without restrictions.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate and
NTA. Suitable for ultrasonic cleaning.
Extran® AP 11
mildly alkaline/
powder
107558
Gentle cleaning action; e.g. in the analytical laboratory.
Cleaning action equivalent to that of AP 14 liquid.
Extran® AP 12
alkaline/powder
107563
Powerful cleaning action. Particularly with starch
and protein residues. Cleaning action equivalent
to that of AP 15 liquid.
Extran® AP 13
alkaline with
detergents/
powder
107565
Powerful cleaning action. Particularly with
fat residues.
Extran® AP 14
mildly alkaline/
liquid
107573
Gentle cleaning action for machines with liquid dosing;
e.g. in the analytical laboratory.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate.
Cleaning action equivalent to that of AP 11 powder.
126
Extran® laboratory cleaning agents
Cat. No.
Notes on use
107575
Powerful cleaning for machines with liquid dosing.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate.
Cleaning action equivalent to that of AP 12 powder.
Extran® AP 16
liquid / mildly
alkaline
concentrate
140001
Gentle cleaning action for machines with liquid dosing;
e.g. in the analytical laboratory.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate and
NTA. Cleaning action equivalent to that of AP 11 powder.
Extran® AP 17
acidic with
phosphoric acid
liquid
140006
Powerful cleaning for machines with liquid dosing.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate and
NTA. Cleaning action equivalent to that of AP 12 powder.
Extran® AP 21
acidic with
phosphoric acid
liquid
107559
First rinse in the presence of residues of carbonates,
hydroxides, proteins, amines, etc. Neutralising
Neutralising final rinse. Also for a gentle main wash.
Prevents the formation of calcareous deposits.
Extran® AP 22
acidic with
citric acid liquid
107561
Gentle prerinse or final rinse with neutralizing
action. Prevents the formation of calcareous deposits.
Environmentally friendly as it contains no phosphate.
107560
Additive for foam-forming residues: proteins, fats,
emulsifiers of all types.
Additive for foam-forming residues: proteins, fats,
emulsifiers of all types. Environmentally friendly as it
contains no formaldehyde.
Extran® AP 31
antifoam/ liquid
Extran® AP 33
liquid / antifoaming agent /
formaldehydefree
Extran® AP 41
enzymatic/
powder
NN
107570
Other useful tables
Name
Extran® AP 15
alkaline/liquid
For medical and dental practices, anaesthetic equipment.
For the removal of mucus, saliva, blood etc. Temperature:
55–65 °C.
Extran® cleaning agents in renowned Merck quality are the
key to reliable cleaning of your labware
Immediate, residue-free cleaning is prerequisite to reliable
work in the lab and production department and is
indispensible for producing accurate scientific results. All
items of equipment coming into contact with chemical
or biological substances must be contaminant-free before
and after use.
Merck’s high-quality Extran® cleaning agents have provided
the solution for more than 25 years now.
The benefits to you:
Extran cleans reliably without leaving any residues, so preventing contaminant carry-over to the next analysis
performed. Extran is free from scented materials, colorants,
chlorine and toxic ingredients. It therefore produces no
unwanted odors and poses no health risk to analysts and
operators. Its active ingredients are biodegradable, so
environmental demands are also met.
zu viel Text!
127
Particle sizes
Mesh size w
DIN 4188
(D)
[mm]
ASTM
E11–70
(USA)
[mesh]
0.02
0.022
0.025
ASTM
E161–70
(USA)
[µm]
5
10
15
BS
410 : 1969
(GB)
[µm]
Tyler
[mesh]
22
27
0.028
0.032
0.036
0.04
0.045
0.05
0.056
0.063
0.071
0.08
0.09
0.1
0.112
0.125
0.14
0.16
0.18
0.2
0.224
0.25
0.28
0.315
0.355
0.4
128
32
400
38
38
400
325
45
45
325
270
53
53
270
230
63
63
250
200
75
75
200
170
90
90
170
140
106
106
150
120
125
125
115
100
150
150
100
80
180
80
70
212
65
60
250
60
50
300
48
45
355
42
Particle sizes
Mesh size w
(D)
[mm]
0.45
0.5
0.56
0.63
0.71
0.8
0.9
1
1.12
1.18
1.25
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
2.24
2.5
2.8
3.15
3.55
4
4.5
5
5.6
ASTM
E11–70
(USA)
[mesh]
ASTM
E161–70
(USA)
[µm]
BS
410 : 1969
(GB)
[µm]
Tyler
[mesh]
40
425
35
35
500
32
30
600
28
25
710
24
20
850
20
18
1000
16
16
1180
14
14
1400
12
12
1700
10
10
2000
9
8
2360
8
7
2800
7
6
3350
6
5
4000
5
4
4750
4
3 ⁄2˝
5600
31⁄2
1
Other useful tables
DIN 4188
129
NMR: Carbon (13C) chemical shifts
TMS = 0 ppm
H3C – C -
220
200
180
220
200
180
220
200
180
C primary
H3C – Halogen
H3C – O –
H3C – N
H3C – S –
– CH2 – C -
C secondary
– CH2 – Halogen
– CH2 – O –
– CH2 – N
– CH2 – S –
CH – C -
C tertiary
CH – Halogen
CH – O –
CH – N
CH – S –
–C–C-
C quaternary
– C – Halogen
–C–O–
C–S–
–C–C-
Alkanes
–C≡C–
Alkynes
C=C
Alkenes
C=C
Aromatics
C=C
Heteroaromatics
–O–C≡N
Cyanates
–S–C≡N
Thiocyanates
–C≡N
Cyanides
C=N–
Azomethines
(– CO)2O
Anhydrides
– COOR
Esters
(– CO)2NR
Imides
– CONHR
Amides
– COOH
Acids
– COCI
Acid Chlorides
–C=O
Aldehyde
C=O
130
Ketone
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
–20
–40
Cl
I
aliphates — cyclopropanes
I
Cl
I
Cl
I
Other useful tables
Cl
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
–20
–40
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
–20
–40
131
NMR: Proton chemical shifts
TMS = 0 ppm
H3C – CR3
13
12
11
10
13
12
11
10
Methyl protons
H3C – Halogen
H 3C – O –
H3C – N
H3C
C=C
H3C
C=O
H3C – Ar
– CH2 – CR3
Methylene protons
– CH2 – Halogen
– CH2 – O –
– CH2 – N
– CH2
C=C
– CH2
C=O
– CH2 – Ar
CH – CR3
Methine protons
CH – Halogen
CH – O –
CH – N
CH
C=O
CH – Ar
–C≡C–H
Alkynes
C-C–H
Alkenes, nonconjugated
C-C–H
Alkenes, conjugated
Ar – H
Aromatics
Ar – H
Heteroaromatics
O-C–H
Aldehydes
ROH*
Alcohols, very dilute solution
ROH*
Alcohols, 0.1–0.9 mol/l
RCO2H*
Carboxylic acids, dimer
– SO3H
Sulfonic acids
RSH*
Thiols
ArSH*
Thiophenols
RNH2*
Amines, 0.1–0.9 mol/l
R2NH*
Amines, 0.1–0.9 mol/l
ArNH-(H, R, Ar)*
Aromatic amines, primary, secondary
RNH3+, R2NH2+, R3NH+
in TFA solution
ArNH3+, ArRNH2+, ArR2NH+
in TFA solution
*The chemical shifts of these groups are concentration-dependent and are shifted to lower
ppm values in more dilute solutions
132
8
7
6
5
4
3
8
7
6
1
F
I
F
I
F
9
2
0
Other useful tables
9
I
5
4
3
2
1
0
(ppm)
133
H
Acetone
Acetonitrile
Carbon tetrachloride
Chloroform
Cyclohexane
1.2-Dichloroethane
Dichloromethane
Diethyl ether
Dimethyl formamide
Dimethyl sulfoxide
1.4-Dioxane
Ethanol
Ethyl acetate
Heptane
Hexane
Methanol
Methyl-tert-butyl ether
Pentane
1-Propanol
2-Propanol
Tetrahydrofuran
Toluene
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Water
miscible
immiscible
134
Diethyl ether
Dichloromethane
1.2-Dichloroethane
Cyclohexane
Chloroform
Carbon tetrachloride
Acetonitrile
Acetone
Miscibility tables
135
Other useful tables
Water
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Toluene
Tetrahydrofuran
2-Propanol
1-Propanol
Pentane
Methyl-tert-butyl ether
Methanol
Hexane
Heptane
Ethyl acetate
Ethanol
1.4-Dioxane
Dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl formamide
Stoichiometry formulary
Density
p = mg
v mL
Substance amount fraction
x(x) = n(x) [1]
n(x) + n(Lm)
x(x) = n(x)
n(ges.)
[1]
Substance amount concentration
c(x) = n(x)
V(Lsg)
mol
L
n(x) = m(x)
M(x)
[mol]
Substance amount concentration of the equivalent
1
n x
c 1 x = z mol
z V(Lsg) L
n 1 x = m(x)
z M 1 x
z
mol
Per cent by weight
ω(x) =m(x)
m(Lsg)
[1]
Mass per unit volume β
β = m(x)
V(Lsg)
g
L
Per cent by volume φ
φ (x) = V(x) [1]
V(x) + V(Lm)
Volume concentration σ
σ (x) = V(x)
V(Lgs)
[1]
Molar volume
Vm = V
n
136
L
mol
Equation of mixtures
ω1 * m1 + w2 * m2 + … = ωMi * mMi
Dilution
ω1 * m1 = ωMi * mMi mMi = m1 + m2 + …
Reconcentration
ω1 * m1 = ωMi * (m1 - m2)
Equation of mixtures for the substance amount of the concentration
c1 * V1 + c2 * V2 + … = cMi * (V1 + V2 + …)
Gravimetry
F = M(ges. Stoff)
M(ges. Stoff)
[%]
Other useful tables
ω(x) = m(Ausw) * F * 100 * VF
m(Einw)
[1]
m(x) = m (Auswaage) * F [g]
Volumetry
c(x) = c̃(x) * t(x)
t(x) = c(x) [1]
c̃(x)
mol
L
n(x) = c̃(x) * t(x) * V(Lsg)
[mol]
Recovery calculation
ω(% d.Th.) = m(P) * 100
m(T)
[%]
m(T) = m(Einw) * F
pH-value calculation
KW = c(H3O+) * c(OH-) = c2(H2O)
pH = -Ig c(H3O+)
pH = -lg � KS * c(acid)
-7
KW = 10 mol * 10-7 mol = 10-14 mol2
L
L
L L
pOH = -lg c(OH-)
pOH = -lg � KB * c(base)
Buffer solution
c (acid) )
pH = -lg (KS *
c(salt)
137
Notes
Notes
Periodic table of the elements
For any further information
please contact your local agent
We provide information and advice to our customers
to the best of our knowledge and ability, but without
obligation or liability. Existing laws and regulations are
to be observed in all cases by our customers.
This also applies in respect to any rights of third parties.
Our information and advice do not relieve our customers
of their own responsibility for checking the suitability of
our products for the envisaged purpose.
Lab Tools
W.280111
060605
Lab Tools
Tables for laboratory use
Table for laboratory use
For any further information
please contact your local agent
Merck KGaA
64271 Darmstadt
Germany
Fax 0049 (0) 151 72-6080
E-Mail reagents@merck.de
Inernet www.merck-chemicals.com