Coriolis Effect Worksheet: Wind Deflection & Earth Rotation
advertisement
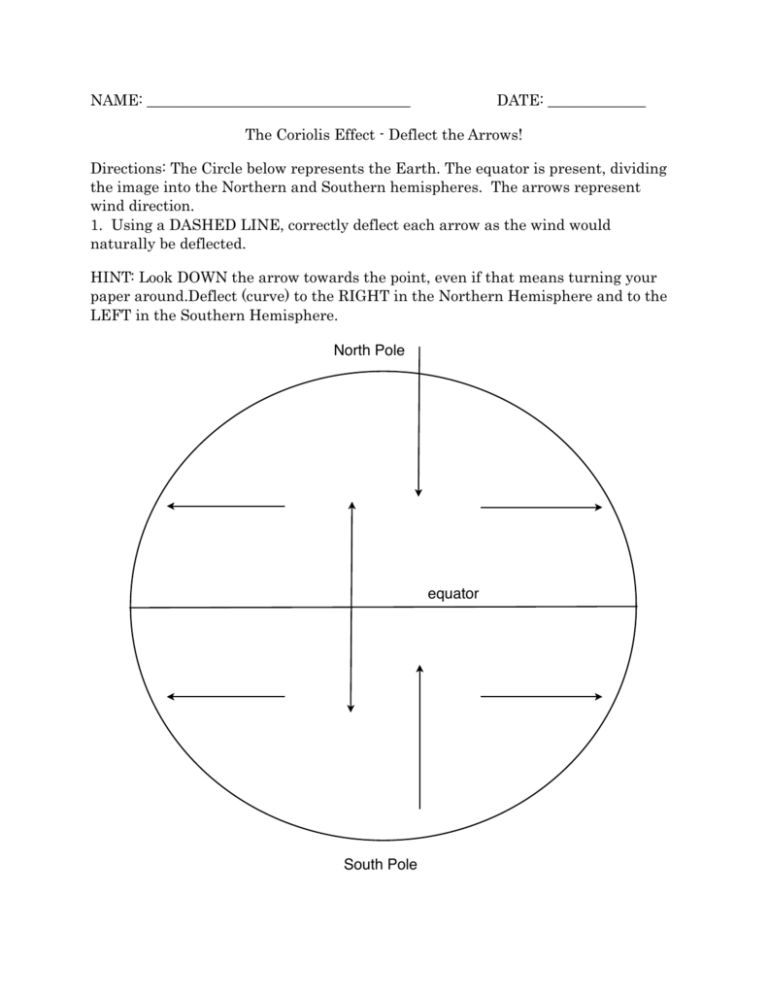
NAME: ___________________________________ DATE: _____________ The Coriolis Effect - Deflect the Arrows! Directions: The Circle below represents the Earth. The equator is present, dividing the image into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The arrows represent wind direction. 1. Using a DASHED LINE, correctly deflect each arrow as the wind would naturally be deflected. HINT: Look DOWN the arrow towards the point, even if that means turning your paper around.Deflect (curve) to the RIGHT in the Northern Hemisphere and to the LEFT in the Southern Hemisphere. ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! North Pole equator ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! South Pole ! Answer all questions on this page. If you need help, you can visit this site for a short summary about the Coriolis Effect: Infoplease Encyclopedia: Coriolis Effect. 1- What is the Coriolis Effect? ___________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ! _______________________________________________________________________ ! 2- What causes the Coriolis Effect? _______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ! _______________________________________________________________________ ! 3- Name 3 things affected by the Coriolis Effect • ____________________________________________________________ • ____________________________________________________________ • ____________________________________________________________ 4- What do you think a soldier firing a missile or a pilot flying a plane must do in order to accurately land the missile or the plane at the correct destination? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! 1.Using the picture above, please draw, label, and indicate the direction of air as seen by an earthling for the following: 1. An arrow showing which way the Earth rotates. 2.The four Hadley cells, four Ferrel cells, four Polar cells. 3.The Westerlies 4.The Tradewinds ! ! ! ! ! ! Do the following activity. You will need to work with a partner. Materials You will two balloons and two markers (different colors) Procedure 1. Blow up a balloon. 2. With a marker, draw the equator on the balloon and label the North and South Poles. 3. Hold the balloon at eye level and rotate it left to right, simulating the rotation of the earth. 4. While one partner rotates the earth balloon, the other examines the movement of the earth from the North Pole perspective and from the South Pole perspective. 5. While one partner continues to rotate the balloon steadily from left to right, the other slowly tries to draw a line straight south from the North Pole to the equator. Using the other marker and while the earth continues to rotate, draw a line straight north from the South Pole to the equator. 6. Do the experiment again but switch roles. Conclusion Answer questions 1-5 below. 1. As you look down from the North Pole toward the equator, which way is the balloon spinning, clockwise or counterclockwise? ! ! 2. As you look up from the South Pole toward the equator, which way is the balloon spinning, clockwise or counterclockwise? ! ! 3. What happened when you tried to draw a straight line from the North Pole to the equator? ! ! 4. What happened when you tried to draw a straight line from the South Pole to the equator? ! 5. ! Predict what would happen if you again drew lines in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres but with the earth rotating in the opposite direction. Fill in the blanks below 1. Warm air __________, expands and cools. Then it sinks downward to where the rising warm air was located. This thermal cycle of moving air is called a _________________ current. Unequal heating of Earth’s surface causes air circulation: air at the equator gets more energy from the Sun, and the heated air rises and moves toward the _____________ regions. Here it cools in the upper atmosphere, sinks towards the ___________, and is drawn back to the warmer regions of the equator. 2. Since the Earth ______________ on its axis, the pathway of the moving air is affected. All free- moving objects, including air and water, aircraft and missiles, appear to deviate from their straight-line paths. This apparent shift due to Earth’s rotation is called the _________________________. 3. The Coriolis effect deflects winds toward the ___________ in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left in the ____________ Hemisphere. The faster the wind, the greater the deflection. This deflection causes global wind patterns. At the equator the atmospheric circulation is referred to as ____________________ cells. On the surface of the Earth the global wind pattern is called the ________________ winds. Between 30 and 60 degrees north and south latitude the atmospheric circulation is referred to as ___________________ cells. On the surface of the Earth the global wind pattern is called the ________________________. ! Answer the question below to summarize the Coriolis Effect 1. In the Northern Hemisphere, free-moving objects traveling over large distances ! are deflected to the ____________ of their intended path of motion. ! 2. In the Southern Hemisphere, free-moving objects traveling over large distances ! are deflected to the ____________ of their intended path of motion. ! 3. If a missile is launched from the North Pole, toward an object on the equator, should it be aimed to the left, to the right, or directly at its target? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER. ! ! ! ! ! ! 4. If a missile is launched from the equator toward an object in the Northern Hemisphere, should it be aimed to the left, to the right, or directly at its target? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER. ! ! ! ! ! ! 5. A flight from Salt Lake City, CT to New York, NY takes about 6 hours. The return trip takes about 5 hours. Why does this happen? !











