Pre Lab C7
advertisement
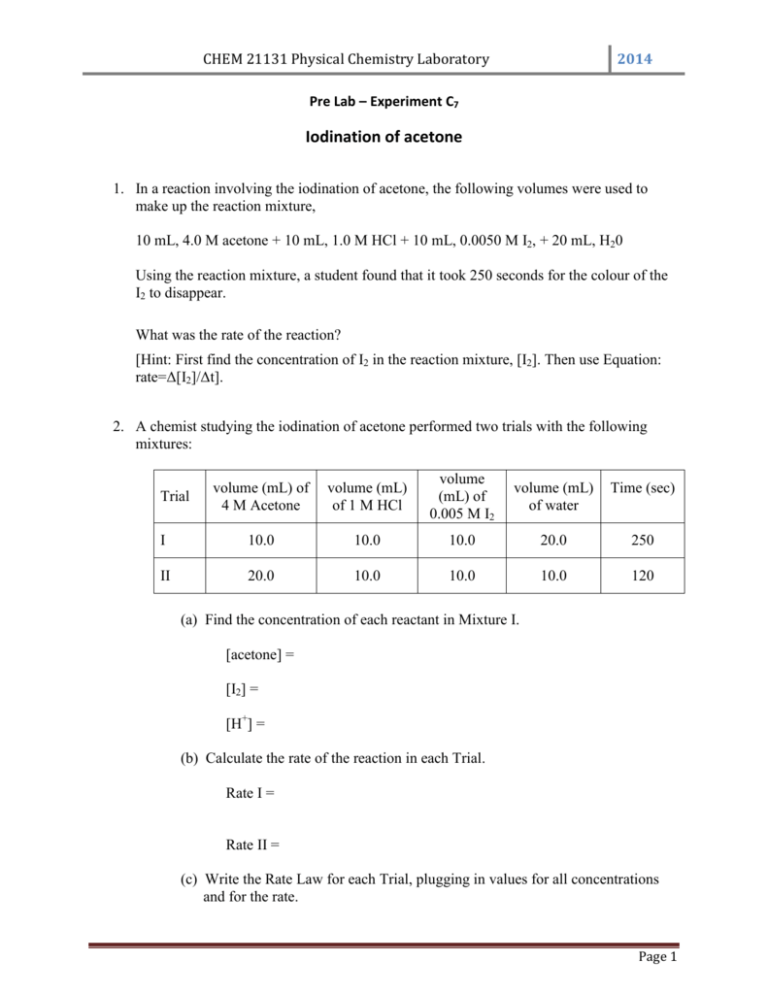
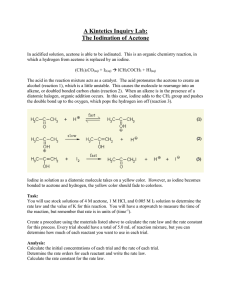
CHEM 21131 Physical Chemistry Laboratory 2014 Pre Lab – Experiment C7 Iodination of acetone 1. In a reaction involving the iodination of acetone, the following volumes were used to make up the reaction mixture, 10 mL, 4.0 M acetone + 10 mL, 1.0 M HCl + 10 mL, 0.0050 M I2, + 20 mL, H20 Using the reaction mixture, a student found that it took 250 seconds for the colour of the I2 to disappear. What was the rate of the reaction? [Hint: First find the concentration of I2 in the reaction mixture, [I2]. Then use Equation: rate=Δ[I2]/Δt]. 2. A chemist studying the iodination of acetone performed two trials with the following mixtures: volume (mL) of 4 M Acetone volume (mL) of 1 M HCl volume (mL) of 0.005 M I2 volume (mL) of water Time (sec) I 10.0 10.0 10.0 20.0 250 II 20.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 120 Trial (a) Find the concentration of each reactant in Mixture I. [acetone] = [I2] = [H+] = (b) Calculate the rate of the reaction in each Trial. Rate I = Rate II = (c) Write the Rate Law for each Trial, plugging in values for all concentrations and for the rate. Page 1 CHEM 21131 Physical Chemistry Laboratory 2014 Rate II = Rate I = Divide Rate II by Rate I to determine the order with respect to acetone. 3. Define the following terms, (a) differential rate law (b) integrated rate law. 4. Summary of the kinetics for reactions of the type A→ products that are zero, first or second order in [A] is given below. Complete the table. Order Rate Law 0 rate = k Integrated Rate Equation Linear Plot Slope Units for k [A] vs time -k M/s 1 2 Page 2