Hadley Cell worksheet answers
advertisement

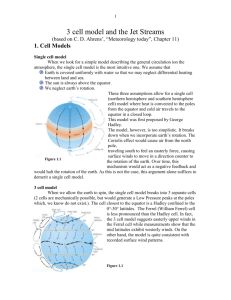
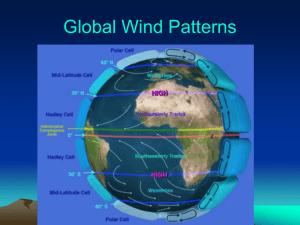
Name: _________________________ Sequencing the Hadley Cell System 1) Accurately completing this activity will allow you to achieve the following learning objective: To be able to describe and explain how the Hadley Cell system is responsible for air circulation in the tropics. Task Re-arrange and write out the jumbled theory statements in the table below to: a) Describe in order what is happening at each point in the Hadley Cell; b) Give information about any pressure types, weather conditions, names of features or movement of air masses at each point of the Cell. Refer to the labeled figure of the Hadley Cell. You may want to cross out each statement once you have used it. Point A: Water vapour condenses to form heavy rain/ thunder. 4 Ground surface at the equator becomes very hot. 2 Convection currents. 6 Sun is directly overhead & high in the sky. 1 The area of low pressure in the equatorial latitudes is.. Low pressure develops.7 Known as inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ). 8 Water at/on the surface evaporates. 3 Hot air and water vapour rises by… 5 Point B: The air circulates as upper westerly winds around the planet due to the deflection effect… 2 The poleward movement of air at high altitudes. 1 The air that has risen moves in a poleward direction.. 4 Known as the Coriolis effect…3 Both north and south of the equator. 5 The overall / net effect is that the air still moves polewards. 6 …At 30 degrees N and 30 degrees S, there are areas of high pressure called…5 An area of high pressure is created at the ground surface…3 As the air descends, it warms and evaporates any residual moisture. 2 …which generally means cloudless skies. 4 On reaching the ground at the subtropical anticyclones, some of the air returns to the….1 Hence, the northeast trades blow north of the equator and the southeast trades blow south of the equator.3 …also affected by the Coriolis effect..5 Point C: …Colder air at the high altitude begins to sink / subside back to the surface.1 …subtropical anticyclones. 6 Point D: These movements of air from both N and S of the equator are…4 …and to the left in the southern hemisphere.7 …and are deflected to the right in the northern hemisphere…6 …equatorial latitudes as consistent winds. 2