EcologyCrossword
advertisement
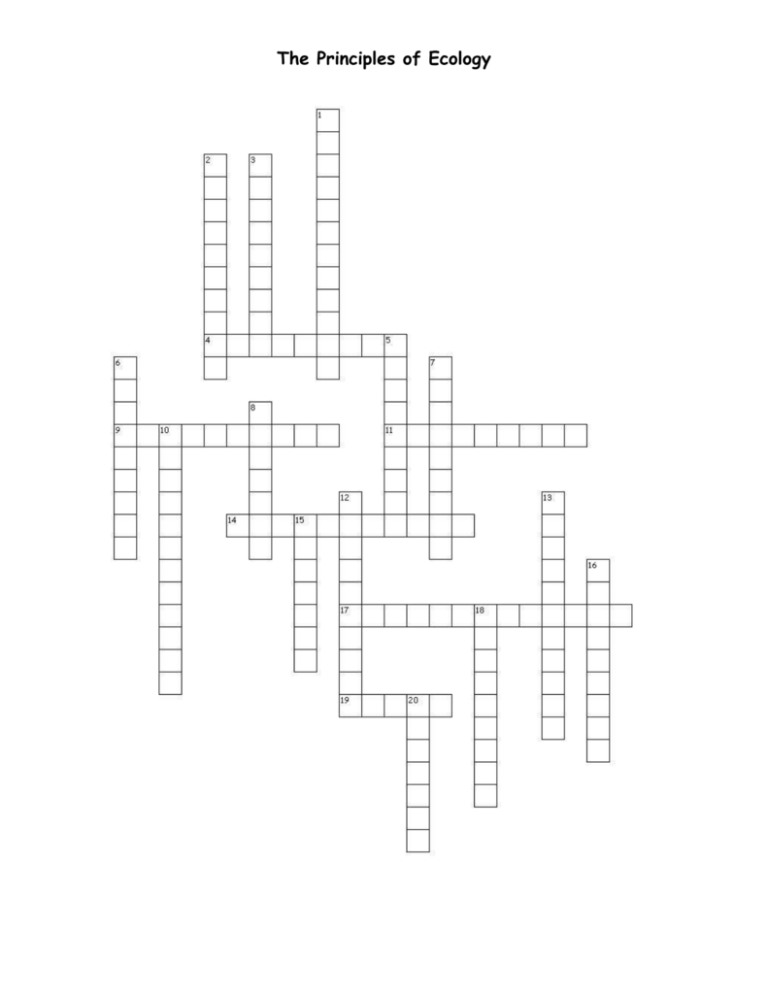
The Principles of Ecology Across 4. Permanent, close association between two or more organisms of different species. 9. Organisms, such as fungi, that break down and absorb nutrients from dead organisms. 11. Interactions among populations in a community; the community's physical surrounding, or abiotic factors. 14. Organisms that cannot make their own food and must feed on other organisms for energy and nutrients. 17. Nonliving parts of an organism's environment; temperature, light, and soil are examples. 19. Role and position a species has in its environment; includes all biotic and abiotic interactions as an animal meets its need for survival and production. Down 1. All living organisms that inhabit an environment. 2. Symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits at the expense of the other species. 3. A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit. 5. Animals that feed on animals that have already died. 6. Simple model that shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem; can consist of three steps, but must have no more than five steps. 7. Organism that used energy from the sun or energy stored in chemical compounds to manufacture their own nutrients. 8. Model that expresses all the possible feeding relationships at each trophic level in a community. 10. Symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor benefited. 12. Group of organsms of one species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. 13. Organism in a food chain that represents a feeding step in the passage of energy and materials through an ecosystem. 15. Scientific study of interactions among organisms and their environment. 16. Portion of Earth that supports life; extends from the atmosphere to the bottom of the oceans. 18. Collection of several interacting populations that inhabit a common environment. 20. Place where an organism lives out its life. Home