Urbanization Notes
advertisement
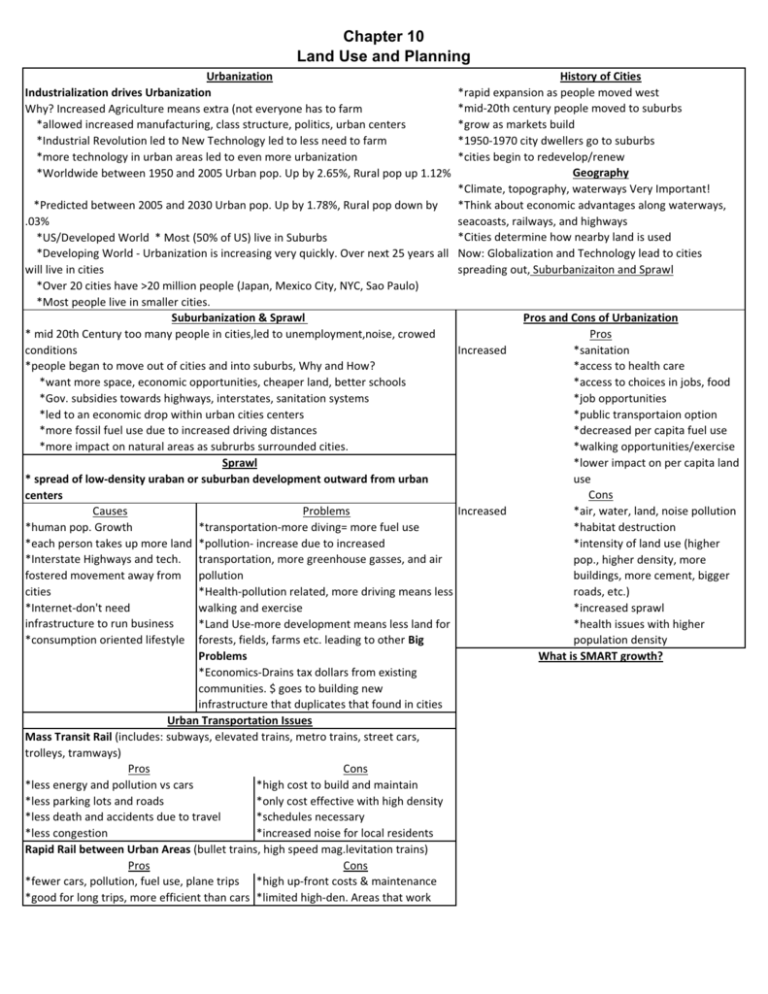
Chapter 10 Land Use and Planning History of Cities *rapid expansion as people moved west *mid-20th century people moved to suburbs *grow as markets build *1950-1970 city dwellers go to suburbs *cities begin to redevelop/renew Geography *Climate, topography, waterways Very Important! *Predicted between 2005 and 2030 Urban pop. Up by 1.78%, Rural pop down by *Think about economic advantages along waterways, .03% seacoasts, railways, and highways *Cities determine how nearby land is used *US/Developed World * Most (50% of US) live in Suburbs *Developing World - Urbanization is increasing very quickly. Over next 25 years all Now: Globalization and Technology lead to cities will live in cities spreading out, Suburbanizaiton and Sprawl *Over 20 cities have >20 million people (Japan, Mexico City, NYC, Sao Paulo) *Most people live in smaller cities. Pros and Cons of Urbanization Suburbanization & Sprawl Pros * mid 20th Century too many people in cities,led to unemployment,noise, crowed Increased *sanitation conditions *people began to move out of cities and into suburbs, Why and How? *access to health care *want more space, economic opportunities, cheaper land, better schools *access to choices in jobs, food *Gov. subsidies towards highways, interstates, sanitation systems *job opportunities *led to an economic drop within urban cities centers *public transportaion option *more fossil fuel use due to increased driving distances *decreased per capita fuel use *more impact on natural areas as subrurbs surrounded cities. *walking opportunities/exercise Sprawl *lower impact on per capita land use * spread of low-density uraban or suburban development outward from urban Cons centers Causes Problems Increased *air, water, land, noise pollution *human pop. Growth *habitat destruction *transportation-more diving= more fuel use *each person takes up more land *pollution- increase due to increased *intensity of land use (higher *Interstate Highways and tech. transportation, more greenhouse gasses, and air pop., higher density, more fostered movement away from pollution buildings, more cement, bigger *Health-pollution related, more driving means less cities roads, etc.) walking and exercise *increased sprawl *Internet-don't need infrastructure to run business *Land Use-more development means less land for *health issues with higher *consumption oriented lifestyle forests, fields, farms etc. leading to other Big population density What is SMART growth? Problems *Economics-Drains tax dollars from existing communities. $ goes to building new infrastructure that duplicates that found in cities Urban Transportation Issues Mass Transit Rail (includes: subways, elevated trains, metro trains, street cars, trolleys, tramways) Pros Cons *less energy and pollution vs cars *high cost to build and maintain *less parking lots and roads *only cost effective with high density *less death and accidents due to travel *schedules necessary *less congestion *increased noise for local residents Rapid Rail between Urban Areas (bullet trains, high speed mag.levitation trains) Pros Cons *fewer cars, pollution, fuel use, plane trips *high up-front costs & maintenance *good for long trips, more efficient than cars *limited high-den. Areas that work Urbanization Industrialization drives Urbanization Why? Increased Agriculture means extra (not everyone has to farm *allowed increased manufacturing, class structure, politics, urban centers *Industrial Revolution led to New Technology led to less need to farm *more technology in urban areas led to even more urbanization *Worldwide between 1950 and 2005 Urban pop. Up by 2.65%, Rural pop up 1.12%









