ResultSet and Statements

JDBC
Framing
•
•
•
•
•
Accessing DBMS from your code
•
A possible way of writing applications accessing DBMS
You’ll see other ways via Web technologies
•
ODBC: Open Data Base Connectivity
C/C++ API
•
JDBC: Java Data Base Connectivity
Java API
•
Both define interfaces , i.e.
Set of methods you can use to do SQL queries (both DDL and DML)
2
JDBC Architecture
3
Advantages
•
•
•
•
Separate your code from the native language of the DBMS
You can use JDBC with any DBMS that provides a driver (or for which a bridge is available, see later)
•
Not necessarily a relational DBMS
But JDBC always accepts SQL-like statements!
You can re-use your code with any DBMS
•
Provided you have the relative driver
4
Lab setup
•
•
PostgreSQL provides native Java drivers
•
•
•
•
Postgresql JDBC library must be included in
NetBeans projects project’s properties libraries run and/or compile add postgresql JDBC driver
8
Typical actions within the code
•
•
•
•
Load the DBMS driver
Create a Connection with the DBMS
•
•
•
•
Any number of times
Submit SQL statements
Retrieve results
Process data/errors
Commit or rollback
Close the connection
9
Code spots
•
•
•
•
•
Using (at least) one java package to interact with the JDBC driver import java.sql.*; in your import list javax.sql
: advanced feature (we will not cover them)
•
•
Load the driver
Class.forName(“org.postgresql.Driver”);
Catch a ClassNotFound exception!!!
•
Connect to the DBMS
String url=
“jdbc:postrgesql://delmastrof.iit.cnr.it/u01db”;
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url, “u01”, “m-s-t+20+12”); user password
10
(A bit more) General format of the URL string
•
•
Connect to the DBMS
String url=
“jdbc:postrgesql://delmastrof.iit.cnr.it/u01db”;
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url, “u01”, “m-s-t+20+12”);
11
Submit SQL statements
•
•
•
•
•
DML
•
Statement st = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(
“SELECT * FROM net WHERE gw=‘192.168.2.1’”);
Or, you can use PreparedStatements :
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(
“SELECT * FROM net WHERE admin=?”); pst.clearParameters(); pst.setString(1, “gianni”);
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
•
DDL
Statement st = con.createStatement(
“INSERT INTO net VALUES
(‘andrea’,’192.168.5.1’,’192.168.5.0/24’)”); int numRows = st.executeUpdate();
12
Getting results back
•
•
•
DDL statements return the number of rows modified
Statement st = con.createStatement(
“INSERT INTO net VALUES
(‘andrea’,’192.168.5.1’,’192.168.5.0/24’)”); int numRows = st.executeUpdate();
•
•
DML statements return a
ResultSet
(an iterator)
•
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query); while(rs.next()){
String ad = rs.getString(“admin”);
// or, String ad = rs.getString(1); if admin is the first
// field of the table
…
}
Move in the ResultSet with methods previous(), absolute(int), relative(int), first(), last()
13
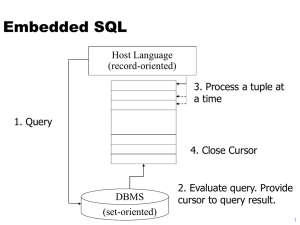
ResultSet and Statements
•
•
A ResultSet is associated with the previous statement
•
Don’t issue another query via the same statement before getting back all results:
•
WRONG
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query); while(rs.next()){
String ad = rs.getString(“admin”);
ResultSet rs1 = st.executeQuery(query1);
…
}
CORRECT
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query);
Statement st1 = con.createStatement(); while(rs.next()){
String ad = rs.getString(“admin”);
ResultSet rs1 = st1.executeQuery(query1);
…
}
14
Data types
•
•
•
•
Most are already defined by Java integer, String, …
•
Other are defined in the java.sql package java.sql.Date, java.sql.Time, java.sql.Timestamp, …
•
•
Other within the driver package
Org.postgresql.geometric.PGcircle,
Org.postgresql.geometric.PGline, …
See http://jdbc.postgresql.org/documentation/publicapi/ index.html
15
Transactions
•
•
By default, each statement is a transaction
•
•
To alter this,
Connection con = …; con.setAutoCommit(false);
// con.getAutoCommit() to retrieve the current commit mode con.commit(); to close a transaction explicitly
16
Exceptions
•
•
•
•
Methods throw SQLException getSQLState() return a SQL state identifier getErrorCode() return a vendor-specific error code
•
So, typically try{
Statement st = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query); while(rs.next()){
// process results
}
} catch SQLException(e){
// process exception here
}
17
Getting metadata
•
•
•
Use ResultSetMetaData type to get metadata about a ResultSet
Information such as the name and type of fields
Have a look at host.java
•
•
In general, use the Java API specs for documentation http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/api/index.html
18
Secure connections
• String url = “jdbc:postrgesql://delmastrof.iit.cnr.it/u01db?
user =u01& password =m-s-t+20+12& ssl=true ”;
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
19
Secure connections
•
•
String url = “jdbc:postrgesql://delmastrof.iit.cnr.it/u01db?
user =u01& password =m-s-t+20+12& ssl =true& sslfactory =org.postgresql.ssl.NonValidatingFactory”;
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
String url =
"jdbc:postgresql://delmastrof.iit.cnr.it/u01db”;
Properties props = new Properties(); props.setProperty(" user ",”u01"); props.setProperty(" password ",”m-s-t+20+12"); props.setProperty(" ssl ","true"); props.setProperty(" sslfactory ",
"org.postgresql.ssl.NonValidatingFactory"); // no cert. validation
•
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, props );
See http://jdbc.postgresql.org/documentation/84/connect.html
http://jdbc.postgresql.org/documentation/84/ssl-client.html
20
Useful examples
•
•
•
• provaFile.java
Managing I/O from/to file
• provaIO.java
Managing input from keyboard
• provaInet.java
Managing network data types
21
NetBeans working directory
• header of any relative path in your source code
22