Biology
Slide
1 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary
System
Slide
2 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
(The skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands make up
the integumentary system.
The skin is the largest organ in the body.)
Slide
3 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
What are the functions of the
integumentary system?
Slide
4 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
A. The integumentary system:
• 1. serves as a barrier against infection
and injury.
• 2. helps to regulate body temperature.
• 3. removes waste products from the
body.
• 4. provides protection against
ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Slide
5 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
B. The Skin
1. two main layers:
a. epidermis
b. dermis.
2. Hypodermis:
a. layer of fat and connective tissue
b. insulates the body
Slide
6 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
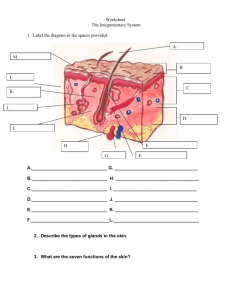
Structures of the Skin
Nerves
Sweat pore
The Skin
Blood
Hair
vessels
Sebaceous
gland
Hair follicle
Epidermis
Dermis
Muscle
Sweat
gland
Hypodermis
Fat
Slide
7 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
C. Epidermis
1. outer layer of the skin.
2. Made up of 2 layers:
a. outer layer-- dead cells.
b. inner layer -- living cells.
Slide
8 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
(Cells in the inner layer undergo rapid cell division,
producing new cells that push older cells to the
surface of the skin.
Older cells flatten and their organelles disintegrate.
Older cells also begin making keratin, a tough,
fibrous protein.
When these cells die, they form a waterproof
covering on the skin’s surface.)
Slide
9 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
3. Keratin: tough, fibrous protein, helps skin be
waterproof
4. Melanin:
a. dark brown pigment
b. protects skin from sun damage
c. amount melanin present produces
different skin colors
Slide
10 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
D. Dermis
1. inner layer of the skin
2. contains:
* collagen fibers,
* blood vessels,
* nerve endings,
*glands,
*sensory receptors,
*smooth muscles
*hair follicles.
Slide
11 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
The Skin
3: contains 2 types of glands:
a. sweat glands-
Produces sweat to help cool
the body
b. sebaceous (oil) glandsProduces sebum, spreads out
skin surface to keep it flexible
and waterproof
Slide
12 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
Hair and Nails
E. Hair (Hair covers most body surfaces)
1. Function:
a. protects scalp from uv light from sun.
b. provides insulation from cold.
c. prevents dirt and other particles from
entering the body.
Slide
13 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
Hair and Nails
(Hair is produced by hair follicles, which are tubelike
pockets of epidermal cells that extend into the
dermis.
An individual hair is a column of cells that have filled
with keratin and died.
The oily secretions of sebaceous glands help
maintain the condition of each individual hair.)
Slide
14 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3 The Integumentary System
Hair and Nails
F. Nails
1.grow from rapidly dividing cells in the nail root.
(white half moon at base of nail)
2.During cell division, cells fill with keratin to
produce a nail
3. cover/ protect the fingertips and toes.
Slide
15 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
Click to Launch:
Continue to:
- or -
Slide
16 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
Keratin provides
a. insulation.
b. a waterproof covering.
c. pigmentation.
d. protection from UV radiation.
Slide
17 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
The dermis contains two types of glands: sweat
glands and
a. sebaceous glands.
b. pigment glands.
c. hair follicles.
d. dermal glands.
Slide
18 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
All of the following are found in the dermis
EXCEPT
a. nerve endings.
b. blood vessels.
c. sebaceous glands.
d. melanocytes.
Slide
19 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
The function of melanin is to
a. help control the rate of heat loss by the skin.
b. produce sweat.
c. produce a waterproof covering on the
surface of the skin.
d. absorb harmful UV radiation.
Slide
20 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
36–3
The basic structure of human hair and nails is
a. melanin.
b. sebum.
c. keratin.
d. dermal cells.
Slide
21 of 23
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
END OF SECTION