Power review handout
advertisement
,ÿ, Biology Fall Exam
Biochemistry
What are organic compoonds?
What are the four main organic compounds?
.\
ao
b.
c.
d.
Which shows the correct relationship between monomers and polymersÿ.
\
a. monomer + monomer = polymer
b. polymer +.polymers = monomer
b. monomer ÷ polymer = polymer
d: monomer + polymer = monomer
What is the process called that forms polymers?
Organic Compound
"
Polymer
Monomers
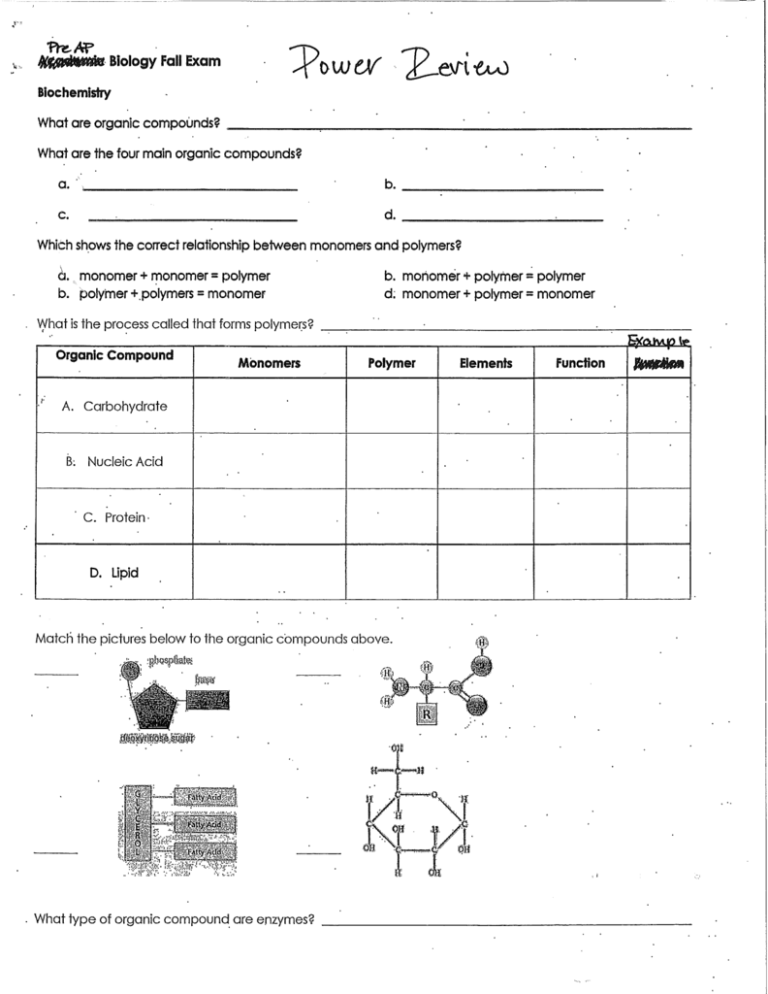
": A. Carbohydrate
B: Nucleic Acid
C. Protein.
D. Lipid
Match the pictures below to the organic cbmpounds above.
"
• What type of organic compound are enzymes?
..
Elements
Function
-v
How do enzymes relate to chemical r eÿqÿt[qrÿs? '.
t
What environmental variables would cause an enzyme to denature?.
Label where dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis occurs:
/
\
Cells and Viruses
Why aren't viruses living?
What do viruses have in common with cells? What internal component do they share?
How do viruses reproduce?
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Give an example of a prokaryotic cell
Give examples of eukaryotic cells
What are th.e differences between plant and animal cells?
What are organelles?
:
Give the function of the following organelles.
Nucleus
Chloroplast•
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Central Vacuole
Cell Transport
Describe the.structure of a cell membrane:
What is the differen(=e between active and passive transport? ' '
Define osmosis:
Illustrate the following solutions.
Hypotonic
Isotonic
Hyped. onic
\
Cell .Energy
What molecule stores and releases energy in organisms.ÿ
How is energy released from ATPÿ
What is the source of all energy on ead h?
What process chaÿnges light energy to chemical energy?
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
Fill out the chart for all Jypes of Cellular Processes:
Location
Uses
Process
(Cytoplasm or
Mitochondria?)
Oxygen?
Aergbic or
"anaerobic?
Reactants
Products (What
(What goes in)
comes Out)
Glycolysis
Lactic Acid
Fermentation.
Alcoholic
Fermentation
Cellular
Respiration
(Krebs & ETC)
,=.
Label where the Calvin Cycle and Light Dependent reactions occur:
DNA & Cell Cycle
The model of DNA was identified by scientists
DNA is made up of 4 nucleotides that are represented by the letters:
An organism's genetic code is determined by the order of the
DNA !s.r.eplicated in what structure of a cell?
If the original strand of DNA is ATrGCA the strand formed during replication would be
The process of a cell grgwing and dividing is called the
Identify and explain what happens in each stage of the cell cycle
B.
C.
D.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
What happens if the cellcycle isn't properly controlled? What problem might this cause?
What is it called when there is a c.hange in the DNA sequence?
Identify the type of mutation in the DNA strands below:
Original Strand
GCATTA
Mutation # 1
GGATTA
Mutation #2
GCCATÿrA
, mutation will get passed on to offspring if it is ina (body cell/sperm or egg cell)
The DNA in one person's cells is (identical/different) than other people's DNA.
The DNA in a person's eye cell is {identical/different) to the D NA jn all. of the Cells of their body
Protein Synthesis
What are the 3 components that make up nut:leic acids?
I.
2.
3. '
In the
first step of protein synthesis, DNA gets copied to
,\
in the.
(ÿpe of RNA)
(location)
This first step is called
In the second step of protein synthesis
carries
(type of RNA)
to
{monomer)
(location)
to form a protein chain.
This second step is called
If the DNA strand is GCTTAG, then the corresponding mRNA strand will be
Use the codon chart to determine the amino acids chain that wou d be formed from the RNA strand above
Explain why a change in the DNA sequence may have an effect on an organism's trait?
l=undamentals of Genetics
What is the purpose of meiosis?
Label ttle following diagram w.ith the following terms:
meiosis, fertilizationÿ 46 chromosomes, 23 chromosomes, gametes
Egg and sperm cells are types of
Label the types of inheritance paHems illustrated below: •
complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance
a.
Blue Frog + Green Frog. = Blue. Frog with Green spots
b. "
Blue Frog + Red Frog = Purple Frog
\
Blue Frog + Yellow Frog = Blue Frog
C.
What would the genotypes be for the previous frog offspring?
\
a.
b.
c.
Brown eyes are dominant (B) and blue eyes are recessive '(b). Fill out the following comb.inations
Homologous Recessive:
Heterozygous:.
.Homoÿgous Dominant:
Blue eyes are recessive to brown eyes. A man that is heterozygous for brown eyes marries a woman with blue
eyes. Do a punnett square to find out.the possibilities of their kids have brown or blue eyes.
Father's genotype
Genotype Ratio
Mothers genotype
Phenotype Ratio
Hemophiia is a recessive sex-linked trait. A male with genotype XHy is married to a woman with genotype XHXh.
DO a punnett square to find out the possibility of their kids having hemophilia.
Genotype Ratio
Phenotype Ratio
Application of Genetics
A
shows a picture of homologous chromosomes
What is a pedigree? What can they trace?
A karyotype can show
mutations, but not
mutations
What error in meiosis can cause an individual to have one too many or one too few chromosomes?
Explain the following genetic engineering techniques:
Steps in DNA Rnger printing:
lo
2.
3.
4.
Selective breeding
Transgenic Organisms
steps in €loqing
o
2.
3.
4.






