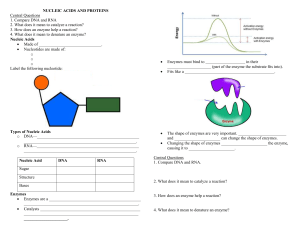
Name: 9th grade Biology Midterm STUDY GUIDE • What day is my
advertisement

Name: 9th grade Biology Midterm STUDY GUIDE What day is my biology midterm exam? What time is my biology midterm exam? What is going to be on the midterm exam? The exam will ask questions about topics you have learned for the 1st and 2nd marking periods. Expect to see questions about the following topics: o Scientific Method o The Cell & Microscope o Cellular Energy (Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration) o Enzymes o DNA o Human Impacts on the Environment How is the test organized? What type of questions should I expect? The midterm exam will consist of two parts, and is worth a total of 125 points. Part I (known as the “core””) will be worth 75 points and consist of 75 multiple choice questions. This part of the test was created by all of the biology teachers of the science department. Part II (known as the “addendum”) will be worth 50 points and contain short answer questions and some multiple choice. This part of the exam is created by just your teacher. How will this review packet help me study for the midterm exam? You have learned many details of biology so far this school year, the midterm will not cover every little detail. This packet will let know you what specific vocabulary words and biology topics will be asked on the midterm exam. How will the midterm exam be calculated into my grade? Your midterm exam score will count towards 10% of your overall biology grade. Your overall grade will be calculated at the end of the school year. Here is the breakdown: 1st MP = 20% 2nd MP = 20% Midterm Exam = 10% 3rd MP = 20% 4th MP = 20% Final Exam = 10% How can I study smarter instead of longer? o Cramming & all-nighters can negatively affect your memory. Study sessions are best as repeated small chunks (20-30 minutes). Set a goal on what you want to study during each session, focus on one topic. o Study flash cards. Use Quizlet or make your own. o Teach the topic you have just studied to someone else (friend, parent, sibling, etc). Your brain will organize the information in a more logical and coherent manner. If you can’t find someone, you can always talk out loud and teach to yourself. o Have a designated place for studying. Somewhere with minimal distraction. Make sure it has everything you will need to help you study. If your home or bedroom is distracting consider going to the public library. They have quiet study rooms that you can request to use. o Avoid listening to your favorite music, classical music is okay. o Put away your phone!!!! Give it to someone so you are not tempted to check notifications and updates. MIDTERM VOCABUALRY Scientific Method Problem Statement Independent Variable Dependent Variable Hypothesis Control Group Experimental Group Controls/Constants Conclusion Validity Qualitative data Quantitative data Cell Energy Continued Autotroph Heterotroph Reactants Products Enzymes Enzyme Substrate Active Site Denaturation Acid Base pH Microscope Eye piece Stage Objective lenses Coarse adjustment Fine Adjustment Base Total magnification DNA Nucleotides Gene Chromosome DNA Replication Guanine Cytosine Thymine Adenine Uracil DNA RNA Ribosome Amino Acids Codon Protein Cell Structure & Function Nucleus Ribosomes Cell membrane Cytoplasm Mitochondria Vacuole Cell Wall Prokaryote Eukaryote Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Passive Transport Semi-permeable Permeable Impermeable Human Impacts on the Environment Renewable Energy Fossil Fuels Methane CFC Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Cycle Brownfield Site Remediation Eutrophication Bioaccumulation Landfill Incinerator Cell Energy Carbohydrates Lipids Protein Nucleic Acids Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration ATP Glucose 2 SCIENTIFIC METHOD: Read the definition and identify the vocabulary word. the investigation or question to be answered. : A statement that accurately defines the goal(s) of : An educated guess that addresses the problem statement, is testable, and predicts the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. : The variable in an experiment this is purposely changed or manipulated, either in quality or quantity, by the researcher. “What I change at the beginning of the experiment”. : The variable in an experiment that changes in response to the independent variable. “What I measure at the end of the experiment”. : The group or trials in an experiment that receive all the same conditions except varying amounts or qualities of the independent variable. : The group in an experiment that receives the exact treatment as the experimental groups except it does not receive any change of the independent variable. It is the group to which the experimental groups are compared. : Factors within an experiment that are kept the same for all groups or trials to ensure that all trials of an investigation were equally impacted by the controlled variables, therefore allowing one to see the impact of the independent variable. : The replication of experimental and control groups; used to decrease the influence of variations associated with the independent variable or researcher measurement error. : Data that describe characteristics of qualities, such as color, odor, or texture, or data that describes category frequency or ratings (ex. flower stem sturdiness is “sturdy” or “somewhat sturdy”). (liters, grams, meters, Celsius, minutes etc.) : Data that use numbers with a unit of measurement Describe two ways a scientist can make sure their lab experiment is considered VALID: 3 The Motts Apple Juice Company wanted to improve apple juice production. The company knows that it can use an enzyme to help break down apple sauce into apple juice, but wants to figure out which enzyme will work best. Motts designed and conducted experiments to determine which enzyme, cellulase or pectinase, when added to apple sauce, would give the greatest amount of apple juice. Below is the procedure and results of an experiment. PROBLEM STATEMENT- INDEPENDENT VARIABLE – DEPENDENT VARIABLE – Write a proper HYPOTHESIS – CONTROL GROUP- EXPERIMENTAL GROUP(S)- CONTROLLED VARIABLES (CONSTANTS) – 4 THE CELL and MICROSCOPE 1. Know the parts of the microscope. Base Coarse adjustment Diaphragm Eye piece Fine Adjustment Light source Objective lenses Stage 2. When you are using the microscope, what is the function of the coarse adjustment verses using the fine adjustment? 3. Calculate total magnification. 4.A student looked at onion cells through a microscope. Underneath each picture write down if the student used HIGH, MEDIUM or LOW power objectives to see the onion cells. 5 5. We use microscopes to look at cells. What is a cell? 6. Describe a prokaryotic cell. Name one type of cell that is prokaryotic. 7. Describe a eukaryotic cell. Name two types of cells that are eukaryotic. 8. Fill in the chart below Organelle Function Cell membrane Cell wall Mitochondria Chloroplast Nucleus Ribosome Vacuole 6 Found in: Plant cell? Animal cell? Bacteria cell? 9. Label the plant and animal cell images. DRAW IN THE RIBOSOMES (they are missing in the picture). Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Chloroplast, Vacuoles 10. One of cell’s functions is to transport materials across the cell membrane. Write down the definitions of each type of cellular transportation. CELL TRANSPORTATION PASSIVE TRANSPORT: ACTIVE TRANSPORT: What does it mean for a cell membrane to be… DIFFUSION: a. semi-permeable: OSMOSIS: b. permeable: c. impermeable: 7 11. Scientists model the process of diffusion and osmosis using specialized plastic bags. Consider the following experiment: a bag containing starch and water is placed in a beaker of water containing an iodine solution. When iodine and starch come in contact, a bluish-black color is formed. At the beginning of the experiment, the bag contained a solution of water + starch (which was clear in color) and the beaker contained a solution of water + iodine (which was brown in color). The end the bag swelled up and weighed heavier than initially. Was it permeable, impermeable or semipermeable to the bag? What is the evidence to support your answer? Iodine Starch Water CELL ENERGY 12. Describe the function of the organic molecules listed in the chart below and provide examples for each. Carbohydrates Lipids Protein Function Examples 8 TWO Nucleic Acid 13. What are the names of each of the molecules shown below? Which one is the molecule your cells need to perform cellular activities? 14. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are important chemical reactions that provide energy for cells. Complete the chart to help you compare the two. Definition Reactants Products Organisms that perform this process Autotrophs or Heterotrophs or both Organelle Respiration Cellular Photosynthesis Process Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are interdependent, which means they rely on each other. Explain why. 9 15. Using the information you gathered previously, write the formula for photosynthesis. Use words, you don’t have to memorize the chemical formula version. 16. Write the formula for cellular respiration. Use words, you don’t have to memorize the chemical formula version. ENZYMES 17. What is the role or function of enzymes? 18. Which type of organic molecule are enzymes made of? 19. Label the image below with the following vocabulary terms. ACTIVE SITE, ENZYME, SUBSTRATE, & PRODUCT. 20. Specific enzymes react with specific substrates. Explain why. 10 21. Enzymes reaction are sensitive to temperature conditions. Describe the rate of enzyme activity and why this is happening for the following temperature conditions: a) 0 oC – 39 oC b) 40 oC c) 41 oC – 65oC 22. Enzyme reactions are also sensitive to pH levels. a) pH levels 1 – 6 are known as b) pH level 7 is known as c) pH levels 8 – 14 are known as 23. When an enzyme is exposed to temperatures of pH conditions beyond its optimal range the process of denaturation occurs. Explain what it means for an enzyme to be denatured and why this is a problem. 11 DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 24. What are the building blocks of DNA called? Label the diagram. 25. What makes one person’s DNA different from another? 26. List and describe the 3 steps of DNA replication. STEP 1: STEP 2: STEP 3: 12 27. Compare DNA & RNA. single-stranded ribose sugar guanine (G) uracil (U) double-stranded deoxyribose sugar made of nucleotides adenine (A) phosphate DNA Both 28. Label the diagram. Using the following word bank: Amino Acids DNA Nucleus Protein Ribosome RNA 29. What is the purpose and function of RNA? 30. What are the building blocks of proteins? 31. What is a codon? 13 thymine (T) cytosine (C) RNA 32. Protein Synthesis takes place through two steps. Fill in the chart below to explain the process. Process Location in the Cell What is happening during this process? Which molecules are involved? TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION 33. Transcribe the DNA and then translate the RNA strand to create an amino acid chain. You will be provided a amino acid / codon chart to help you on the midterm exam. WARNING: the start and stop codon was not included for this sequence. DNA A G T T A T C A C G A A C C A T G C C C C T T G RNA Amino Acid Chain (PROTEIN) 14 HUMAN IMACTS ON THE ENVIRONMENT 34. The following diagram describes the process of the greenhouse effect. How do greenhouse gases affect the atmosphere? 35. Name three examples of greenhouse gases. 36. Global warming is the enhancement of the greenhouse effect. How are human contributing to global warming? 37. What is a Brownfield Site? 38. What is the name of the process that cleans Brownfield sites? How does it work? 15 Below are two examples of water pollution caused by humans. Answer the following questions: EUTROPHICATION 39. What is Eutrophication? What initially causes this to occur? Why is this a problem? BIOACCUMULATION (MAGNIFICATION) 40. What is Bioaccumulation (also known as biological magnification)? Why is this problem? 16 Scientists study biogeochemical cycles. In class we studied one of them called Carbon Cycle. Review the diagram below and answer the questions that follow. 41. What type of organisms release CO2 into the atmosphere? 42. What is the name of the process these organisms perform to release CO2 into the atmosphere? 43. What type of organisms take in CO2 from the atmosphere? 44. What is the name of the process these organisms perform to take in CO2 from the atmosphere? 45. What type of human activities causes extra carbon dioxide to accumulate into the atmosphere? 17 46. List Pros/Cons on the following types of waste management. The reasons have to relate to the ENVIRONMENT, ECONOMICS or HEALTH (nothing personal or subjective). PROS CONS LANDFILL INCINERATOR RECYCLING 18