Latin 2 Curriculum - Marblehead High School
advertisement

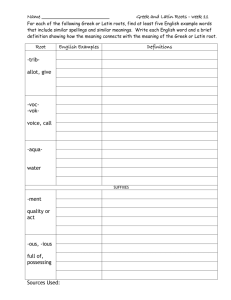
Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Credits: Grades: Revision date: Latin 2 Curriculum 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Conversation 2 Essential Questions: • How do I communicate in another langauge? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.2: Students use orally, listen to, and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Ask someone how they are (Quid agis?) or what’s new (Quid novi?) and respond to those questions • Ask someone if he/she likes something and say if I like something (Placetne tibi...? Mihi placet...) • Understand and follow classroom directions given in Latin (e.g. Sedēte! Surgite! Aperīte librōs!) • Ask and say what color something is (Quī color est...?) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Classroom conversation Student dialogs Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) Pictures as prompts for conversations ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Formative assessment NLE questions Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Numbers, Roman Numerals, and Dates Essential Questions: • • What different ways are there for counting? What can I do with Latin numbers? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans Standards for Classical Language Learning, 4.2: Students compare and contrast their own culture with that of the Greco-Roman world The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Translate and produce cardinal and ordinal numbers in Latin (1-20, 50, 100, 500, 1000) • Convert Roman numerals to Arabic numerals and vice versa • Ask and say how many of something there are • Ask and say what time it is (Quōta hōra est?) • Explain and apply the Roman customs of identifying the day of the month with reference to the Kalends, Nones, and Ides • Understand and idenfity different ways in which the Romans indicated what year it was (e.g. consular year, AUC date) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Classroom conversation Student dialogs Have students give their birthdays using the Roman dating system Write the date each day using the Roman dating system Included on final exam (end of Quarter 4) Calendar for the current year Formative assessment Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Credits: Grades: Revision date: Latin 2 Curriculum 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Mythology 2 Essential Questions: • • What is a myth? What can we learn about civilizations by studying their mythology? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Tell about the stories and deeds of major heroes (e.g. Jason, Odysseus, Perseus, Theseus, Daedalus) • Tell about the stories and characteristics of famous monsters (e.g. Minotaur, Chimera, etc.) • Tell about the stories and characters related to the Underworld (e.g. Cerberus, Charon, Proserpina, Styx, Pluto, etc.) • Summarize and discuss some major myths told by Ovid in his Metamorphoses (e.g. Orpheus and Eurydice, Pyramus and Thisbe, Baucis and Philemon, Actaeon, Niobe, Callisto, Arachne and Minerva) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Students teach about a myth or a mythological topic ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Formative assessment NLE questions Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) and final exam (end of Quarter 4) Supplementary books and materials on mythology Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Geography and the Roman World 2 Essential Questions: • • Who were the Romans? What places in the world were important to the Romans? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES MA 4.7: Demonstrate knowledge of the target culture’s geography by naming features such as rivers, mountains, cities, and climate on maps. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Important bodies of water (e.g. Adriatic, Aegean, Black Seas) • Rivers (e.g. Rhine, Po, Nile, Rubicon) • Important islands (e.g. Sicilia, Creta, etc.) • Important provinces (e.g. Germania, Aegyptus, etc.) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Map activities ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Formative assessment NLE questions Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) and final exam (end of Quarter 4) Maps of Italy and the Roman world Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Recreation and Entertainment Essential Questions: • • Who were the Romans? What was life like in ancient Rome? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.2: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Describe Roman chariot racing and the Circus Maximus • Describe (and possibly play) common games/pastimes of Roman children and adults • Discuss Roman attitudes toward the Colosseum and its games, and discuss what the Colosseum represented to Rome. • Discuss gladiators in ancient Rome: Who were they, what types were there, what did they do, what were their lives like? • Describe the rooms and features of a standard Roman bath, describe activities that Romans might enjoy at the baths, and explain how Romans provided hot water for the baths SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Video: “A Gladiator’s Story” (BBC) Formative assessment NLE questions Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Food, Meals, and Dining Essential Questions: • • Who were the Romans? What was life like in ancient Rome? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.2: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Identify and describe typical Roman foods • Identify and describe typical daily meals and dining habits • Identify and describe elements of an elegant Roman cēna SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Plan a Roman dinner Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) Formative assessment NLE questions Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Credits: Grades: Revision date: Latin 2 Curriculum 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Roman Housing Essential Questions: • • Who were the Romans? What was life like in ancient Rome? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.2: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Identify and describe the parts of a typical Roman domus • Describe Roman īnsulae and discuss some of the potentially good and bad things about them SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Create diagram or model of a Roman house Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) Formative assessment NLE questions Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Education, Writing, and Literature Essential Questions: • • Who were the Romans? What was life like in ancient Rome? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.2: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the products of the Greeks or Romans. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Discuss and explain Roman practices regarding education for boys and girls • Describe typical Roman customs regarding writing personal letters • Describe and explain Roman customs regarding writing, letters, and books • Discuss the life and contributions of the Roman poet Vergil • Read, translate, and recite the opening seven lines of Vergil’s Aeneid SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Create and use scrolls and tablets Formative assessment Read and discuss examples of Roman letters Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) and final exam (end of Quarter 4) Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Word Study, Derivatives, and Latin Expressions Essential Questions: • • • Why study another language? What Latin influences can we find in English and other languages? Where does Latin live around us? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 5.1: Students use their knowledge of Latin or Greek in a multilingual world MA 5.3: Give examples of ways in which the target language differs from / is similar to English MA 5.4: Give examples of borrowed and loan words The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Recognize and give the meanings of common Latin prefixes, including their alternate forms • Deduce the meaning of English words by considering their Latin prefixes, roots, and/or suffixes • Define the linguistic term assimilation and identify words that have undergone assimilation • Give the principal parts of faciō, teneō, rapiō, capiō, iaciō, claudō, sedeō, and dō, and give the principal parts of those same verbs when a prefix is added • Explain the meaning and significance of Latin expressions, mottoes and abbreviations SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Daily sententiae (Latin sayings, mottoes, abbreviations, etc.) Analyze compound verbs, breaking them down into roots and affixes Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) Unit: Roman History, Government, and Politics Formative assessment Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Essential Questions: • • • • Who were the Romans? What was ancient Rome like? How did government work in ancient Rome? What did the Romans value? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 2.1: Students demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives of Greek or Roman culture as revealed in the practices of the Greeks or Romans. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 3.1: Students reinforce and further their knowledge of other disciplines through their study of classical languages. The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Discuss the growth of Rome in size and dominance between the years Use supplementary readings Use library for research 201-146 B.C. • Discuss the characteristics, roles, and deeds of prominent historical characters from Roman history (e.g. Augustus, Hannibal, Julius Caesar, Cleopatra, Marc Antony, Spartacus) • Identify and discuss major events of Roman history (e.g. Punic Wars, Caesar’s conquest of Gaul) • Describe the political factions called populares and optimates and explain their roles in Rome during the period from 146-63 BC • Discuss the political views, motivations, and accomplishments of Republican leaders such as the Gracchi brothers, Gaius Marius, Sulla, and Pompey • Discuss the threat that pirates posed to the ancient Mediterranean and how the Romans dealt with piracy • Discuss key people and events from the late Republic including Cicero, Catiline, Julius Caesar, and the First Triumvirate • Discuss the life and accomplishments of the Roman emperor Augustus • Discuss the state of affiars in Roman government after Augustus as ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 well as the identities, characteristics, and accomplishments of the several emperors who followed Augustus (from Tiberius to Marcus Aurelius). SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Included on midterm exam (end of Quarter 2) and final exam (end of Quarter 4) Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Reading and Writinig Skills, Quarter 1 Essential Questions: • • • What is an inflected language? What are pronouns, and why use them? What are cases, and what are they used for? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.1: Students read, understand, and interpret Latin or Greek. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.2: Students use orally, listen to, and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 3.2: Students expand their knowledge through the reading of Latin or Greek and the study of ancient culture. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 4.1: Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. Course Standard: Translate Latin sentences and short passages, accurately accounting for the vocabulary, grammar, and syntax that has been studied The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Decline nouns of the 4th and 5th declension in all cases • • • • • Use 4th and 5th declension nouns in Latin sentences Identify, translate, and practice the partitive use of the genitive case Decline, translate, and correctly use forms of the demonstratives hic, haec, hoc and ille, illa, illud Translate hic and ille both when used as pronouns and as adjectives Supply the correct form of hic or ille to agree with a noun in a Repetition is important: Practice both orally and in writing Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Repetition is important: Practice both orally and in writing Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum • • • • • • • • sentence Identify special verbs that take the dative case (nocēre, cōnfīdere, favēre, appropinquāre, occurrere, crēdere) (H) Decline, translate, and correctly use forms of the personal pronouns ego, tū, nōs, vōs Decline, translate, and correctly use forms of the personal/demonstrative pronoun is, ea, id Decline, translate, and correctly use forms of the reflexive pronoun suī, sibi, sē, sē Recognize, translate, and correctly use ablative pronouns with the suffix -cum Identify, translate, and correctly use possessive adjectives meus, tuus, noster, vester, suus Understand and apply the difference in meaning between the 3rd person possessive pronouns eius/eōrum/eārum and the reflexive adjective suus, -a, -um Decline the relative pronoun quī, quae, quod • Define the terms clause, relative clause, relative pronoun, antecedent and identify them in English and Latin sentences • Explain and apply the rules about determining the case, gender, and number of the relative pronoun SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Formative assessment Repetition is important: Practice both orally and in writing Formative assessment Formative assessment Formative assessment Repetition is important: Practice both orally and in writing Bracket off relative clauses and identify the relevant parts of the sentence Common summative exams, middle and end of Quarter 1 Formative assessment Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Reading and Writing Skills, Quarter 2 Essential Questions: • • How does changing the form of a word affect its meaning? Why do Latin verbs have so many different forms? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.1: Students read, understand, and interpret Latin or Greek. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.2: Students use orally, listen to, and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 3.2: Students expand their knowledge through the reading of Latin or Greek and the study of ancient culture. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 4.1: Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. Course Standard: Translate Latin sentences and short passages, accurately accounting for the vocabulary, grammar, and syntax that has been studied The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Identify relative pronouns and translate sentences containing them • Identify, translate, and correctly use forms of the indefinite adjective quīdam, quaedam, quoddam • Identify, translate, and correctly use forms of the interrogative pronoun Quis?, Quid? • Identify and translate the causal conjunction quod • Identify and translate the exclamatory adverb Quam…! • Identify, decline, and translate the interrogative adjective quī ___?, quae ___?, quod ___? Formative assessment Presentation explaining formation Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Readily distinguish between the six types of qu-words listed above Define and explain the difference between active voice and passive voice Give (and recognize) the passive voice personal endings Identify, conjugate, and translate regular verbs + ferō in the present tense, passive voice Identify, conjugate, and translate regular verbs + ferō in the imperfect tense, passive voice Identify, conjugate, and translate regular verbs + ferō in the future tense, passive voice Restate simple Latin sentences so that the meaning is similar but the verb is passive voice Give and translate the present passive infinitives of regular verbs Change present active infinitives to passive (and vice versa) Identify and explain the uses of the ablative learned so far: time, means/instrument, manner, cause, price, personal agent, with prepositions Decline the demonstrative ipse, ipsa, ipsum Decline the demonstrative īdem, eadem, idem Translate both ipse and īdem appropriately in all cases Demonstrate a mastery of all the pronouns we have studied so far: hic, ille, ego, tū, nōs, vōs, is/ea/id, suī/sibi/sē/sē, quī, quīdam, quis, ipse, īdem Identify, conjugate, and translate verbs in the perfect tense, passive voice Identify, conjugate, and translate verbs in the pluperfect tense, passive voice Identify, conjugate, and translate verbs in the future perfect tense, passive voice Use the person, number, and gender of a perfect, pluperfect, or future perfect passive verb as a clue to determining its subject Write/produce perfect, pluperfect, and future perfect passive verbs in the correct person, number, and gender according to their subject Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Formative assessment Formative assessment Formative assessment Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Formative assessment Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Formative assessment Formative assessment Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • • Credits: Grades: Revision date: Common summative exam, middle of Quarter 2 Common midterm exam, end of Quarter 2 4 9-12 12/18/14 Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Reading and Writing Skills, Quarter 3 Essential Questions: • • Why do Latin verbs have so many different forms? How does a language describe people, places, things, and actions? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.1: Students read, understand, and interpret Latin or Greek. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.2: Students use orally, listen to, and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 3.2: Students expand their knowledge through the reading of Latin or Greek and the study of ancient culture. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 4.1: Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. Course Standard: Translate Latin sentences and short passages, accurately accounting for the vocabulary, grammar, and syntax that has been studied The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Identify and translate present, perfect, and future participles • Identify and translate present, perfect, and future infinitives • Demonstrate understanding of the difference between verbs in the perfect passive system and perfect passive participles by translating each kind of word appropriately • Demonstrate understanding of the action of a participle or infinitive relative to the action of the main verb o Present: happening at the same time o Perfect: already completed Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum • • • • • • • • • • • • • • o Future: happening at some future point Identify the degree of an adverb as positive, comparative, or superlative Correctly translate positive, comparative, and superlative adjectives Correctly translate quam with a comparative as “than” Correctly translate omnium with a superlative as “of all” Isolate the stem of any adjective Form and translate comparatives and superlatives of: o 1st and 2nd declension adjectives o 3rd declension adjectives o 1st and 2nd declension adjectives that end in -er o 3rd declension adjectives ending in -er o the six special 3rd declension adjectives that end in -lis o the irregular adjectives bonus, malus, magnus, parvus, multus/multī Use the partitive genitive with the word plūs Decline positive degree adjectives (declensions 1-3) Decline comparative adjectives and make them agree with nouns in sentences Decline superlative adjectives and make them agree with nouns in sentences Use both quam and the ablative case to express comparisons Recognize, translate, and use the ablative of degree of difference using multō and paulō Identify Latin adverbs and the words they modify Recognize, form, and translate: o positive degree adverbs from 1st/2nd declension adjectives (e.g. longus, miser) o positive degree adverbs from 3rd declension adjectives (e.g. fortis, fēlīx) o positive degree adverbs from 3rd declension adjectives whose stems end in -nt- (e.g. prūdēns) o the positive degree adverb from facilis, -is, -e Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum • Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 o comparative adverbs o superlative adverbs o comparatives and superlatives of the irregular adverbs bene, male, facile, magnopere, paulum, multum o comparatives and superlatives of the adverbs saepe, diū, and sērō Correctly translate quam with a superlative adjective or adverb as “as ___ as possible” SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • Common summative exams, middle and end of Quarter 3 Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum Credits: Grades: Revision date: 4 9-12 12/18/14 Unit: Reading and Writing Skills, Quarter 4 Essential Questions: • • How does Latin express place and time? What is the subjunctive? STANDARD INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.1: Students read, understand, and interpret Latin or Greek. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 1.2: Students use orally, listen to, and write Latin or Greek as part of the language learning process. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 3.2: Students expand their knowledge through the reading of Latin or Greek and the study of ancient culture. Standards for Classical Language Learning, 4.1: Students recognize and use elements of the Latin or Greek language to increase knowledge of their own language. Course Standard: Translate Latin sentences and passages, accurately accounting for the vocabulary, grammar, and syntax that has been studied The Standards, Deconstructed (“I can do...” statements): • Identify and correctly translate place expressions (accusative, ablative, and locative) when the place is a city, town, small island, or the words domus or rūs • Correctly translate accusative and ablative time expressions both with and without prepositions • Recognize and correctly translate adverbs that indicate time, e.g. crās, hodiē, iam, iterum, nunc, abhinc, post, ante • Give the principal parts and meanings of the semi-deponent verbs audeō, gaudeō, soleō • Correctly translate semi-deponent verbs with respect to person, Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Web Publication Date: 1/10/15 Marblehead High School: World Language Department Latin 2 Curriculum • • • • • • • • • • • Credits: Grades: Revision date: number, and tense Identify and translate present participles Form present participles from regular verbs, deponent verbs, and the verb eō, īre Decline present participles and make them agree with nouns Isolate participles/participial phrases in sentences and identify what nouns they modify Recognize when present participles are used as substantives and translate accordingly Recognize, form, and translate the perfect active infinitive of regular verbs Recognize and translate sentences with the construction dīcitur + infinitive Identify and translate imperfect and pluperfect subjunctives Form and conjugate verbs in the imperfect and pluperfect subjunctive Identify and translate cum circumstantial and cum causal clauses Identify and translate indirect questions SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: SPECIAL MATERIALS: PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT NEEDS: REFLECTION/NOTES: • • • • • Common summative exam, middle of Quarter 4 Common final exam, end of Quarter 4 4 9-12 12/18/14 Minor assessment/Chapter quiz Formative assessment Formative assessment Formative assessment Minor assessment/Chapter quiz