Chapter 9
advertisement

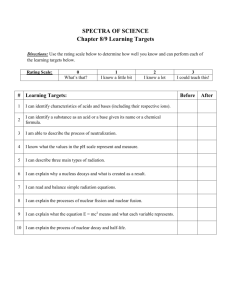
Key Terms Radioactivity Nuclear Radiation Alpha Particles Beta Particles Gamma Rays Half-life Nuclear Radiation Many elements change through radioactivity. Radioactivity is a process by which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why do elements that are unstable go through nuclear decay? To become stable. By becoming stable the element may be an isotope of the original element or an entirely new element. Nuclear radiation is the particles that are released during radioactive decay. There are four different types of nuclear radiation 1. Alpha Particles 2. Beta Particles 3. Gamma Rays 4. Neutron Emission 1. Alpha Particles consist of protons and neutrons - positively charged atom that is released in the disintegration of radioactive elements and that consists of two protons and two neutrons. - can be stopped by a sheet of paper - massive in size 2. Beta Particles are electrons produced from neutron decay - charged electron emitted during certain types of radioactive decay, such as beta decay - easily pass through paper, but are stopped by 3mm of aluminum or 10mm of wood - less massive than alpha particles 3. Gamma Rays are very high energy - high-energy photon emitted by nucleus during fission and radioactive decay - can penetrate up to 60cm of aluminum or 7cm of lead. Since they are not easily stopped they pose a greater danger to health than either alpha or beta particles. 4. Neutron radioactivity may occur in an unstable nucleus - neutron emission consists or matter that is emitted from an unstable nucleus - are stopped by lead 15cm thick Nuclear Decay Anytime an unstable nucleus emits alpha or beta particles, the number of protons or neutrons changes. A nucleus gives up two protons and two neutrons during alpha decay. A nucleus gains a proton and loses a neutron during beta decay. In all cases of beta decay, the mass number before and after the decay does not change. Radioactive Decay Rate Although it is impossible to predict the moment when any particular nucleus will decay, it is possible to predict the time it takes for half the nuclei in a given sample to decay. This is a substances half-life. Half-life is the time required for half of a sample of a radioactive substance to disintegrate by radioactive decay or by natural processes. Start 1st half-life 2nd half-life 3rd half-life 4th half-life =½ =¼ = 1/8 = 1/16 Half-life is a measure of how quickly a substance decays. Carbon-14 is used to date materials Key Terms Fission Nuclear Chain Reaction Critical Mass Fusion The stability of a nucleus depends on the nuclear forces that hold the nucleus together. Where do these forces act? Between the protons and neutrons If like charges repel one another how do protons remain in the nucleus? Nuclei are held together by a special force. These special forces are stronger than the repelling force. However, this force only occurs over short distances. Neutrons also contribute to nuclear stability Too many protons or neutrons can cause a nucleus to become unstable and decay While neutrons help hold the nucleus together, if there are too many or too few the nucleus is unstable and undergoes decay. Nuclei with more than 83 protons are always unstable, no matter how many neutrons there are. These nuclei always decay releasing large amounts of energy and nuclear radiation. Nuclear Fission Fission is the process by which a nucleus splits into two or more fragments and releases neutrons and energy What is released during nuclear fission? Energy. The energy that is released makes up for the mass that is lost during the process. Neutrons released by fission can start a chain reaction Nuclear chain reaction is a continues series of nuclear fission reaction The ability to create a chain reaction partly depends on the number of neutrons released. Chain reaction can be controlled Critical mass is the minimum mass of a substance that can undergo a fission reaction and can also sustain a chain reaction. How do power plants control chain reactions? By the use of control rods. Control rods are used to regulate splitting and slowing the chain reaction. Nuclear Fusion Fusion is the process by which light nuclei combine at extremely high temperatures forming heavier nuclei and releasing energy. Why are high temperatures needed for fusion to occur? Energy is required to bring the nuclei together until the repelling forces are overcome by the attractive nuclear forces between two protons. Key Terms Background Radiation Rem Radioactive Tracer Where Is Radiation? Nuclear radiation is all around us. Most of it comes from natural sources, such as the sun, heat, soil, rocks, and plants. This type of radiation is known as background radiation Background radiation is nuclear radiation that arises naturally from cosmic rays and from radioactive isotopes in the soil and air. Radiation is measured in units of rems. Rem is the quantity of ionizing radiation that does as much damage to human tissue as 1 roentgen of highvoltage X-ray Exposure varies from one location to another ( Table 3 pg 300) Some activities add to the amount of nuclear radiation exposure (Table 4 pg 300) Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear radiation is used in a controlled way to take advantage of its effects on other materials. Smoke detectors help save lives by using small radioactive sources. Nuclear radiation is used to detect diseases 1. Ultrasound scanning 2. CT scanning 3. PET 4. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) What is a radioactive tracer? A radioactive material that is added to a substance so that its distribution can be detected later. They are short-lived isotopes that tend to concentrate in affected cells and are used to locate tumors. Nuclear radiation therapy is used to treat cancer Radiotherapy is treatment that uses controlled doses of nuclear radiation for treating diseases such as cancer. Possible Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear radiation can ionize atoms by changing the number of electrons in living material. The risk depends upon the amounts of radiation. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of nuclear radiation can cause cancer. High concentration of radon gas can be hazardous What is Radon? It is a colorless and inert gas that is produced by the radioactive decay of uranium-238. Radon emits alpha and beta particles as well as gamma rays Nuclear Power Nuclear fission has both advantages and disadvantages Advantages 1. Does not produce gaseous pollution 2. More energy in uranium reserves that coal or oil Disadvantages 1. Produce radioactive waste 2. Storage of waste Nuclear fusion reactors are being tested Scientist estimate that 1 pound of hydrogen in a fusion reactor could release as much energy as 16 million pounds of burning coal. Nuclear fusion also release very little waste or pollution. Nuclear fusion also has advantages and disadvantages Advantages 1. Fuel is abundant Disadvantages 1. Produce fast neutrons 2. Expensive