Carnation eyes, guenons, and other IB Bio Exam review problems!
advertisement
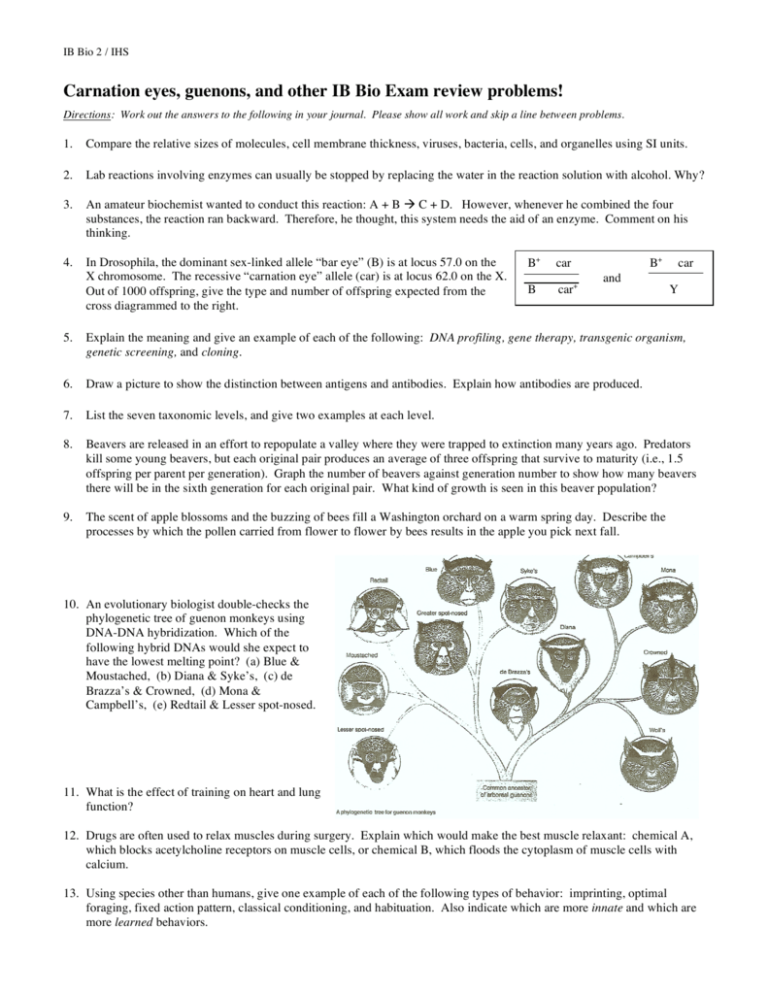
IB Bio 2 / IHS Carnation eyes, guenons, and other IB Bio Exam review problems! Directions: Work out the answers to the following in your journal. Please show all work and skip a line between problems. 1. Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria, cells, and organelles using SI units. 2. Lab reactions involving enzymes can usually be stopped by replacing the water in the reaction solution with alcohol. Why? 3. An amateur biochemist wanted to conduct this reaction: A + B C + D. However, whenever he combined the four substances, the reaction ran backward. Therefore, he thought, this system needs the aid of an enzyme. Comment on his thinking. 4. In Drosophila, the dominant sex-linked allele “bar eye” (B) is at locus 57.0 on the X chromosome. The recessive “carnation eye” allele (car) is at locus 62.0 on the X. Out of 1000 offspring, give the type and number of offspring expected from the cross diagrammed to the right. B+ B B+ car car+ and car Y 5. Explain the meaning and give an example of each of the following: DNA profiling, gene therapy, transgenic organism, genetic screening, and cloning. 6. Draw a picture to show the distinction between antigens and antibodies. Explain how antibodies are produced. 7. List the seven taxonomic levels, and give two examples at each level. 8. Beavers are released in an effort to repopulate a valley where they were trapped to extinction many years ago. Predators kill some young beavers, but each original pair produces an average of three offspring that survive to maturity (i.e., 1.5 offspring per parent per generation). Graph the number of beavers against generation number to show how many beavers there will be in the sixth generation for each original pair. What kind of growth is seen in this beaver population? 9. The scent of apple blossoms and the buzzing of bees fill a Washington orchard on a warm spring day. Describe the processes by which the pollen carried from flower to flower by bees results in the apple you pick next fall. 10. An evolutionary biologist double-checks the phylogenetic tree of guenon monkeys using DNA-DNA hybridization. Which of the following hybrid DNAs would she expect to have the lowest melting point? (a) Blue & Moustached, (b) Diana & Syke’s, (c) de Brazza’s & Crowned, (d) Mona & Campbell’s, (e) Redtail & Lesser spot-nosed. 11. What is the effect of training on heart and lung function? 12. Drugs are often used to relax muscles during surgery. Explain which would make the best muscle relaxant: chemical A, which blocks acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells, or chemical B, which floods the cytoplasm of muscle cells with calcium. 13. Using species other than humans, give one example of each of the following types of behavior: imprinting, optimal foraging, fixed action pattern, classical conditioning, and habituation. Also indicate which are more innate and which are more learned behaviors.