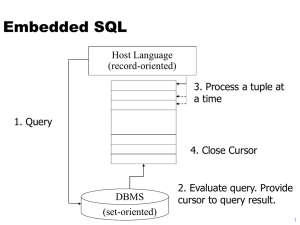
JDBC:Java Database Connectivity What does JDBC do
advertisement

JDBC:Java Database Connectivity
z
What is JDBC™?
z
z
z
Java™ API for executing SQL statements
Consists of a set of classes and interfaces written in
the Java programming language
Provides a standard API for tool/database
developers and makes it possible to write database
applications using a pure Java API
Establishing a Connection
z
Connection
z
z
Manages connection between database and program
Create connection
z
1. Checking for driver
z Using static method forName (class Class)
z
Load class definition for database driver (complete package name)
Throws ClassNotFoundException
2. Open a connection
z Using Class DriverManager
The basic service for managing a set of JDBC drivers
getConnection(url, user-name, password)
What does JDBC do?
z
z
z
Establish a connection with a database
Send SQL statements
Process the results
package: java.sql
Has classes and interfaces for using relational databases
Example:
Connection con ;
try {
Class.forName(“sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
String url = "jdbc:odbc:nwind" ;
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"admin","");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException cnfe){
System.out.println(“No specific driver..”);
}
z
url:
Protocol for communication (jdbc)
Subprotocol (odbc)
- indicates Microsoft ODBC data source
- Driver allowing Java to access any ODBC source:
sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver
Database name (nwind)
Sending SQL Statements
z
JDBC provides three classes for sending SQL
statements to the database.
z
z
z
Statement
z Created by the method createStatement
z Used for sending simple SQL statements
PreparedStatement
z Created by the method prepareStatement
z Used for SQL statements that take one or more parameters as
input arguments (IN parameters)
CallableStatement
z Created by the method prepareCall
z Used to execute SQL stored procedures
Example:
Class.forName(“sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
String url = "jdbc:odbc:nwind";
Connection con;
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "admin", "");
The Statement Objects
z
z
z
z
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
The Statement interface provides three different methods for
executing SQL statements
z executeQuery
z executeUpdate
Execute INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements and also
SQL DDL (Data Definition Language) statements like
CREATE TABLE and DROP TABLE
z execute
The execute method should be used only when it is possible
that a statement may return more than one ResultSet object,
more than one update count, or a combination of ResultSet
objects and update counts
The PreparedStatement Objects
z
Creating PreparedStatement
Class.forName(“sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
String url = "jdbc:odbc:nwind" ;
Connection con ;
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "admin", "");
PreparedStatement pstmt =
con.prepareStatement("UPDATE Customer SET
companyname=? WHERE customerid=?");
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = “SELECT * FROM Customers”
The object used for executing a static SQL statement
and returning the results it produces
A Statement object is created with the Connection
Executing Statement Objects
z
Passing IN parameters
z Use method setXXX(order, value)
pstmt.setString(1,“IT-SOFT”) ;
pstmt.setLong(2, 41254) ;
pstmt.executeUpdate();
ResultSet
z
z
z
z
Example:
Contains all of the rows which satisfied the conditions
in an SQL statement
Provides access to the data in those rows through a
set of get methods
The ResultSet.next method is used to move to the
next row of the ResultSet, making the next row
become the current row
The general form of a result set is a table with column
headings and the corresponding values returned by a
query
ResultSetMetaData
z
z
Use to get information about the types and
properties of the columns in a ResultSet
object
Created by the method getMetaData()
z
Example:
ResultSet rs =
stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM
Customers");
ResultSetMetaData rsmd ;
rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int cols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
ResultSet rs =
stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM
Customers");
while ( r.next() ) {
int i = r.getInt("customerid") ;
String s = r.getString("companyname");
float f = r.getFloat("discount_rate");
System.out.println(“ROW = " + i + " " + s + " " +
f);
}