Document
advertisement

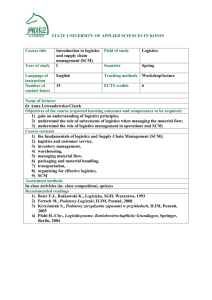
SCM 301 Spring 2010 The Pennsylvania State University – Lehigh Valley SCM 301: Business Logistics Syllabus and Course Information Instructor Class Hours Office Office Hours Email Telephone Text : Dinesh R. Pai : M 6:30-9:00 PM Location: Saucon 318 : 213 L, Saucon : MW 2:30–4:00 PM/By Appointment. : drp18@psu.edu (Please DO NOT mail to ANGEL Mail) : 610-285-5029 : Management of Business Logistics: A Supply Chain Perspective by Coyle, Bardi, Langley, South-Western Pub; 7th ed., ISBN-10: 0324007515 Course Mission and Learning Outcomes: Over the past decade, Logistics or Supply Chain Management (SCM) has gained increasing focus in all forms of organizations. Supply Chain Management focuses on managing material and information both within and outside of an organization including aspects of globalization and low-cost country sourcing, product design collaboration, demand planning and forecasting, inventory management, distribution, procurement, and logistics. This course explores the basic issues underlying SCM and the challenges facing companies to achieve effective management of their supply chains. Supply chain management is described as a set of approaches utilized to efficiently integrate suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and stores, so that merchandise is produced and distributed at the right quantities, to the right locations, and at the right time, in order to minimize system wide costs while satisfying service level requirements. Course Learning Outcomes: You will explain the role of logistics and supply chain management (SCM) in enhancing the overall performance of an organization. You will compare inventory management models and apply appropriate models to given situations. You will explain the role of procurement and strategic sourcing in achieving competitive advantage for an organization. You will evaluate various transportation options and select appropriate options for a given problem. You will discuss the role of warehousing in SCM, and apply warehouse designing techniques in a given situation. You will discuss the application of Information Technology in SCM. We will use a combination of theory, simulations, numerical examples, and practical applications to reinforce above concepts and tools. 1 of 4 SCM 301 Spring 2010 Teaching Philosophy The course is designed to make learning an enjoyable experience. We will look at real world supply chain cases to assimilate the intricacies of managing a supply chain. To achieve this, I intend to deviate from the largely understood traditional means of learning i.e. prolonged lecturing which does little more than providing information. Instead, I plan to have an interesting mix of learning strategies comprising of Readiness Assessment Tests (RATs), Application Exercises (APEXs), Case Studies, Short Videos, Home Assignments and of course some lecturing. The objective is to provide you an opportunity to become more actively involved in the learning process. However, you must accept responsibility for your learning and complete all the in-class and after-class activities sincerely and on time. I encourage you to participate in the class activities and discussions, as also interact with your peers outside the class. Feel free to visit me in my office* or wherever we meet on campus to discuss your queries. Good luck!!! Student Evaluation and Grading There will be one mid-term examination and one final examination. A typical exam will include a mix of objective (multiple choice and T/F), and subjective and/or computational questions, based on the material presented in the class, RATs and assignments. The point’s breakdown for determining final grades is as follows: Assignments (15%) You will have an assignment almost every week. Assignments will comprise of reflection paper and occasionally a problem set. See the ‘Reflection Paper Guidelines’ for grading standards. All assignments should be submitted typed (double space) using MS Word software. Class Participation (25%) Class participation includes your involvement in the class discussions (more specifically the quality of your observations and inputs in leading a class discussion), your performance in the RATs (individual as well as team), APEXs and Case Studies. Midterm Exam (30%) Mid-Term will be a take-home exam comprising of a case study, a couple of numericals, and some multiple choice questions. Final Exam (30%) Final exam will be an in-class (during the finals week) comprising of a case study, a couple of numericals, and some multiple choice questions. Make-up exams will be given in exceptional circumstances and with proper documentation only. Final letter grades will be assigned using the following scale (expressed in terms of the percentage of total possible points earned): 2 of 4 SCM 301 Spring 2010 A AB+ B BC+ C D F Letter Grade Percentage >= 93 90-92 87-89 83-86 80-82 77-79 70-76 60-69 < 59 Attendance You are strongly encouraged to attend every class. Since a large portion of the learning in this course will come from in-class discussions, APEXs, and RATs, a missed class is a missed opportunity to participate in class and to learn from your peers. In the event that you must miss a class, it is your responsibility to obtain a copy of any materials distributed during your absence and to find out what you may have missed, including homework’s. You MUST check your ANGEL account AT LEAST twice every week. Students with Disabilities Penn State welcomes students’ with disabilities into the university’s educational programs. If you have, or think you may have, a disability (including an ‘invisible disability’ such as a learning disability, a chronic health problem, or a mental health condition) that interferes with your performance as a student in this class, you are encouraged to arrange support services through Linda Rumfield in Disabilities Services, 610-285-5124, Room 134 Saucon. Academic Integrity Academic integrity is the pursuit of scholarly activity in an open, honest and responsible manner. Academic integrity is a basic guiding principle for all academic activity at The Pennsylvania State University, and all members of the University community are expected to act in accordance with this principle. Consistent with this expectation, the University's Code of Conduct states that all students should act with personal integrity, respect other students' dignity, rights and property, and help create and maintain an environment in which all can succeed through the fruits of their efforts. Academic integrity includes a commitment not to engage in or tolerate acts of falsification, misrepresentation or deception. Such acts of dishonesty violate the fundamental ethical principles of the University community and compromise the worth of work completed by others. Policies, rules, sanctions and procedures regarding academic integrity can be found in the Academic Policies, Rules & Procedures for Students (http://www.psu.edu/ufs/policies), and the Lehigh Valley Campus web site (http://www.lv.psu.edu/academicintegrity/). 3 of 4 SCM 301 Spring 2010 Course Schedule* Week Topics 1 Introduction to Supply Chain & Logistics 11-Jan Chapter 1: Supply Chain Management Chapter 2: Dimensions of Logistics Video: The Container Story (@60 mins) Video: Supply Chain Management at Regal Marine No Classes 2 3 Sourcing and supplier management Chapter 4: Procurement and Supply 25-Jan Management 4 In-Class Activity Inventory and forecasting 1-Feb Chapter 3: Demand Management 5 Inventory Management I Read: When Supplier Partnerships Aren’t…. Partnerships at Motorola Case: Meditech Surgical (Group 1) Read: Benetton - Global logistics in action Video: Forecasting at Hard Rock Case: Tires For You (Group 4) Video: Inventory Control at Wheeled Coach Game: Inventory Simulation Game Inventory Management III Beer Game Transportation and logistics I Chapter 9: The Transportation System Chapter 10: Transportation Management You will play the Game in Groups Video: Logistics - Made in Bremen Case: Westminster Company - A System Design Assessment (Group 6) Spring Break 9 11 No Classes Video: Product Design and Supplier Inventory Management II 10 Transportation and logistics II 15-Mar Chapter 8: Warehousing Decisions Read: The Supply-Chain Management Effect Read: Which Supply Chain Design? M L K Jr. Day 8-Feb Chapter 6: Managing Inventory Flows in the SC Case: Dell Computers (Group 5) Chapter 7: Inventory Decision Making 6 15-Feb 7 22-Feb 8 1-Mar Out of Class Activity for the Week Spring Break Case: Bath King Industries (Group 3) Simulation Model: Warehouse Read: Four Steps to Forecast Total Market Demand Read: How IKEA Designs Its Sexy Price Tags Read: Managing Supply Chain Inventory – Pitfalls and Opportunities Read: Supply Chain Hero Read: Instructions for the Inventory Simulation Game Read: Read: Read: Read: Instructions for the Beer Game How Philips Reduced Returns The New Wave in Giant Ships New Hope for Trucks and Trains Spring Break Read: Thinking Ahead Read: Lessons from a Coffee Supply Chain Marketing and channel restructuring Information and electronic mediated 22-Mar environments Chapter 12: Logistics and SC Information Sys. 12 Product design and new product introduction Video: E-Commerce and Teva Sports Sandals Read: The Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chains Read: Internet Fulfillment - The Next Supply Case: Catnap Pet Products (Group 2) Chain Frontier 29-Mar Service and after sales support Chapter 3: Customer Service Case: Customer Service at WoodsonChemical Company (Group 4) 13 Location Chapter 14: Network Design and Facility 5-Apr Location 14 Reverse logistics and green issues 12-Apr Outsourcing and strategic alliances, SC Risk 15 Chapter 11: Logistics Relationships and 3PL Metrics and incentives 19-Apr Chapter 13: SC Performance Measurement Chapter 15: SC Finance 16 Global issues Video: Product Design at Regal Marine Read: HP-The Power of Postponement Read: Out of Touch with Customer Needs Spare Parts and After Sales Service Video: Where to place Hard Rock’s next Café Read: 7 Keys to Facility Location Case: Western Pharmaceuticals (A), (B) Read: Location means Business (Group 5) Read: The Green Supply Chain – An Video: JIT at Arnold Palmer Hospital Overview Read: Managing Risk To Avoid SC Case: TBD (Group 1) Breakdown Read: The Outsourcing of Logistical Activities Case: Cooper Processing (Group 3) Read: Supply Chain Metrics Case: Performance Control at Happy Chips Read: Performance metrics in SCM (Group 6) Case: Red Fish, Blue Fish, LLP - A Sequel (Group 2) 26-Apr Chapter 5: Global Logistics Chapter 16: Logistics and SC Challenges for the Future Read: Sharing Global Supply Chain Knowledge Read: Cut-Rate Swedish Retailer Enters the Italian Market * Please note that the course schedule is tentative and minor changes based on instructor’s discretion are possible. 4 of 4