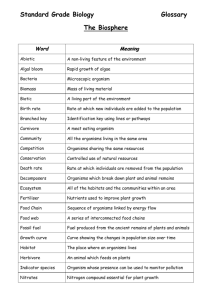
Environmental Science—Chapter 4 Vocabulary 1. Ecology: study of
advertisement

Environmental Science—Chapter 4 Vocabulary 1. Ecology: study of the interactions of living organisms with one another and with their nonliving environment of matter and energy 2. Organism: any form of life 3. Population: group of individual organisms of the same species living in a particular area 4. Genetic diversity: variability in the genetic makeup among individuals within a single species 5. Habitat: place or type of place where an organism or population of organisms lives 6. Community: populations of all species living and interacting in an area at a particular time 7. Ecosystem: community of different species interacting with one another and with the chemical and physical factors making up its nonliving environment 8. Biosphere: zone of the earth where life is found 9. Atmosphere: whole mass of air surrounding the earth 10. Hydrosphere: the earth’s liquid water, frozen water, and small amounts of water vapor in the atmosphere 11. Lithosphere: outer shell of the earth, composed of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle outside the asthenosphere 12. Greenhouse effect: natural effect that releases heat in the atmosphere (troposphere) near the earth’s surface 13. Biome: terrestrial regions inhabited by certain types of life, especially vegetation 14. Climate: physical properties of the troposphere of an area based on analysis of its weather over a long period (at least 30 years); the two main factors are temperature and precipitation 15. Ecotone: transitional zone in which one type of ecosystem tends to merge with another type of ecosystem 16. Abiotic: nonliving 17. Biotic: living organisms 18. Autotroph: organism that uses solar energy (green plant) or chemical energy (some bacteria) to manufacture the organic compounds it needs as nutrients 19. Heterotroph: organism that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients it needs and gets its organic nutrients by feeding on the tissues of producers or of other consumers 20. Herbivore: plant-­‐eating organism 21. Carnivore: animal that feeds on other animals 22. Omnivore: animal that can use both plants and other animals as food sources 23. Scavenger: organism that feeds on dead organisms that were killed by other organisms or died naturally 24. Detritivore: consumer organism that feeds on detritus, parts of dead organisms, and cast-­‐off fragments and wastes of living organisms 25. Detritus feeder: organism that extract nutrients from fragments of dead organisms and their cast-­‐off parts and organic wastes 26. Decomposer: organism that digests part of dead organisms and cast-­‐off fragments and wastes of living organisms by breaking down the complex organic molecules into simpler inorganic compounds and then absorbing the soluble nutrients 27. Food Chain: series of organisms in which each eats or decomposes the preceeding one 28. Trophic level: all organisms that are the same number of energy transfers away from the original source of energy that enters an ecosystem 29. Food web: complex network of many interconnected food chains and feeding relationships 30. Biomass: organic matter produced by plants and other photosynthetic producers 31. Nutrient: any food, element, or compound an organism must take in to live, grow, or reproduce 32. Water cycle: biogeochemical cycle that collects, purifies, and distributes the earth’s fixed supply of water from the environment to living organisms and then back to the environment 33. Carbon cycle: cyclic movement of carbon in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment 34. Nitrogen cycle: cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment 35. Phosphorus cycle: cyclic movement of phosphorus in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment 36. Sulfur cycle: cyclic movement of sulfur in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment