Untitled
advertisement

I
t
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Foreword
it
Conceptual Model Of Teacher Education
'U
Introduction
I
Goals
2
Overall Objectives
3
Content and Time Allocation
4
Instructional Strategies
5
Supplementary Activities
6
Educational Psychology
8
Pedagogy
20
Teacher Professionalism
34
Assessment
42
Suggested Course Work
41
References
43
Panelists Of Subject Outline and Syllabus
For Post Graduate Diploma in Teaching
Primary School
50
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
Translation Panelists of Subject Outline and Syllabus
For Post Graduate Diploma in Teaching Primary
School
51
Review Panelists of Subject Outline and Syllabus
For Post Graduate Diploma in Teaching Primary
School
51
Appendix
52
Appendix A : Struktur dan Komponen KPLI Sekolah Rendah
Ambilan 2003
Appendix B : Mata Pelajaran KPLI Sekolah Rendah Ambilan 2003
Appendix C : Kombinasi mata pelajaran Major dan Minor KPLI
Sekolah Rendah
Appendix D : Theory of Constraint
Appendix E : Caring Intellectual
Appendix F : Terminology for Educational Studies
KATA ALU-ALUAN
Kualiti pendidikan bermula dengan kualiti guru. Peningkatan kualiti
pendidikan guru merupakan satu usaha berterusan untuk melahirkan guru
yang kreatif, berketrampilan dan berakhlak mulia. Kurikulum pendidikan
guru adalah dinamik dan sentiasa diubah suai supaya guru dikemaskinikan
dengan ketrampilan baru, pengetahuan baru dan sikap positif sejajar
dengan pembentukan negara yang progresif. Pengubahsuaian kurikulum
menuntut para pendidik guru membuat peranjakan minda untuk
melahirkan guru permulaan yang cekap teknologi dan yakin menghadapi
perubahan dan menangani cabaran persekitaran sekolah semasa.
Kursus Perguruan Lepas Ijazah (KPLI) Sekolah Rendah akan diperkenalkan
mulai 3anuari 2003 untuk meiatih guru siswazah dalam bidang perguruan
sekolah
rendah.
Kurikulum
i ni
digubal
berasaskan
keperluan
mengoptimumkan
perkembangan
kognitif kanak-kanak,
keperiuan
meningkatkan ilmu pedagogi dan pengalaman berasaskan sekolah rendah
serta keperluan mernupuk niiai positif dan amalan profesional di kalangan
guru. Keperluan-keperluan tersebut diterjemahkan dalam kandungan
kurikuium latihan perguruan yang mendefinisikan bagaimana seseorang
guru periu mereka bentuk pengajaran yang berkesan, mewujudkan
suasana bilik darjah yang selesa, mewujudkan suasana keseronokan untuk
menimba ilmu serta memupuk ciri-dri guru profesional yang disanjung
tinggi oleh masyarakat. Kurikulum ini juga menuntut agar guru-guru yang
mengikuti program labhan ini berketrampilan dalam penggunaan
kemahiran teknologi makiumat dan komunikasi (ICT).
Dengan kurikulurn ini, kami di Bahagian Pendidikan Guru percaya mutu
pendidikan guru dapat dipertingkatkan bersesuaian dengan keperluan
pendidikan masa kini dan akan datang.
Harapan kami ialah untuk
melahirkan guru siswazah sekolah rendah yang berkualiti supaya segala
kemahiran dan pengetahuan yang diperolehi dapat dicurahkan dengan
sebaik-baiknya kepada pelanggan.
r
DATO' ABU BAKAR BIN BACHIK
Pengarah Pendidikan Guru
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia
Oktober 2002
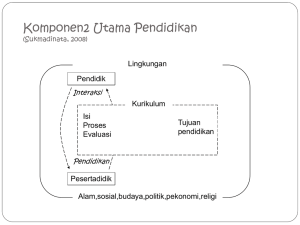
MODEL KONSEPTUAL PENDIDIKAN GURU
Model Konseptual Guru dibina berasaskan Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan (FPK) da
Falsafah Pendidikan Guru (FPG) yang menekankan kepentingan tiga aspek asas iait
pengetahuan, kemahiran dan nilai yang disepadukan merentasi semua disiplin mata pelajara
serta program yang dirancangkan seperti gambar rajah di bawah:
KETUHANAN
KENDIRi
KEMASYARAKATAN
...s^
!.
..
^r,
Model konseptual pendidikan guru mengutamakan akauntabiliti guru kepada tiga dimensi
utama iaitu kendiri, kemasyarakatan dan ketuhanan. Citra ketiga-tiga dimensi ini dijelmakan
dalam program yang dirancangkan seperti berikut:
Ketuhanan :
Kemasyarakatan
Kendiri
Menganjurkan peningkatan ilmu, penghayatan dan amalan individu
sebagai insan yang percaya dan patuh kepada ajaran agama.
Menekankan peranan guru sebagai pendidik, pemimpin dan sebagai
agen perubahan.
Menjurus kepada pembinaan daya ketahanan, patriotisme, pemupukan
budaya ilmu, pembentukan sahsiah dan berpekerti mulia
Selaras dengan FPK dan FPG, model ini menggambarkan suatu usaha membina kekuatan
dan ketahanan diri guru berasaskan kepatuhan kepada Tuhan dan kesejahteraan
bermasyarakat. Hasrat ini dapat dicapai menerusi pelaksanaan kurikulum pendidikan guru
yang menyepadukan aspek-aspek pengetahuan, kemahiran ikhtisas dan amalan nilai-nilai
keguruan.
Kurikulum Kursus Perguruan Lepas Ijazah (KPLI) Sekolah Rendah digubal dengan mengambil
kira usaha menterjemahkan ketiga-tiga aspek iaitu pengetahuan, kemahiran dan nilai secara
bersepadu yang diperjelas seperti berikut:
Pengetahuan :
Kemahiran :
Nilai :
Merangkumi pengetahuan am dan pengetahuan dalam mata pelajaran
KBSR dan KBSM serta pengetahuan ikhtisas keguruan.
Merangkumi kemahiran ikhtisas yang menjurus kepada kemahiran
berkomunikasi, kemahiran belajar, kemahiran berfikir, literasi komputer
dan
pedagogi.
Pembinaan dan pengukuhan aspek "how to" dengan
memberi tumpuan kepada pengintegrasian teknologi maklumat dalam
pelaksanaan kurikulum.
Merujuk kepada penerapan, penghayatan dan amalan nilai-nilai murni
keguruan yang menampilkan sahsiah dan perlakuan sebagai guru yang
penyayang, berpekerti mulia, berdaya tahan, patriotik, inovatif, kreatif,
berketrampilan dan berwibawa serta patuh kepada profesion perguruan.
IV
I NTRODUCTION
The Teacher Education Division continuously upgrades the ability of teachers to
transform the aspirations of the National Philosophy of Education into the teaching and
l earning processes envisaged by the Integrated Curriculum For Primary Schools. This
effort ensures quality education in schools.
I n this respect, the professionalism of teachers always needs to be enhanced so as to
enable the teaching fraternity to confront the challenges emanating from the transition
from the industrial era to the e-learning era. To respond to this challenge, previously
adopted strategies to produce teachers need to be reviewed from time to time so that
teachers can continue to play a meaningful and relevant role. As such, the knowledge
base of teachers has to be developed in an integrated and balanced manner in
accordance with the National Philosophy of Education. The aspect that requires
emphasis is holistic thinking in order that the management of the teaching and learning
processes can be deployed in an integrated manner.
I n line with the above requisite, the syllabus for Education Studies {KPLI (SR)} has been
designed integratively to enable the prospective graduands to perform their duties as
effective educators. To ensure all teachers attain an overall exposure, this syllabus
contains the following three components1.
2.
3.
Educational Psychology
Pedagogy
Professionalism of Teachers
GOALS
The syllabus for Education Studies KPLI (SR) has been designed to produce efficacious
graduate teachers who are conversant with all aspects of the knowledge world.
The components incorporated into this syllabus include educational psychology,
pedagogy for primary schools and the professionalism of teachers.
The Educational Psychology component highlights the producing of teachers who
understand child development and who are capable of developing the potential of a
child. With communication and interactive skills, the teachers are capable of preparing a
conducive classroom environment and a meaningful learning milieu for pupils. Apart
from that, the teachers play the role of guides who are mindful of the needs of their
pupils. The presence of such teachers ' wilt engender a sturdy psycho-social support
system in schools.
The contents of the Pedagogy component have been formulated to enable teachers to
plan and manage classrooms effectively. The knowledge and skills acquired enable
teachers to implement and develop the curriculum besides carrying out quality
evaluation in primary schools.
The contents of the Professionalism of Teachers component have been planned to
produce teachers who possess a high degree of professional knowledge and skills, who
are resilient, authoritative and capable of facing current and future challenges.
2
Overall Objectives
The curriculum for Education Studies (Primary School) has been designed to enable
students to:
1.
2.
equip themselves with knowledge in psychology, psychology of education and
child development;
i nculcate thinking skills of students and to identify various learning styles to
i mprove learning;
3.
master and practise effective communication when helping students learn;
4.
understand and appreciate the aims of the National Philosophy of Education
and the Philosophy of Teacher Education in curriculum management and
development;
5.
6.
7
interpret the aims of the Integrated Curriculum For Primary Schools and to
i mplement it;
understand the various roles and duties of a professional teacher and practise
sound educational values and attitudes to enhance professionalism
acquire knowledge and skills in classroom management so as to establish a
conducive classroom environment for teaching and learning;
8.
apply teaching models in the teaching and learning process;
9,
carry out evaluation on teaching practices to discern the performance of pupils as
well as to improve the quality of teaching and learning;
10,
acquire skills for carrying out remedial, enrichment and inclusive
activities in the classroom.
3
education
CONTENT AND TIME ALLOCATION
Component
Hours/
Credit
30
2
2_ Pedagogy
45
3
3.
30
2
105
7
1.
Educational Psychology
Teacher Professionalism
Total
is
4
I NSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES
The following approaches and strategies will be employed to achieve the subjects
objectives;
• Andragogy
Synergogy
•
•
Pedagogy
Discussion
•
Seminar
•
• Brainstorming
• Lecture
• Socio-drama
•
Project
• Role play
• Singing
• Creative movements
Self-access
•
Storytelling
•
Discovery-Inquiry approach
•
• Tele-conferencing
• Practical Sessions
I ndividual/Group performances
Critiques of audio-visual materials
Field trips
Exhibitions
Forum
Quiz
• Generative
Mediative
•
•
Directive
Cooperative
•
• Collaborative
Mastery Learning
•
5
SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES
Supplementary activities are supportive exercises to enable students to experience
interactive and reflective learning processes. This is to encourage them to think
critically and creatively. The activities conducted require them to recall, explain and
apply theories and concepts taught in the classroom. The supplementary activities
consist of project-based learning, seminar and field trip in accordance with the
requirement of the curriculum
Component
Educational
Psychology
Pedagogy
Topic/ Subtopic
2.3
Activity
Motivation
Discuss myths related to motivation
3.2 Self-Concept
Taking notes, analyzing and interpreting
quotations regarding self-concept
5.2 Role of teachers in
guidance and
counseling
Analyzing the Annual Guidance and
Counselling Programme of a Guidance
and Counselling Unit and identify the
planned guidance activities
6.0 Bahavioural
Problems
Students gather newspaper articles
about pupils with behavioural problems.
They are to categorize these problems
and identify the contributing factors.
Students then suggest suitable
behavioural modification techniques to
be used to decrease I make extinct
undesirable behaviour
1.3 Classroom Routine
Identify an effective teacher and
describe his/her classroom routine
practice and leadership styles
4.5 Strategies of teaching
and learning of smart
pedagogy
Study CDCITED documents on teachingl earning strategies of smart pedagogy to
see its application in the classroom
6.5 Item Construction
Use computer software Quest to
formulate and analyze test items
8.5 Alternative
Assessment
Prepare a teaching portfolio
6
Component
9.1
Teacher
Professionalism
Activity
Topic/ Subtopic
Remedial Education
Smart partnership with State Education
Department/school to obtain information
on learning problems.
Participate in remedial resource
preparation workshop
9.3 Inclusive Education
Field trip to school with inclusive
education programme
7.0 Challenges to the
teaching profession
Attend courses: trainer training, stress
management, time management etc to
enhance internal strength
ii
7
COMPONENT 1:
EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY ( 2 Credits, 30 Hours)
SYNOPSIS
This component focuses on basic concepts of psychology and educational psychology
and their importance to teachers. Students will be guided to understand the principles of
growth and development of pupils to develop their potential to the optimum. The
students will also be introduced to topics on individual differences, needs, personalities
and learning styles of children. With this knowledge students will be able to improve the
effectiveness of pupils' learning process.
Students will also be equipped with effective communication skills to ensure that they
have the ability to play the role of a guide for the pupils. In addition, the students will be
equipped with skills and knowledge for identifying behavioral problems as well as for
making modifications to such behaviors.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of this component, students will be able to:
explain the basic concepts of psychology and educational psychology and
their importance to teachers;
ii.
explain with examples the principles and characteristics of growth and
development of pupils in the process of helping them expand their potential to the
optimum;
M.
i dentify individual differences, needs and personalities of children;
iv.
inculcate the thinking habit in pupils and discern various learning styles in order
to enhance the learning process of the pupils;
v.
clarify the basic concept and principles of guidance,
vi.
master and practise effective communication skills; and
vii.
explain the behavioral problems of pupils and apply ways to modify
such behaviors.
8
COMPONENT I:
EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY
TOPICS AND TIME ALLOCATION
1.
Concepts of Psychology and Educational Psychology
2 hours
2.
Nature of Man
8 hours
3.
Development of Personality and Self-Concept
3 hours
4.
Thinking and Learning Styles
4 hours
5.
Guidance in Education
8 hours
6.
Behavioral Problems
5 hours
TOTAL
9
30 hours
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
VALUES/NOTES
1. Concepts Of Psychology
And Educational
Psychology (2 Hours)
1.1 Concept of
Psychology and its
Importance
Explanation of
concepts and their
respective
importance
o Psychology
o Education
o Educational
1.2 Concept of
Education
1.3 Concept of
Educational
Psychology and its
Importance
Strategy
• Lectures
• Group discussion
• Futuristic Studies
Psychology
•
Relating
knowledge of
educational
psychology to
make
observations,
predictions and
control of pupil
behavior
•
Understand
concepts of growth
and development
Strategy
• Group discussion
•
Explain the
principles and
factors influencing
growth and
development of
the child
(childhood to
adolescence)
Values
• Understand theories of
child development
• Appreciate the
magnificence of God's
creation
2. Nature Of Man (8 Hours)
2.1 Growth and Development Of
Children (from Childhood to
Adolescence)
•
•
Concept and Principles
of Growth and
Development
Factors Influencing
Growth and Development
• Hereditary
Environment
l0
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
•
Stages Of Growth and
Development (from physical,
cognitive, social, emotional
and moral aspects) in
accordance with the
Theories of
• Jean Piaget
∎ Arnold Gesell
• Robert Havighurst
• Erik Erikson
• Lawrence Kohlberg
•
Elucidate main
characteristics of
the various stages
as contained in the
theories
Ways a Teacher Can Help
Pupils to Achieve Optimal
Development
Plan ways a
teacher can help
students achieve
optimal
development
22 Human Potential
• Multiple Intelligences
Concept and Types of
Multiple Intelligences
•
Explain various
types of
intelligences and
ways a teacher
applies them in
teaching and
learning
• Ways a Teacher
Applies Multiple
Intelligences in The
Teaching and Learning
Process
• Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
∎ Concept of Emotional
I ntelligence
•
Explain the
concept and
characteristics of
emotional
intelligence (Daniel
Coleman)
•
I dentify ways a
teacher can help
students develop
and manage their
emotional
i ntelligence
• Daniel Goleman's
Theory
• Ways a Teacher
Can Help Students
Develop and
Manage Their
Emotional
I ntelligence
11
VALUES/NO
Strategy
• Metacognition
• Lectures
• Group discuss
Thinking Skills
Graphic organ
comparing and
contrasting
Strategy
• Project
Strategy
• Group Discussio
Thinking Skills
Graphic organiz
classification
t
Thinking Skill
• Compare and co
IQ and EQ
I
Strategy
Examples of case
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
2.3 Motivation
• Concept and Types of
Motivation
• Factors Influencing
Motivation
•
Maslow's Hierarchy
of Needs
∎
Skinners's Behavioral
Theory
(reinforcement)
•
•
•
Effects of Motivation on
Students
•
Anxiety
•
Attitude Change
∎
Curiosity
Locus of Control
•
∎
Learned
Helplessness
Environment of Pupils
•
•
•
•
•
Explain concept
and types of
motivation
Describe factors
that influence
motivation
Visualization of
factors that shape
motivational levels
VALUES/NOTES
Strategy
Metacognition
Supplementary Menu
• Discuss myths related to
motivation
(refer to Travers, Elliot &
Kratochwill, 1993:285286)
Predict pupil
behavior based
upon their
motivational levels
Thinking Skills
• Compare and contrast
the effects of positive
and negative motivation
on students
Ways a Teacher Can
I ncrease Motivation of
Pupils
•
Environment for
Teaching and Learning
• Cooperative and
Collaborative Learning
• Positive and Negative
Reinforcement
List ways a
teacher can
motivate pupils in a
variety of situations
Implications of Motivation
on the Teaching and
Learning Process
(before, while and after
the teaching and
learning process)
Strategy
Cooperative learning
• Collaborative learning
Values
• Every individual has the
potential to succeed
12
SKILLS,
KNOWLEDGE
2.4 Individual Differences
• Concept and Types of
I ndividual Differences
(physical, cognitive, social,
emotional and spiritual)
•
•
•
•
Discerning
individual
differences through
observation
•
Pupils at Risk
Mixed Ability Pupils
Culturally Diverse Pupils
Pupils from Different
Social Classes
Differences in
Socialization
Differences in Location:
Urban versus Rural
•
•
• Effects of Individual
Differences
Thinking Skill
• Graphic organiz
comparing and
contrasting
Values
• Every human b:ti~
unique
•
• I mplication for Teachers
3.
VALUESINO
Relating
i ndividual
differences to the
teaching and
l earning process
Development Of
Personality and SelfConcept (3 Hours)
3.1 Personality
• Concept and
Classification of
Personality
•
Role of Teachers
i n Shaping Positive
Personality in Pupils
•
Factors Influencing
personality
Al-Ghazali
Soul
Mind
Desire
Ability to make
conceptual
visualization on
personality of pupils
and give responses in
accordance with their
personalities.
i3
Strategy
• Examples of case
Values
• Awareness
• Concern
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
Freud
-
Id
Ego
Superego
Supplementary Menu
Taking notes, analyzing
and interpreting
quotations regarding
self-concept
3 .2 Self-concept
Definition and Types of
• Self-concept
• Ways a Teacher Can
Help
to Form Positive SelfConcept
3.3 Positive and Negative
Defence Mechanisms
4.
VALUES/NOTES
•
Relating behavior of
pupils to types of
defence mechanisms
I dentify ways to help
pupils form a positive
self-concept
Strategy
Contextual learning
•
Understand
concept and
definitions of types
of thinking
Strategy
• Generative
• Collaborative
•
Master types of
thinking through
simulation
activities
Thinking And Learning
Styles (4 Hours)
4.1 Thinking
• Concept of Thinking
•
Types of Thinking
• Lateral
• Vertical
• Critical
• Creative
• Divergent
• Convergent
14
KNOWLEDGE
•
Ways to Cultivate Pupils'
Thinking Skills
SKILLS
•
Relating Right
Brain t Left Brain
hemispheres with
critical and creative
thinking skills (Split
Brain Theory by
Roger Sperry)
•
4.2 Learning Styles
•
Definition and Types of
Learning Styles
•
•
Dunn and Dunn
Model
I mplications on
Teaching and
Learning Process
Identify ways
teachers can
cultivate pupils'
thinking skills
•
Identifying learning
style preferences
of students
•
List teaching and
learning activities
i n accordance to
learning styles of
pupils
VALUES/NO
Strategy
• Generative(D
I nquiry)
Values
•
Every human
unique
Guidance In Education
(8 Hours)
5.1 Introduction to
Guidance
• Concept, Principles and
Aims of Guidance
•
• Give operational
definitions for
concept,
approaches and
types of
guidance
Approaches to Guidance
• Development
• Prevention
• Remedial Education
• Crisis
15
Strategy
Problem solvinc
u
Strategy
•
Project
: KNOWLEDGE '
VALUESINOTES
.Types of Guidance
• Individual
• Group
Planning and
implementing
guidance
activities in
schools
5.2 Role of Teachers
i n Guidance and
Counseling
5.3 Communication Interpersonal
•
Concept
•
I nterpersonal
Communication Skills
•
Building
Relationships
Paying Attention
∎
∎
Active Listening
•
Using Appropriate
Language
•
Understanding Body
Language
•
Giving Appropriate
Responses
Generating
analogies on
barriers to
communication
•
Supplementary Menu
• Analyze an Annual
Guidance and
Counseling Programme
of a Guidance and
Counseling Unit in a
school and identify
planned guidance
activities
Thinking Skills
Comparing and
contrasting
Strategy
Applying
effective
communication
skills
•
Values
•
Barriers to communication
•
Physical
•
Psychological
•
Environmental
•
Social
Discussion based on
situational pictures
Awareness of the
importance of
interpersonal
relationship
Strategy
•
Directive
•
Simulation
Implication of Using
Communication Skills in
Creating Effective
I nterpersonal Relationships
16
r
;_SKILLS
NOWLEDG
VALUES/NOT
6. Behavioral Problems
(6 Hours)
~'
6.1 Definition
6.2 Types of Behavioral
Problems
6.3 Methods to Identify Pupils
with Behavioral Problems:
•
Test-based Methods
• psychological
∎ diagnostic tests
•
Non-test Methods
• observation
• interview
•
Research Methods
• case studies
• document studies
• cross-sectional
studies
• l ongitudinal studies
List and classify
types of
behavioral
problems
Strategy
Ways to identify
pupils with
behavioral
problems
Thinking skills
•
Graphic organ
classification
Strategy
6.4 Behavior Management
•
Definition
•
Process
•
Objectives
Values
•
• I ncrease and
Maintenance of
Desirable
behaviours
Mediative
Simulation
Futuristic Studi
Empathy towar
needs of studen
Thinking skills
Graphic organiz
classification
• Decrease and
extinction of
undesirable
behaviors
17
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
VALUES/NOTES
Behavior Management
Techniques
•
Reinforcement
•
Punishment
•
Behavior Extinction
•
Reverse Psychology
•
Shaping
•
Token Economy
•
•
Contract (oral and
written)
•
Time-out
•
Modeling
•
Self-restraint
•
Self- management
•
•
Applying behavior
management
techniques
•
Predicting the
behavior of pupils
which emanates from
the action of teachers
•
Identify behavior
modification
techniques suitable to
the cognitive levels of
pupils
Self-reinforcement
Isolation
6.5 Implication on the
Teaching and Learning
Process
Able to identify
suitable techniques to
maintain and increase
desirable behavior /
decrease and make
extinct undesirable
behaviors on a case
by case basis
18
I
Strategy
•
•
Mediative
Examples of case
studies
Futuristic Studies
Supplementary Menu
• Students gather
newspaper articles about
pupils with behavioral
problems. They are to
categorize these
problems and identify the
contributing factors.
Students then suggest
suitable behavioral
modification techniques
to be used to decrease 1
make extinct undesirable
behavior
INDICATIVE READING
Beebe, S.A. & Beebe, S.J. (1996). Interpersonal Communication. Relating Others.
Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Dorothy, J.B. (1998). The School Counselor's Book of List. New York: Macmillan.
Harris,J.K. & Lierbert,R,M. (1987). The Child: Development from Birth Through
Adolescence. London: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (1996). Panduan Pelaksanaan Perkhidmatan
Bimbingan dan Kaunseling. Kuala Lumpur: Bahagian Sekolah.
Slavin,R.E. (1991). Educational Psychology: Theory into practice. Englewood Cliffs:
Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Travers, J.F.et.al_(1993). Educational Psychology: Effective Teaching, Effective
Learning. Madison: Brown & Benchmark.
Wooifolk,A. (2001). Educational Psychology. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
19
COMPONENT 2;
PEDAGOGY (45 Hours, 3 Credits)
SYNOPSIS
This component aims to enable students to transform the aspirations of the National
Philosophy of Education into the process of teaching and learning in order to produce
effective learning. This component is structured to integrate pedagogical and evaluation
aspects. It is expected with the mastery of knowledge, skills and values, students will be
able to manage their classroom and be knowledgeable in planning and conducting the
teaching and learning process effectively. The aspect of school assessment is also
stressed to enable students to plan, conduct and manage classroom assessment.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of this component, students will be able to:
i.
i nterpret their roles as class managers based on the elements of
organizational management to promote a conducive teaching and learning
environment;
ii.
relate learning theories with classroom management, planning and
implementation of teaching;
iii.
apply various teaching models in the teaching and learning process:
i v.
implement evaluation on teaching and learning practice with the aim of
identifying pupils performance to enhance the quality of teaching and
learning;
v.
i dentify various learning problems for remedial purposes;
vi.
conduct remedial and enrichment activities in the classroom, and
vii.
identify roles of teacher in inclusive education.
20
COMPONENT 2: PEDAGOGY
TOPICS AND TIME ALLOCATION
1.
Classroom Management
4 hours
2.
I nteraction and Communication in the Classroom_
4 hours
3.
Theories and Process of Learning
8 hours
4.
Teaching
13 hours
5.
Testing and Evaluation
4 hours
6.
Basic Statistics
4 hours
7.
Primary School Based Assessment
2 hours
Remedial, Enrichment and Inclusive Education
6 hours
Total
21
:
45 hours
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES
Classroom Management
(4 hours)
1.1. Concept of Classroom
Management
1.2. Factors that Influence
Effective Classroom
Management
•
Physical
• Lay-out Plan
•
•
•
Provide conducive
classroom environment
to promote effective
teaching and learning
process.
Functions of
Lay out Plan
Identify aspects of good
classroom management
Social
•
•
Class Rules
and
Regulations
Sociometry
Emotional
∎
Teacher
Leadership
Strategies
• Generative
• Discussion
• Brainstorming
Values
•
Sensitive to the
significance of
classroom
management.
Aware of the needs of
mixed ability pupils in
the context of
classroom
management
1.3. Classroom Routine
•
•
Concept of Routine
Types of Routine
∎ Class Routine
(non academic)
∎
Administrative
Routine
•
Pupil Movement
Routine
•
Task
Management
Routine
•
Record pupils'
i nventories; attendance,
academic profile, health
and discipline
Manage classroom
routine to promote
pupils' self discipline
22
Values
Aware of the
importance of routine in
teaching and learning
SKILLS
KNOWLEDGE
•
Learning
Routines (that
support
teaching and
learning:
collecting
books,
marking,
distributing
resources and
books etc)
•
Describe and set up
classroom routines that
promote learning
•
I nteraction
Routine (that
determine
patterned
interaction;
when and how
interaction
should happen)
1.4. Classroom Discipline
'
Concept
•
Causes of Discipline
Problems in the
Classroom
•
Ways to handle
Discipline Problems
in the Classroom
•
•
∎
•
•
VALUES/NOTES
• Identify causes of
discipline problems in
the classroom
Constructive
warning
Punishment
Prevent
misbehaviour
Managing
Discipline
without stress
Practise
appropriate
disciplinary
strategies
Supplementary Menu
•
Practise appropriate
procedures to enhance
classroom discipline
23
• I dentify an effective
teacher and describe
his / her classroom
routine practice and
leadership styles.
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES
Z, I nteraction and
Communication in the
Classroom ( 4 hours)
2.1- Classroom Interaction
•
Create various
interaction patterns in
the classroom
•
Create effective
classroom interaction
in the classroom
2.2. Types of Interaction
and their Significance
2.3. Ways to Create
Effective Classroom
Interaction
Strategies
Discussion
Simulation
•
Directive
2.4. Classroom
Communication
•
Types of
Communication
•
Communication
Models
•
•
Obstacles and
Barriers to
Communication
Ways to Create
Effective
Communication in
the Classroom
• I nterpret definitions of
communication based
on models of
communication
• Suggest ways to
overcome barriers in
communication
• Practise effective
communication in the
classroom
Thinking-Skills
•
Graphic Organizer:
Conceptual
Values
Aware of the needs
of interaction in
i nterpersonal and
intrapersonal
development
Aware of the
importance of
effective
communication in
teaching and human
relations.
Note
Refer to article:
•
classroom discourse
•
Models:
Shannon and
Weaver, Wilbur
Schramm
24
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES
3. Theories and Process of
Learning
( 8 hours)
"
3.1. Concept of Learning
3.2. Theories of Learning
•
Behaviourist
•
Social
•
Cognitive
•
Compare and contrast
theories and the
learning process
Strategies
Discussion
•
Library research
Thinking Skills
Graphic Organizer::
Compare and
contrast
Humanistic
Constructivist
Values
•
Aware that a strong
opinion is backed b
a theory,
3.3. Process of Learning
•
•
•
•
•
Learning readiness
Pattern Recognition
(Pengamatan)
Perception
Relate theories and
the process of
learning in the
classroom
(Penanggapan)
Remembering and
Forgetting
Sensitive and
concerned about
matters that
influence effective
l earning
3.2: Focus on the
principles developed
by the following:
Behaviourist: Skinne
Cognitive: Piaget,
Social: Bandura
Humanistic: Carl
Rogers
Constructivist:
Vygotsky)
Transfer of
Learning
3.4. Implications of
Theories and Process
of Learning in Teaching
and Learning
25
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES
4. Teaching
(13 hours)
4.1. Concept of Teaching
4.2. Models of Teaching
and its Implication on
Teaching and
Learning.
•
•
Explain the concept of
teaching
•
Compare and contrast
the models of teaching
and their implications
in teaching and
l earning.
Expository
•
I nformation
processing
•
I nquiry
•
Project
Strategies
•
Directive
• Demonstration
•
Self Directed
Learning
•
Source information
through internet
Values
•
Aware of the
importance of
teaching models in
determining lesson
planning framework
4.3. Teaching Strategies
Teacher Centered
Student Centered
Resource Based
•
Task Based
Describe the
strategies of teaching
4.4. Teaching Approaches
•
Integration
•
Deductive
•
•
Inductive
Eclectic
List down the
characteristics of each
teaching approach.
•
4.5. Strategies of Teaching
and Learning in smart
pedagogy
•
•
•
•
•
Directive
Mediative
Generative
Observation
Values
Identify various
teaching strategies of
smart pedagogy.
Contextual
26
Aware of the needs to
master various
approaches,
methodologies and
techniques of effective
teaching
KNOWLEDGE
•
I
SKILLS
I
VALUES/NOTES
Metacognitive
Field study
•
•
Futuristic studies
•
Mastery Learning
•
Cooperative/
Collaborative
4.6 Integration of Generic
Skills in Teaching and
Learning
Application of generic
skills:
thinking skills,
i nformationcommunication
technology skills (i CT),
facilitating skills, learning
skills, and evaluation and
assessment skills.
4.7 Methods and
Techniques of Teaching
•
•
•
•
•
Learning through
Play
Role Play
Brainstorming
Thematic
I ntegration
•
Story Telling
•
Discussion
•
•
•
•
Facilitating
(including
facilitating skills)
• Decide on appropriate
methods and
techniques for effective
teaching and learning.
• Explain the
characteristics of
facilitation: questioning,
sampling, scaffolding,
directive, cognitive
structuring
Inquiry
Demonstration
Problem Solving
[Theory of
Constraint (TOC)]
27
Supplementary Menu
Refer to CDC/TED'
documents on
teaching and iearnO
strategies of smart
pedagogy to look int
its application in
classroom .
Note
• TOC
(refer to Appendix D
Major subject lecturer
will focus in detail on
methods and
techniques of
teaching, lesson
planning and
micro/macro teaching
KNOWLEDGE
4.8 Factors affecting the
choice of Methods and
Techniques of Effective
Teaching.
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES
Identify the factors
that influence the
choice of
methodologies and
techniques of effective
teaching.
Testing and Evaluation
(4 hours)
5.1 Concept of
Measurement, Testing
and Evaluation.
Aims of Testing and
Evaluation
5.2 Main Characteristics of
Tests
5.3 Types of Testing and
Evaluation
•
•
•
•
Formative and
Summative Tests
Performance and
` Pencil and Paper'
Tests
Elaborate the aims and
functions of evaluation in
teaching and learning
Identify the main
characteristics of tests
Compare and contrast:
types of tests and types
of evaluations.
Speed and
Endurance Tests
Strategies
Directive
∎ Lecture
Experiential Learning
Self Directed
learning
•
Learning through the
i nternet
Thinking Skills
•
Graphic Organizer
Compare and
Contrast
Note
Refer to primary
school format and
test questions
Values
Aware of the
importance of
evaluation in the
process of teaching
and learning
Norm-referenced
and Criterionreferenced Tests
28
KNOWLEDGE
5.4 Test Blueprint / Table of
Specifications (JPU)
•
•
•
Main
Characteristics
Constructing Test
Blueprints
The Importance of
Test Blueprints
5.5 Item Construction
•
•
Objective Items
Subjective Items
5.6 Marking Approaches
•
•
Analytic Marking
Holistic Marking
SKILLS
• Construct Test Blueprint
(apply principles of testing
I main characteristics of
tests)
• Elaborate on the steps in
building tests.
VALUESINOTES
Values
Having a sense of
responsibility and
honesty in conducti
testing and evaluati
• State the importance of
test blueprints in item
building.
• Determine test item
quality.
• Compare and contrast
subjective and objective
tests.
• Application of analytic and
holistic/global marking
Supplementary Men
•
Use computer
software Quest to
formulate and analyi
test items
Basic Statistics
(4 hours)
6.1 Graph, Ogive,
Histogram, Distribution
Curve, Frequency
6.2 Min, Median, Mode
6.3 Standard Deviation
(non cumulative data,
cumulative data)
6.4 Standard Scores:
Score z and Score t
• Master the skills of
transferring raw scores
into graphs : histogram,
polygon and ogive
• Apply statistical formulae
to interpret scores for
report writing purposes
29
Strategies
•
Directive
•
Module
Self Directed
•
Learning
•
Self/Peer evaluation
Values
Aware of the
•
significance of
transferring data into
graphs for the
purpose of
i nterpretation
KNOWLEDGE
6.5 Data Interpretation and
Report Writing
SKILLS
I
VALUESINOTES
Analyze and interpret
data for report writing
Aware of the
importance of data
as a foundation for
follow-up activities
Resource
EXCEL or SPSS
programme
7
Primary School Based
Assessment (PKSR)
(2 hours)
Strategies
•
I nterview primary
school teachers on
the implementation
of PKSR
Directive
•
7.1 Definition
7.2 Principles
7.3 Aims
7.4 Methods of Conducting
PKSR
7.5 Alternative Assessment
Portfolio
•
Use various types of
authentic and valid
assessment to
evaluate pupils
performance
Values
Aware of various
•
authentic alternative
evaluation methods.
•
State types and
characteristics of
portfolios
•
•
Use portfolio as an
alternative assessment
Presentations l
Practicals
Observation
r
30
Supplementary Menu
Prepare a teaching
portfolio
KNOWLEDGE
8
SKILLS
VALUESINOTES~
Remedial, Enrichment
and Inclusive Education
(6 hours)
8.1
•
Remedial Education
(3 hours)
Concept, Rational
and objectives of
Remedial Education
Learning Difficulties
•
Causes of Learning
Difficulties
•
Types of Learning
Difficulties (3Rs)
•
Methods of
Identifying Learning
Difficulties
•
Role of Teachers in
Conducting
Remedial Teaching
•
∎
•
•
conducting skills
remedial
activities
resources for
remedial activities
• Explain concept, rational
and objectives of
remedial education
• identify factors causing
learning difficulties
• Identify types of
l earning difficulties (3Rs)
• Master the skills of
identifying learning
difficulties
•
∎
•
•
•
•
Construct inventories
Observation
Interpret performance
record
Construct paper and
pencil tests
Plan daily exercises
Conduct question and
answer sessions 1
quizzes
• Describe important
steps in organizing and
carrying out remedial
teaching
• Master the skills of
conducting remedial
teaching
• Acquire the skills of
preparing remedial
resource materials
31
Strategies
•
Directive
•
Lecture
Generative
•
•
Discussion
Supplementary Menu
•
Smart partnership
with State
Education
Department/school
to gather information
on learning
difficulties
Note
•
Remedial and
enrichment activities
need to be related to
Mastery Learning
Supplementary Menu
Participate in
•
remedial resource
preparation
workshop.
Values
Empathy towards
pupils with learning
difficulties.
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS
8.2 Enrichment
Education
(2 hours)
•
Explain concept, rational
and objectives of
enrichment
Concept, Rational,
and objectives of
Enrichment
Programmes
•
I dentify various types of
enrichment activities:
•
Reading
Writing
•
Arithmetic
Types of
Enrichment
Activities
VALUES/NOTES
Strategies
Directive
•
Lecture
Generative
'
Discussion
Methods of
Conducting
Enrichment
Activities
8.3 Inclusive Education
(2 hours)
•
Concept of
I nclusive Education
•
Children with
Special Needs
•
Roles of Teachers
and Resource
Teachers
• Show difference in
concept between
inclusive and special
education
•
I dentify the
characteristics of
children with special
needs
∎
•
•
•
•
•
Mentally retarded
Learning Disabilities
Behavioural
Disorders
Communication and
Hearing Impaired
Visual Impaired
Spastic
Gifted and Genius
Know the role of
teachers and resource
teachers in conducting
i nclusive education
32
Values
•
Aware of the
significance of
inclusive education in
the National
Education System.
Supplementary Menu
Field trip to school
with inclusive
education
programme
INDICATIVE READING
Arends, R.I. (2001). Learning to teach. Boston: McGraw Hill.
Good,T.L. & Brophy,J.E. (1997). Looking into Classroom. New York: Addison- Wesley
Longman,lnc
Gronlund,N.E & Linn, R.L.(1 990). Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching. New
York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
Hadfield,J, (1992), Classroom Dynamics. Oxford: OUP.
Hopkins, C. D. & Antes, R. L. (1990). Classroom Measurement and Evaluation.ltacas:
Peacock Publishers.
Joyce,B. & Weil,M.(1986). Models of Teaching. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall Inc.
Robiah Sidin.(1993). Classroom Management. Kuala Lumpur: Fajar Bakti Sdn Bhd.
Sergiovanni, T.L. & Starratt,R.J. (1993). Supervision: A Redefinition. New York:
McGraw-Hall International Editions.
Wragg, E.C. (1993). Primary Teaching Skills. London: Routledge.
33
COMPONENT 3: TEACHER PROFESIONALISM
(2 Credits, 30 Hours)
SYNOPSIS
This component focuses on the role of teachers in realizing the National Philosophy of
Education (FPK) and the Philosophy of Teacher Education(FPG). The various aspects of
teaching professionalism covered in this component aim to enable students to face and
conquer various challenges in the teaching profession. Students are exposed to different
philosophical schools of thought and to the main characteristics of the National
Philosophy of Education and the Philosophy of Teacher Education to enable them to
understand the aspirations of the National Education Policy. Students need to
understand the goals of the Primary School Integrated Curriculum (KBSR) to enable
them to organize and develop the curriculum in planning, teaching and learning in order
to meet the needs of the National Philosophy of Education. Students need exposure on
professional skills to enable them to make decisions and take necessary actions in the
teaching and learning context. Students are also expected to practise knowledge culture
through research. The enhancement of knowledge and skills will also help in preparing
them to face various changes and future challenges in the teaching profession,
LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of this component, students will be able to
i.
state the needs of the National Philosophy of Education and Philosophy of
Teacher Education in the teaching service;
ii,
describe the concept of curriculum, types of curriculum and factors
that influence development and change in the curriculum;
I l l.
interpret the needs of the Primary School Integrated Curriculum in the
context of the National Philosophy of Education;
iv
explain the roles of teachers in implementing changes in curriculum;
v.
conceptualize teaching as a profession and identify characteristics of
professional teachers;
vi.
outline the various tasks and roles of professional teachers;
vii.
practise teaching values and attitudes to enhance professional qualities, and
viii.
interpret the imminent challenges in the teaching profession.
f4
TOPICS AND TIME ALLOCATION
Fundamentals of the National Philosophy of Education and Philosophy
of Teacher Education
2.
Management and Development of Curriculum
3.
Teaching as A Profession
4.
Teachers and the World of Education
5.
Teacher Professional Skills
6.
Enhancement of Professionalism of Teachers
7.
Challenges in the Teaching Profession
6 hours
9 hours
4 hours
2 hours
2 hours
3 hours
TOTAL
35
4 hours
30 hours
Y
S,.
~, Fundamentals of the
National Philosophy of
Education and Philosophy
of Teacher Education
(6 hours)
1.1 Basic Concept of
Philosophy of Education
Explain the basic concepts of
philosophy and education in
relation to FPK
Philosophy
•
•
Education
1.2 Western Philosophy of
Education
•
•
Traditional
(Perennialism,
Values
Essentialism)
Modern
(Progressivism
Compare and contrast
philosophies of
education from the
western and Islamic
points of view.
Reconstructionism)
1.3 Islamic Philosophy of
Education
1.4 National Philosophy of
Education (FPK)
1.5 Philosophy of Teacher
Education (FPG)
•
Goals
•
Professional Values
of Teachers
•
Teacher Education
Conceptual Model
Strategies
•
Discussion
•
Brainstorming
•
Lecture
• Forum
Debate
•
Explain the factors that
influence the development of
FPK.
Elaborate elements in the
FPK
Describe FPG based on
goals and Teacher Education
Conceptual Model.
1.6 Implications of FPK and
FPG to teachers as
educators
36
I nternalise FPK and
FPG towards nation
building
• Aware of the roles of
educators in nation
building.
Thinking Skills
• Graphic Organizer
Compare and contrast
SKILLS
XNOWLEDGE.`
Management and
Development of the
Curriculum (9 hours)
Discuss curriculum
development based on the
following curriculum models • Objective model (Tyler,
Taba)
• Process Model
(Stenhouse)
• Current Trends
2.1. Concept of Curriculum
• Concept and Types
of Curriculum
• Models of Curriculum
(Tyler, Taba,
Stenhouse)
2.2. Factors that influence
Development and
Change in the
Curriculum
2.3. Primary School
I ntegrated Curriculum
( KBSR)
•
Goals
•
Main
Characteristics
•
•
•
•
•
•
Objectives
Structure
Components
2.4. Modifications in KBSR
Syllabus
2.5. Role of Teachers in
implementing
Curriculum
VALUESINOT
•
•
•
Explain the factors that
i nfluence development and
change in the curriculum
• I ndividual
• Community and
Nation
• Universal
•
Play role as curriculum
i mplementer
•
Describe the role of teachers
in implementing KBSR that is
appropriate with the era of
I nformation Communication
Technology (ICT).
• Interpret
• Plan
• Modify
• Evaluate
37
Discussion
Directive
Group
Values
Describe the of curriculum
• Formal curriculum
• Hidden curriculum
Analyze and interpret main
characteristics of KBSR in
the context of FPK.
Strategies
I nternalise the rol
the education sy
nation building
•
Aware of the
i mportance of
curriculum in the
context of episte
•
I nternalise the cha
of curriculum and
responsibility of
teachers in
implementing the
curriculum
Have commitmentiO
i mplement curricu
relation to education
roles and innovation
Resource
•
•
Refer to Documents
KBSR (Min. of Edu.
Surf: Min. of Edu Ma
website,
httpalwww.moe.gov
3. Teaching as A Profession
(4 hours)
3.1. Concepts of
Professional and Nonprofessional
•
3.2. Code of Ethics of the
Malaysian Teaching
Profession
Compare and contrast
professional and nonprofessional characteristics
of teaching career
3.3. Teacher Accountability
towards:
•
•
•
•
Study and discuss the
characteristics and qualities
of professional teachers
School
Behaviour
Pupil
Profession
Study and analyze the code
of ethics of the Malaysian
Teaching Profession
Community
•
The Teacher and the
World of Education
(2 hours)
•
•
•
•
•
Knowledge
Practitioner
Skill Practitioner
Value Inculcator
Educator
(Educare I
Educere)
Socialization
Agent
Study professional and nonprofessional concepts and
its relation to the teaching
profession
Relate the code of ethics
and accountability to
teachers' task in school
Strategies
•
Discussion
•
Examples of cases
Collaborative
learning
•
Values
I nternalise and value
knowledge
Virtue
•
•
Sensitive to change and
ready for changes
•
I nternalise the code of
ethics and strive to
become an excellent
teacher
•
Appreciate, love and be
fully committed to the
teaching profession
•
Thinking Skills
•
Analyze the roles and
responsibilities of teachers
as
Effective provider of
knowledge, skills and
values.
Educator in the teaching
career
Agent of socialization and
change in community
38
Graphic Organizer
Compare and contrast
Strategies
•
•
•
•
Group Discussion/Buzz
Session (based on
current issues)
Workshop
Brainstorming
Examples of cases
Simulation activities
h
~-
K
SKILLS
WLED
Change Agent
•
Consultant and mentor to
pupils in classroom
Manager, planner,
implementer and researcher
who can contribute new
ideas in teaching and
l earning.
Role model and patriotic to
the nation
Community
innovator
•
•
Nation-Builder
Knowledge
Disseminator
•
•
Caring
I ntellectual
•
AI'UESINOTr,,
Values
• Uphold knowledg
• Diligent
• Cooperative
•
Consultant
•
Mentor
Manager
•
•
I nternalise the wo
education and act
line with national
development
a
Researcher
•
Patriot
Professional Skills
(2 hours)
Skills
•
Learning
•
Planning
•
•
Master professional skills in
learning and thinking
Thinking
Facilitating
•
Master skills of interacting
•
Communicating
Master skills of managing
ICT.
•
Managing ICT
Act as information collector
and idea generator
•
•
Managing
Researching and
Acquiring
I nformation 1
Knowledge
Activist and
Knowledge
Generator
Strategies
• Group discussion
Simulation
Tele-conference
•
E-learning
•
Values
Enhance commitment
towards profession
•
Supplementary Menu:
Attend courses on
Learning Skills
Thinking Skills
Graphic Organizer
Categorizing Professo
Skills
39
Practise knowledge culture.
Enhance teaching knowledge
and skills
Strategies
Group discussion
I ntellectual discourse:
•
seminar, forum, debate
Workshop
'
Action research
•
•
Carry out action research
• Reflect and take action to improve
teaching effectiveness
•
Reflection on action
Reflection in action
Reflection for action
•
•
•
•
Values
Aware of the
i mportance to enhance
teaching
professionalism in
facing challenges and
changes
Sensitive to current
challenges and
development in
education
Prioritize knowledge
Collaborate
Thinking Skills
•
Self Reflection
•
Discuss and study current
issues in education
•
Practise the characteristics
of teachers who can face
current and future challenges
• Commitment
• Vision
• Global view
40
Strategies
•
Futuristic studies
•
I ntellectual discourse:
seminar, forum,
workshop
•
I nternet surfing for
i nformation.
•
Changes in
Education:
∎
•
Smart school
Globalization of
education
•
Optimistic
Knowledgeable
Adaptable
Skillful in
educational
technology
Plan professional
development based on
current trends to face future
challenges
•
Values
I nternalize and
appreciate kno
Sensitive to chap
education and I
technology
Supplementary Menu
•
Attend courses: t
training, stress
management, time
management etc,
enhance internal
strength
I NDICATIVE READING
Day, C. (1999). Developing Teachers: the challenges of life long learning. London: Falmer
Press.
Ornstein,A. C. & Hunkins, F. P. (1998). Curriculum Foundations, Principles and Issues.
Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Ozrnon, H. & Craver,S.M. (1992).
Prentice-Hall, Inc_
Philosophical Foundations of Education. London:
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum>(2001). Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan, Matlamat dan
Misi. Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Schon,D. (1983). Educating the Reflective Practitioner. San Franscisco: Jossey-Bass.
ASSESSMENT
Students' performance is based upon college-based coursework and a
centralized examination. Evaluation is based on 50% course work and 50%
examination.
SUGGESTED COURSE WORK
Below is the suggested course work guideline
Component
Educational
Psychology and
Pedagogy
Task
) Folio
(groups of 3 or 4)
(a) Produce one Folio on classroom
management
(b) Based on the folio, discuss how
classroom management takes
into consideration the aspects of
i ntellectual, physical, social and
emotional development in
conducting teaching and
learning
Teacher
Professionalism
Percentage
10
20
Reflect the outcome of the
discussion in the form of a short
essay not exceeding 1000
words.
(c) Presentation of outcome using
information and communication
technology (ICT)
10
2) Journal Writing
(Individual)
10
Choose one teaching and learning
problem that you have encountered
during Practicum Phase 1.
Submit a journal report on the
stated problem, describing the ways
you have taken to overcome the
problem.
Your report should not be more than
500 words
42
REFERENCES
TEXT
Abd. Halim Hj. Hassan (1994). Komunikasi Dalam Pengurusan Pendidikan.
Kuala Lumpur: Delmu ( Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Abdul Rahman Arof & Zakaria Kasa. (1994). Falsafah dan Konsep Pendidikan.
(Edisi Kedua). Kuala Lumpur: Fajar Bakti Sdn Bhd.
Abdal- Haqq, I. (1998). Professional Development Schools: Weighing the
Evidence. California: Corwin Press, Inc.
Adair, J. (1984). The Skills of Leadership. Aldershot: Gower Publishing Co. Ltd.
Ahmad Rafaai Ayudin (1994). Kaedah Pengajaran Berkesan.
Kuala Lumpur: Penerbitan Al - Kausar.
Aini Hassan et. Al. (1999). Pengajian Sosiologi Dalam Pendidikan: Satu Koleksi
Bahan Bacaan. Kuala Lumpur: Universiti Malaya
Ainon Mohd & Abdullah Hassan. (1999). Kursus Berfikir untuk Kolej dan
Universiti. Kuala Lumpur: Utusan Publication & Distributors Sdn Bhd.
. ( 1996). Pemikiran Lateral Edward De Bono.
Kuala Lumpur: Utusan Publication & Distributors Sdn Bhd.
Aminah Hj. Hashim & Llya, A. P. (1995). Bimbingan dan Kaunseling. Kuala
Lumpur: Federal Publications.
Amir Awang. (1984). Pengantar Bimbingan dan Kaunseling di Malaysia.
Pulau Pinang: Penerbitan USM
Ang Huat Bin. (1999). Konsep dan Kaedah Pengajaran dengan Penekanan
lnklusif. Kuala Lumpur: Utusan Publication & Distributors Sdn Bhd_
Arends,R.l. (2001). Learning to Teach. Boston: McGraw Hill.
Astrid, F. (1994). Interpersonal Skills. Petaling Jaya: Pelanduk Publications.
Baird, B.N. (1999). The Internship, Practicum and Field Placement Handbook.
New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Beder, S. (1993). The Nature of Sustainable Development.
Australia: Scribe Publication.
Beebe,S.A. & Beebe,S.J. (1996). Interpersonal Communication. Relating Others.
Needham: MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Bono, E. de. (1990). Six Thinking Hats. London: Penguin Books Ltd.
43
Bono, E. de. (1991). Teaching Thinking. London: Penguin Books Ltd.
Borders, L.D. & Drury, S. U. (1992). Counseling Programs - A Guide to
Evaluation. California: Corwin Press.
Bruner,J. (1966). Towards a Theory of instruction. New York: Newton
Bruner,J. (1960). The Process of Education. New York : Vintage
Carr, W. & Kemmis, S. (1987). Quality in Teaching. London: The Falmer Press
Chang, R.Y. & Kelly, P.K_ (1993). Step-By-Step Problem Solving.
London: Kogan Page.
Chua Tee Tee & Koh Boh Boon. (1992). Pendidikan Khas dan Pemulihan:
Bacaan Asas. Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
Craft, A. (1996). Continuing Professional Development. London: Routledge
Publishing Co.
Dalton, J. (1989). Adventures in Thinking and Co-operation Talk in Small Group.
Melbourne: Thomas Nelson Australia.
Day, C. (1999). Developing Teachers: the Challenges of life long learning.
London: Farmer Press,
Dorothy, J.B. (1998). The School Counselor's Book of List. New York: Macmillan
Eggen, P. D. & Kauchak,D. P. (1979). Strategies for Teachers. NJ: Prentice Hall.
Elliot, J. (1993a). Three perspectives on Coherence and Continuity in Teacher
Education. In Elliot, J. (Ed.). Reconstructing Teacher Education: Teacher
Development. London: The Faimer Press.
Fleet, Alma & Martin, Lilian (1984). Thinking It Through: Ideas for Classroom
Organisation. Melbourne: Thomas Nelson Australia.
Fleming, L. E. (1994). Becoming a Successful Student. Evanston IL: Harper
Collins.
Fogarty, R. & Bellanca, J. (1990). Teach Them Thinking. Australia: Brownlow
Education for Applied Reseach for Education.
Gardner, H. (1985). Frames of Mind. New York: Basic Books.
-Gardner, H. (1991). Multiple Intelligences: The Theory in Practice. New York:
Basic Books.
Glassman,W.E. (1995). Approaches to Psychology. Open University Press.
Glower, D. & Law, S. (1996). Managing Professional Development in
44
Education. London: Kogan Page Ltd.
Goleman, Daniel.
Bantam.
(1999).
Good, T.C & Brophy. J.E
Longman, Inc.
Working with Emotional Intelligence.
(1997).
Looking into
Guskey, T. R. (2000). Evaluating
Press Inc_
Classroom.
(1992).
York:
New York: Addison-Wesley
Professional Development.
Gutek, L. G. (1998). (2" d . ed.). Philosophical and Ideological
Education. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Hadfield, Jill.
New
California: Corwin
Perspectives on
Classroom Dynamics, Oxford: OUP.
M. (1987). The Child: Development
Through Adolescence. London: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Harris, J. K. & Lierbert, R.
from Birth
Hewit, J. & Whitter, K. S. (1998). Teaching Methods for Today's
Collaboration and Inclusion. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Hopkins, David. (1993). A Teacher's Guide
Buckingham: Open University Press.
to
Classroom
Johnson, K. & Morrow K. (1981). Communication in
Longman Group Ltd.
Joyce, B. & Weil, M. (1986).
Prentice-Hall Inc
Models of Teaching.
Schools:
Research.
the Classroom.
Essex:
Englewood Cliffs, N. J.:
Keating, B. et al. (1990). A Guide to Positive Disciplin. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (1999). Perangkaan Pen didikan/Educa tional
Statistics 1999. Kuala Lumpur: Bahagian Perancangan dan Penyelidikan
Dasar Pendidikan.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (1999). Dasar Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
Kuala Lumpur: Bahagian Perancangan dan Penyelidikan Dasar Pendidikan.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (1996). Panduan Pelaksanaan Perkhidmatan
Bimbingan dan Kaunseling. Kuala Lumpur: Bahagian Sekolah.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (1979). Laporan Jawatankuasa Kabinet Mengkaji
Pelaksanaan Dasar Pelajaran. Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
Lawton, D. (1982). An Introduction
and Stoughton.
Mager, R F. (1990). Preparing
to
Teaching and Learning. London: Hodder
Instructional Objectives.
45
London: Kogan Page
F
I
I
Mizan Adifiah Ahmad Ibrahim. (1992). Pelaksanaan Perkhidmatan Bimbingan
dan Kaunseling di Sekolah. Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
Mohd. Mansur Abdullah. (1987). Proses
Kaunseling. Kuala Lumpur. DNP
Mohd Yusuf Ahmad. (2002). Falsafah dan Sejarah Pendidikan Islam.
Lumpur: Penerbit Universiti Malaya.
Kuala
Mohd, Salleh Lebar, (1993). Bimbingan dan Kaunseling: Tugas Guru dan
Kemahiran. Petaling Jaya: Longman Sdn. Bhd.
Muhamad Daud Hamzah. (1994). Perkembangan Kanak-kanak dan
Pembelajaran. Kuala Lumpur: Utusan Publications & Distributors Sdn Bhd.
Nisbet, J. & Shucksmith, J. (1988). Learning Strategies.
London: Routledge.
Ornstein, A. C. & Hunkins, F. P. (1998). Curriculum Foundations, Principles and
Issues. (3`d Ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Ozmon, H. & Craver, S. M. (1992). Philosophical Foundations of Education.
London: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Pearson, L. & Lindsay, G. (1986). Special Needs in the Primary School.
Berkshire: NFER-NELSON Pub. Co. Ltd.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (Mac 1994). Kurikulum Bersepadu Sekolah
Rendah (KBSR) secara Menyeluruh. Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan
Malaysia
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Pembelajaran secara Kontekstual. . Kuala
Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Aplikasi Teori Kecerdasan Pelbagai dalam
Pengajaran dan Pembelajaran. . Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan
Malaysia.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Pembelajaran secara Konstruktivism. .
Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Pembelajaran Akses Kendiri. . Kuala
Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan,
Matlamat dan Misi. Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2002). Modul Latihan Pengajaran dan
Pembelajaran Kajian Tempatan KBSR. Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian
Pendidikan Malaysia
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Penilaian Kendalian Sekolah. Kuala
Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
46
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Belajar Cara Betajar.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Kuala Lumpur:
Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum. (2001). Pembelajaran secara Kontekstual. .
Kuala Lumpur: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Rathus,S.A.(1998). Psychology in the New Millennium. New York: Holt, Rinehart &
Winston,Inc.
Ratnavadiel, N. (1999). Teacher Education: Interface between Practices and
Policies: The Malaysian Experience 1979-1997. Teaching and Teacher
Education: An international Journal of Research and Studies. 15 : 193-213.
Robiah Sidin.(1993). Classroom Management. Kuala Lumpur: Fajar Bakti Sdn
Bhd.
Schon, D. (1983), The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in
Action. USA: Basic Books.
. (1987). Educating the Reflective Practitioner. San Franscisco:
Jossey-Bass.
Sergiovanni, T. J. & Starratt, R. J. (1993). Supervision: A Redefinition.
New York: McGraw-Hall International Editions.
Severin, W. J. & Tankard, J. W. (1988). Teori Komunikasi. Kuala Lumpur:
Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
Sharifah Alwiah Aisagoff. (1984). Falsafah Pendidikan. Petaling Jaya: Heinemann
Educational Books Ltd.
Shulman, L. (1987). Knowledge and Teaching: Foundations for a New Reform.
Harvard Educational Review. 57: 1-22.
Slavin,R.E. (1991). Educational Psychology: Theory into Practice. Englewood
Cliffs.- Prentice Hall, Inc.
Stenhouse. (1975). An Introduction to Curriculum Research and Development.
London: Heinemann.
Stone, L. (1990). Managing Difficult Children in School. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
Suradi Salim. (1996). Bimbingan dan Kaunseling. Kuala Lumpur: Utusan
Publication.
Swartz, R. (1997). Critical Thinking: The Curriculum and the Problem of Transfer. In
Perkins, D. et. Al. (Ed.) Thinking: Progress in Research and Teaching.
Hillslade: Erbaum
Travers, J. F. et. Al. (1993). Educational Psychology: Effective Teaching, Effective
Learning. Madison: Brown & Benchmark.
47
Tyler, R. W. (1949). Basic Principles of Curriculum and Instruction. Chicago:
University of Chicago Press.
Weinstein, C. S. & Mignano, A. J. (1993). Elementary Classroom Management:
Lesson from Research and Practice. New York: Mc Graw-Hill, Inc.
West-Burnham, J. & O'Sullivan, F. (1999). Kepimpinan dan Perkembangan
Profesional Di Sekolah. Kuala Lumpur: Institut Terjemahan Negara Malaysia
Bhd.
Woolfolk, A. (2001). Educational Psychology. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Wragg, E. C. (1993). Primary Teaching Skills. London: Routledge
Yong, M. S. & Chia, C. F. (1994). Pemikiran Kreatif: Penyelesaian Masalah
secara Kreatif. Kuala Lumpur: Arenabuku.
Yong, M. S. & Karen, L. B. (1996). Guru yang Kreatif. Kuala Lumpur: Arenabuku,
Yong, M. S. (1994). Kreativiti ke arah Pembentukan Masyarakat Malaysia
Kreatif. Kuala Lumpur: Arenabuku.
WEBSITES
httpa/ www.aber.ac.uk/-m-mflwww/seclangacq/langteach8.html
http://Irs.ed.uiuc.edu/studentsim-weeks.technks.html
http://www.toceducationalforall.com
http:Ilwww.edtech.vt.edu/edtech/id/assess/blueprint.html
http://chiron.valdosta.edu/whuitt/col/regsys/maslow.htmI
http:/ /www. ihhp.com
http:llwww. fathom. comlfks/cataloq/feature.jhtmI
http:/1www.nswagtc.orq.au/info/identification/characteristics.htmI
• http: //ivs.uidaho.edu/mod/models/gardner/index.html
http:I/tip,psychology.orq/bruner.thml
http: //www.nwrel.orq/scpd/sirs/6/cull,html
49
http ://www.moe.gov.my
http: //cw.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/srmstrong3/chapterl2ldeluxe.html
http:l/www.siu.edueyctr/cdromup.html
http:Ilwww.soe.purdue.edu/fac/georgeoff/philamed/essentialism.html
http://www.morehead-st.edu/people/w.willis/fourtheories.html
http_//www_infed.orq/udl/EnvisioningFutureCurriculuml89.cfm
http://www.mpls_k12.mn_us/departments/CIT2/ethics.html.
http: //www.learnativity.com
http://www.stanford.edu/dept/SUSE/csm/features/coIlaboration
httpa/www.mtholyoke.edu/acad/intrel/scholte.htm
http:/lwww.unesco.orq/webworid/infoethics-2/enq/papers/paper-23htm
http: //www.gneis.ucla.edu/courses/ed253a/dk/GLOBAL.htm
http: //www2.moe.gov-my /- bpghibestari-htm
49
PANELISTS OF SUBJECT OUTLINE AND SYALLABUS FOR POST GRADUATE
DIPLOMA IN TEACHING PRIMARY SCHOOL 2003
NO.
NAME
QUALIFICATIONS
1.
Dr. Maznah Binti Abdul Samad (Co-ordinator)
Curriculum Unit
Bahagian Pendidikan Guru
Kuala Lumpur
Diploma in Guidance and
Counselling ; B.A.(Hons)
History; ;MEd (Guidance &
Counselling); PhD (Education)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 10 years;
2.
Dr. Jamaliah Binti Ahmad
I nstitut Bahasa Melayu Malaysia
Kuala Lumpur
MEd (Psychology); PhD (Early
Childhood Education)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 11 years
3.
Dr. Bustam Bin Kamri
I nstitut Bahasa Melayu Malaysia
Kuala Lumpur
B.A.(Hons) Malay Studies; MEd
( Early Childhood Education);
PhD ( Early Childhood
Education Planning)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 12 years
4.
Mr. Fun Foo Ying
Maktab Perguruan Perempuan Melayu
Melaka
B.A (Hons) Geography; MEd
(Pedagogy)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 16 years
5.
Dr. Boon Pong Ying
I nstitut Perguruan Bahasa-Bahasa
Antarabangsa
Kuala Lumpur
B.A(Hons), MEd(Testing and
Evaluation), PhD(Testing and
Testing)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 17 years
6,
Ms. Hjh Nas Bt. Mamat
Maktab Perguruan Kuala Terengganu
Kuala Terengganu
B.A.(Hons) History; MEd
Educational Administration)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 18 years
7.
Ms. Aziza binti Mahbob
Maktab Perguruan Ilmu Khas
Kuala Lumpur
B_Ed (Guidance & Counselling);
MA (Human Resource
Development);
School Counselor for 5 years;
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 12 years
50
NO.
QUALIFICATIONS
NAME
8.
Mr. Gurdev Singh Malhi
Maktab Perguruan Ipoh
Hulu Kinta, Ipoh
B.A.(Hons) Malay Studies in
Education; MEd( Education)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 16 years
9.
Mr. Mohd Nazri Bin Wan Senik
I nstitut Perguruan Darul Aman
Jitra, Kedah Darul Aman
B.A.(Hons) History &
Geography; M. Sc (Educational
Psychology)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 14 years
10.
Mr. Nordin bin Tahir
Maktab Perguruan Perlis
Kangar, Perlis
B.A. (Hons) History; MEd
( Educational Management)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 8 years
TRANSLATION PANELISTS OF SUBJECT OUTLINE AND SYLLABUS FOR POST
GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TEACHING PRIMARY SCHOOL 2003
No
NAME
QUALIFICATIONS
1.
Dr. Maznah Abd. Samad (Co-ordinator)
Curriculum Unit
Teacher Education Division
Diploma in Guidance and
Counselling ; B.A.(Hons)
History; MEd (Guidance &
Counselling); PhD (Education)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 10 years;
2.
Ms. Sharifah Fakhriah Binti Syed Ahmad
(Chairman)
Maktab Perguruan Kuala Trengganu,
Trengganu
B.A.(Hons) Literature; MEd
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 16 years
3.
Mr. Hong Kim Guan
Maktab Perguruan Persekutuan
Pulau Pinang
B.A in Education
(Hons)Geography; LLB( Hons) ;
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 17 years
4.
Ms. Nik Noriah Binti Nik Ibrahim
Maktab Perguruan Kota Bharu
Pengkalan Chepa,Kelantan
B.Soc Sc(Hons) Sociology;
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 16 years
51
REVIEW PANELISTS OF SUBJECT OUTLINE AND SYLLABUS FOR POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TEACHING PRIMARY SCHOOL 2003
NO.
NAME
QUALIFICATIONS
Dr. Maznah Abd Samad (Co-ordinator)
Curriculum Unit
Teacher Education Division
Diploma in Guidance and
Counselling ; B.A.(Hons)
History; MEd (Guidance &
Counselling); PhD (Education)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 10 years;
2.
Mr Lee Hah (Chairman)
Maktab Perguruan Ipoh
Huiu Kinta, Ipoh
B.Sc Ed; MEd (Sistem
Penguasaan Maklumat dalam
Pendidikan)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 16 years
3.
Ms. Gomathi Naidu
Maktab Perguruan Teknik
Kuala Lumpur
B.Sc. (lions) Genetics; MEd
Curriculum and Instruction)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 12 years
4.
Mr. Krishnan AIL Narayana
Maktab Perguruan Raja Melewar
Seremban
B.A. (Hons) Indonesian &
Malay Studies; MEd
(Psychology)
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 12 years
5.
Ms Aziza Mahbob
Maktab Perguruan limu Khas
Cheras, Kuala Lumpur
B.Ed (Guidance & Counselling);
MA (Human Resource
Development);
School Counselor for 5 years;
Lecturer in Education Studies
for 12 years
6.
Dr. Boon Pong Ying
I nstitut Perguruan Bahasa-Bahasa
Antarabangsa, Kuala Lumpur
B.A(Hons), MEd(Testing and
Evaluation), PhD(Testing and
Testing)
Lecturer in Education
Studies for 17 years
1.
52
STRUKTUR DAN KOMPONEN
KURSUS PERGURUAN LEPAS IJAZAH ( KPLI ) SEKOLAH RENDAH
MULAI AMBILAN 2003
MATA PELAJARAN _
KOMPONEN
( A)
PENGAJIAN
ASAS
( B)
PENGAJIAN
PROFESIONAL
(C
( D)
(E)
PENGAJIAN
KURIKULUM
PERSEKO LAHAN
KOKURIKULUM
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7_
8.
9
LAMPIRAN A
JUItiILAH'
Bahasa Melayu Komunikasi
Pengurusan Sumber
Tamadun I slam
Pendidikan Islam atau Pendidikan Moral
Pendidikan Negara Bangsa Malaysia
Pendidikan Alam Sekitar
Muzik Dalam Pengajaran dan Pembelajaran
Pendidikan Jasmani
ur ( ..J. Al
ll mu Pendidikan
uttildtt.{B },
1
2
1
1
I
1
1
1
kredit _
kredit
kredit' kredit
kredit
kredit
kredit
kredit
kre(J K
7 kredit
.
10.
Major
8 kredit
11
Minor 1
4 kred t
1
Minor 2
4 kredit
Jur iah tC)
13, Kokurikulum
• Pengurusan kokurikulum
• Unit Berumform
• Sukan
JVT4fah ~D)
JUMLAH KREDIT
J1 I MLAH KREDIT KESELURUHAN
{
)
:...,
3.,
htt
d
'
it
35 kredit
12 M
( 6 kredit )
41 kredit
NOTA
1. Program KPLI sekolah rendah dikendalikan dalam tempoh 39 minggu yang merangkumi 1 minggu
pengurusan pelajar baru dan Bina Insan Guru, 24 minggu interaksi kuliah , 12 minggu praktikum, 1
minggu refleksi dan 1 minggu peperiksaan.
2. Praktikum dikendalikan dalam 2 fasa. Fasa 1 selama 4 minggu dijalankan sebelum cuti semester.
Fasa 2 bermula pada minggu ke-26 sehingga minggu ke - 33 selama 8 minggu_
3. Sebanyak 10 hari diagihkan untuk lawatan pengalaman berasaskan sekolah sebelum
praktikum fasa 1
4. Unsur Bina Insan Guru selama 3 hari, 2 malam diterapkan dalam Pendidikan Jasmani.
5. Ca ( on IPTA tempatan dibenarkan pindah kredit Tamadun I slam.
6. Kandungan Pengurusan Sumber merangkumi 3 bidang pembelajaran iaitu Teknologi Maklumat &
Komunikasi, Teknologi Pendidikan dan Sains Perpustakaan.
7. Pengiraan Kredit
• I kredit kuliah = 15 jam i nteraksi
• 1 kredit amali kokurikulum = 45 jam
• 1 kredit prakt i kum = 2 minggu
LAMPIRAN B
MATA PELAJARAN
KURSUS PERGURUAN LEPAS IJAZAH (KPLI) SEKOLAH RENDAH
PENGAJIAN ASAS
1.
Bahasa Melayu Komunikasi
Pendidikan Alam Sekitar
2.
Pengurusan Sumber
5.
3.
Tamadun Islam
7.
Pendidikan Jasmani Asas
4.
6.
$,
Pendidikan Negara Bangsa
Muzik Dalam Pengajaran clan
Pembelajaran
Pendidikan Islam atau Pendidikan
Moral
PENGAJEAN PROFESIONAL
1.
Il mu Pendidikan
•
•
•
Psikologi Pendidikan
Pedagogi
Profesionalisme Guru
PENGAJIAN KURIKULUM PERSEKOLAHAN ( MAJOR)
1,
2.
Pengajian Bahasa Inggeris
3.
4.
Pengajian Agama I slam
Pengajian Matematik
Pengajian Sains
PENGAJIAN KURIKULUM PERSEKOLAHAN (MINOR)
1.
2.
Matematik
Sains
KUMPULAN SAINS DAN TEKNOLOGI
3.
4.
Kemahiran Hidup
Pendidikan Jasmani
KUMPULAN BAHASA DAN KUMPULAN SAINS SOSIAL
2.
3.
Bahasa Inggeris
Bahasa Arab
Kajian Tempatan
4.
5.
Pendidikan Moral
Pendidikan Seni Visual
LAMPIRAN c
KURSUS PERGURUAN LEPAS IJAZAH (KPLI) SEKOLAH RENDAH
KOMBINASI MAJOR DAN MINOR
MAJOR
Bahmoa\ng g ehm
Agama
slam
., -
i
!
Sqins
i
/
.
~
!.
Ku
~ Bah mnad an~&aks S os ial
°
°
°
~
Matematik
S aina
K anmaNranHidup
Pend i UikonJ a snnan j
•
•
°
KakanTe mpata n
Pendidikan Mom!
Pendidikan Seni Visual
~
°
°
Matematik
Bmino
°
Bahasa Arab
°
°
K e mmNnanH i dup
PmndicUkanJ a srnani
°
Bahasa\n g gohs
°
°
Kemahiran Hidup
PendidikonJoon1ani
°
Bahaya\ng9 e hs
~
\
Mat em atik
Kumputan
MINOR 2 (pilih satu )
Kernmh nanHidup
Pend i dikmnJasnmmni
APPENDIX F
TERMINOLOGY FOR EDUCATIONAL STUDIES
(ENGLISH LANGUAGE - MALAY LANGUAGE)
aim
ENGLISH LANGUAGE
acceptable behaviour
accountability
achievement
adolescent
approach
assumption
attention
attitude
aware
basic needs
beginning teachers
behaviour/character
characteristics
clarify
tujuan
MALAY LANGUAGE
tingkah laku yang diterima
akauntabiliti
pencapaian
remaja
pendekatan
andaian
perhatian/tumpuan
sikap
peka
keperluan asas
guru permulaan
tingkah laku
ciri-ciri
menjelaskan
classroom interaction
interaksi bilik darjah
compensatory education
pendidikan imbuhan
commitment
competency
conflict
concern
consolidation
correction
current education system
depress
describe
development
drive
• education
educational values
effect
emotional needs
iltizam
berketrampilan
konflik/sengketa
kepekaan/keprihatinan
pengukuhan
pembetulan
sistem pendidikan semasa
murung
menghuraikan
perkembangan
desakan
pendidikan
nilai-nilai keguruan
kesan
keperluan emosi
ENGLISH LANGUAGE
MALAY LANGUAGE
environment
persekitaran
evaluation
penilaian
esthetic values
experiential learning
experience
exposition
extra-tutoring
extrinsic stimulus
facilitator of learning
field
frequency
futuristic studies
generate
gesture
habit
honest
inculcation
i ndividual differences
i nfluence
identify
implementation
i mprove/increase/enhance/upgrading
i nherent
i n line
integration/holistic
internalise
inter-related
nilai-nilai estetika
pembelajaran melalui pengalaman
pengalaman
pendedahan
pengajaran tambahan
rangsangan ekstrinsik
pemudahcara pembelajaran
bidang
kekerapan
kajian masa depan
menjana
gerak isyarat
kebiasaan/tabiat
jujur
penerapan
perbezaan individu
pengaruh
kenal pasti
pelaksanaan
meningkatkan
sebati
selaras
bersepadu dan menyeluruh
menghayati
sating berkaitan
insight
celik akal
learning
pembelajaran
inquiry discovery
learning readiness
l ess fortunate
life long learning
inkuiri penemuan
kesediaan belajar
kurang beruntung
belajar sepanjang hayat
ENGLISH LANGUAGE
learning difficulties
hubungkaitkan
managing classroom
mengurus bilik darjah
materials
meaning
measurement
bahan bantu mengajar
makna/pengertian/takrifan
pengukuran
pembimbing
mutual respect
hormat menghormati
National Philosophy of Education
nature of man
needs
obstructing factor
s
bermotivasi rendah
mentor
moral practices
r
masalah pembelajaran
li nk
low motivated
1
MALAY LANGUAGE
opportunity
pattern recognition
perception
performance
Philosophy of Teacher Education
planning
practise
problematic children
pupil
amalan nitai-nilai murni
Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan
fitrah manusia
keperluan
faktor penghalang
peluang
pengamatan
penanggapan
prestasi
Falsafah Pendidikan Guru
merancang
amal
murid bermasalah
murid
questionaire
soal selidik
reasoning
taakulan
relevant authorities
pihak-pihak tertentu
rating
race
reduplication
reinforcement
remedial teaching
remembering and forgetting
restrictive culture
pemeringkatan
ras
penggandaan
pengukuhan
pengajaran pemulihan
i ngatan dan lupaan
budaya tersekat
ENGLISH LANGUAGE
MALAYLANGUAGE
scrutinised
penelitian
School Orientation Programme
Rancangan Orientasi Sekolah
peer
self-concept
self-discipline
self-awareness
self-paced-learning
set induction
skills
social interaction
sequence
sincere
student
student teacher
strengthen
set
socio-drama
supplementary menu
task/assignment
teaching and learning
tenets
sebaya
konsep kendiri
disiplin kendiri
kesedaran kendiri
pembefajaran arah kendiri
induksi set
kemahiran
interaksi sosial
urutan
iklas
pelajar sekolah menengah
guru pelatih
perkukuh
gubal
lakonan
menu sampingan
tugasan
pengajaran clan pembelajaran
Berasaskan prinsip/kepercayaanfteori
Test Blue Print/Table of Specification
Jadual Penentu Ujian
testing
pengujian
ti me allocation
training package
understand
ultimate aim
upright
valid
validity
value
virtue
peruntukanmasa
pukal latihan
faham
tujuan muktamad
l uhur
sah
kesahan
nilai
sifat murni