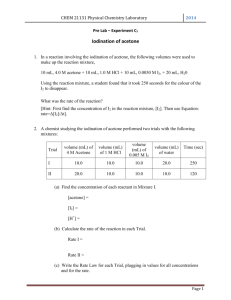
Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Lab Partner: ________________________ Lab Section: ________________________ Lab TA: ________________________ CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Experimental Data A. Determination of Reaction Orders Reaction Mixture Volume of 4.0 M Acetone (mL) Volume of 1.0 M HCl (mL) Volume of 0.0050 M I2 (mL) Volume of Distilled H2O (mL) I 4 4 8 4 II 2 4 10 4 III 4 2 10 4 IV 4 4 10 2 Reaction Mixture Total Volume (mL) Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Time (sec) Temp (ºC) Time (sec) Temp (ºC) Time (sec) Temp (ºC) I 20 20 II 25 25 III 25 25 IV 25 25 B. Energy of Activation Reaction Mixture Trial 1 Time (sec) Temp (ºC) Trial 2 Trial 3 Time (sec) Temp (ºC) Time (sec) Temp (ºC) Low Temp High Temp TA: ________________________ E02-9 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Calculations A. Determination of Reaction Orders 1. Calculate the concentration of the components in each reaction mixture. Show at least one example calculation: Reaction Mixture Concentration of 4.0 M Acetone (M) Concentration of 1.0 M HCl (M) Concentration of 0.0050 M I2 (M) I II III IV 2. Calculate the rate of reaction for every trial of each mixture from Part A. Show at least one example calculation: Reaction Mixture I II III IV E02-10 Trial 1 Rate Trial 2 Rate Trial 3 Rate Average Rate CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Calculations (continued) 3. Determine the order of reaction with respect to each component: (Hint – see textbook Example 14.2) a) Order of reaction with respect to acetone m = _______ b) Order of reaction with respect to acid n = _______ c) Order of reaction with respect to iodine p = _______ 4. Write the rate expression for the reaction: 5. Determine the rate constant, k, for each reaction mixture, using the average rates determined in #2. Show at least one example calculation: Reaction Mixture: Rate constant, k= I II III IV Average E02-11 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Calculations (continued) B. Energy of Activation 6. Calculate the rate of reaction for every trial of each mixture from Part B. Show at least one example calculation: Temperature Trials Low Temp High Temp Reaction Mixture Trial 1 Rate Trial 2 Rate Trial 3 Rate Average Rate 7. Determine the rate constant, k, for each of the temperature trials from Part B. Show at least one example calculation: Temperature Trials Low Temp High Temp Reaction Mixture Rate constant, k= 𝟏 8. Data to use for the graph of 𝐥𝐧 𝒌 versus 𝐓 to estimate 𝐄𝐚 , the energy of activation: Temperature Trials Low Temp Room Temp High Temp E02-12 Temp (K) 1 𝐓 𝑘 ln 𝑘 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Additional Calculations and Results 9. Determine the energy of activation, 𝐄𝐚 for this reaction. Attach the graph you used to determine this value. (Hint – see textbook Example 14.7) Compound ∆𝑯𝒇 ° (kJ/mol) CH3 COCH3 −248.4 CH3 COCH2 I −130.6 I2 13.5 I− −56.0 H+ 0.0 10. Use the energies of formation, given in the table to the right, to determine the heat of reaction, ∆𝑯°𝒓𝒙𝒏 for the iodination of acetone. (Hint – recall textbook Example 9.12) E02-13 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Additional Calculations and Results (continued) 11. a) Having experimentally shown that the rate expression is zero order with respect to iodine, and given the following, determine which is the rate determining (slow) step in the mechanism outlined below: Step 1: __________ (fast or slow?) Step 1: 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐂𝐇𝟑 (𝒂𝒒) + 𝐇 + (𝒂𝒒) ↔ 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐇𝐂𝐇𝟑 + (𝒂𝒒) Step 2: __________ (fast or slow?) Step 2: 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐇𝐂𝐇𝟑 + (𝒂𝒒) ↔ 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐇𝐂𝐇𝟐 (𝒂𝒒) + 𝐇 + (𝒂𝒒) Step 3: __________ (fast or slow?) Step 3: 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐇𝐂𝐇𝟐 (𝒂𝒒) + 𝐈𝟐 (𝒂𝒒) → 𝐂𝐇𝟑 𝐂𝐎𝐂𝐇𝟐 𝐈(𝒂𝒒) + 𝐇 + (𝒂𝒒) + 𝐈− (𝒂𝒒) b) Explain your answer: E02-14 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Name: ________________________ Date: ________________________ Post-Lab Questions 12. Why is knowing the exact concentrations of the acetone, iodine, and acid not critical in determining the orders of reaction, but using the same stock solutions throughout the experiment is critical? 13. In determining the energy of activation, why was it prudent to run the slowest trial done at room temperature in the hot water bath and the fastest trial done at room temperature in the cold water bath? E02-15 CHEM 032 Experiment 2: Chemical Kinetics Analysis of the Iodination of Acetone Results & Discussion: The main experimental result(s) should be clearly summarized and related back to the purpose of the experiment. Should also include a brief discussion of experimental error when applicable. E02-16