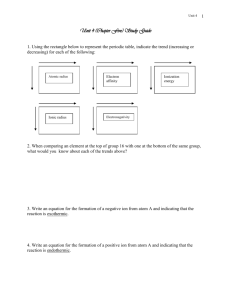
1) Isoelectronic means “having the same
advertisement

1) Isoelectronic means “having the same number of electrons”. For example: F– and Na+ are both isoelectronic with Ne. The isoelectronic series associated with Argon is: P3–, S2–, Cl–, Ar, K+, Ca2+, Ga3+ a. Write the isoelectronic series associated with Ne. b. How many electrons does each atom or ion in this series have? c. What is the electron configuration of each atom or ion in this series? 2) Fill in the following chart for each atom/ion in the neon isoelectronic series. Atom or ion # protons # electrons Ne 10 10 3) The size of an atom or ion depends, in part, on how strongly the positively charged nucleus can attract the surrounding electrons. In other words, a higher proton/electron ratio means a stronger pull on the electrons, and therefore, a smaller atom or ion. Based on this information, see if you can rank the atoms and ions in the argon series from biggest to smallest. Does this ranking make sense logically? Discuss with your group. 4) Draw AND write the ground state, and three possible excited states for Mg. 5) Is 1s22s22p53s3 an excited state? Why or why not?