Human Tissue Types
advertisement

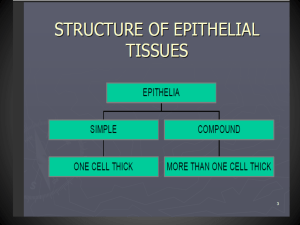
Tissue Types Key Terms • Differentiation = produces specialized cells during embryonic development • Tissues = groups of cells which are similar in structure and which perform common or related functions • Histology = the study of tissues Four Basic Kinds of Tissues • • • • Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue Epithelial Tissue • Locations: – Covers the body – Lines organs, body cavities, and ducts – Forms glands • Functions: – Protection from injury and microbial invasion – Regulates permeability – Secretes fluids to lubricate structures Epithelial Tissue Characteristics: • Avascular (no blood vessels) • Cells may show polarity (apical & basal surface, they are chemically and structurally different from one another) • A basement membrane attaches epithelia to underlying connective tissues • High rate of cell division (allows repair by sloughing off dead or injured cells, important because epithelium is exposed to physical stress) The Polarity of Epithelial Cells Classification of Epithelia • Number of cell layers pg 113 – Simple (single layer) – Stratified (several layers) – Pseudostratified (nuclei are at different levels & not all cells reach the apical surface) • Shape of cells (draw, location, function) – Squamous (thin, flat, irregular cells) pg 115 – Cuboidal (cube shaped cells) pg 116 – Columnar, ciliated and nonciliated (tall & slender cells) pg 116, 117 – Transitional (change shape from flat to cuboidal and back) pg 119 Squamous Epithelia Cuboidal Epithelia Cuboidal Epithelia Cont. Special Cuboidal Epithelia: Transitional Epithelia cells can stretch Columnar Epithelia Columnar Epithelia Columnar Epithelia Glandular epithelia Many epithelia contain gland cells that produce secretions Exocrine glands: – Produce secretions such as mucus and/or watery solution through ducts onto the epithelial surface Endocrine glands: – Ductless, release secretions directly into bloodstream Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Examples of Exocrine Glands Time to Review Simple squamous epithelium (lining of body cavities) Simple cuboidal epithelium (lining of glands and ducts) Simple columnar epithelium (lining of stomach, intestines) Stratified squamous epithelium (skin) Simple columnar epithelium (lining of digestive tract) Simple cuboidal epithelium (lining of ducts in kidneys) Simple squamous epithelium (lining of the heart) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (lining of nasal cavity) Transitional epithelium (urinary bladder) Stratified squamous epithelium (lining of mouth) Type of Tissue Function Location Pseudostratified columnar removing dust and particles lines the respiratory from airways, has cilia passageways Simple Columnar Absorption Simple Cuboidal Secretion and Absorption Simple Squamous Diffusion and Filtration Stratified Squamous Protects underlying cells lines the uterus and most organs of the digestive tract glands, kidney tubules, ovaries lungs, walls of capillaries and vessels skin(keratinized) and the throat, vagina, mouth (soft) Stratified Cuboidal Protection lines ducts of the mammary glands, sweat glands, pancreas Stratified Columnar Protection, secretion male urethra and vas deferens, parts of the pharynx Transitional (unstretched) Specialized to become distended urinary tract