SCHIZOPHRENIA & OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS
advertisement

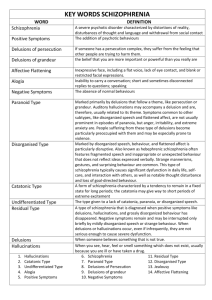
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR SCHIZOPHRENIA SCHIZOPHRENIA & OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS • A. Characteristic symptoms: two ore more of the following, each present for a significant period of time during a 1-month period – – – – – 1) delusions 2) hallucinations 3) disorganized speech 4) grossly disorganized or catatonic behaviour 5) negative symptoms (affective flattening flattening, alogia) • NOTE: Only one Criterion A symptom is required if delusions are bizarre or if hallucinations consist of a voice keeping a running commentary of the person’s behaviour or thoughts, or 2 or more voices are conversing with each other. Schizophrenia 1 SCHIZOPHRENIA & OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS • SCIZOPHRENIA: DSM-IV includes five subtypes of schizophrenia, as shown below: – CATATONIC: at least two of the following psychomotor disturbances…immobility, excessive motor activity, extreme negativism, posturing, repetition of speech, sounds 2 VARYING DEGREES OF PARANOID THINKING • MILD – AVERAGE PERSON: occasional suspicious thoughts • MODERATE – PARANOID: O ppreoccupation p with one or more delusions or frequent auditory hallucinations, absence of prominent schizophrenic symptoms such as disorganized speech or behaviour, catatonic behaviour, or flat or inappropriate affect – UNDIFFERENTIATED: meets criteria for schizophrenia but does not meet criteria for catatonic, paranoid, or disorganized subtype Schizophrenia Schizophrenia 3 – PARANOID PERSONALITY: a suspicious cognitive style – PARANOID PERONALITY DISORDER: a suspicious cognitive style so strong that is impairs effective behaviour. There are no delusions. Reality testing is intact. – DELUSIONAL (PARANOID) ( ) DISORDER: a stable bl andd chronic h i delusional system. Reality testing good in all other areas. • SEVERE – PARANOID SCHIZOPHRENIA: multiple delusions that are likely to be fragmented, accompanied by marked loosening of associations, obvious hallucinations, and other evidence of disorganization. Reality markedly distorted. Schizophrenia 4 1 FOUR TYPES OF DELUSIONS • DELUSIONS – persistent false beliefs, not in keeping with individual cultural background (e.g. suicide in war in middle east), it is accepted as truth by individual • Persecution – the RCMP is out to get me • Reference – people on the bus talk about me, neighbours are making fun of me • Being controlled – the devil is controlling my thoughts and behaviours • Grandeur – I am Jesus, on a special mission from the Lord. • HALLUCINATION – a mental phenomenon that is independent of external organs. a person believes he sees or hears things that have no basis in objective bj ti stimuli ti li • ILLUSIONS – an erroneous perception of a real sensory impression Schizophrenia 5 Schizophrenia DIFFERENCES BETWEEN POSITIVE-SYMPTOM (TYPE 1) AND NEGATIVE-SYMPTOM (TYPE 2) SCHIZOPHRENIA FOUR DIMENSIONS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA • EMOTIONAL Positive (Type 1) Schizophrenia Negative (Type 2) Schizophrenia SYMPTOMS delusions hallucinations incoherence bizarre behaviour poverty of speech flat affect social withdrawal apathy PREMORBID ADJUSTMENT good poor PROGNOSIS good poor SEX DISTRIBUTION more likely to be women more likely to be men – flat affect, disorganized, inappropriate, child-like • COGNITIVE – delusions, hallucinations, poor concentration • BEHAVIOURAL – disorganized, inappropriate, catatonic • PHYSIOLOGICAL – Sleep, sex, autonomic differences (GSR) Schizophrenia 6 7 Schizophrenia 8 2 100 accepted, more support systems, married MEN WOMEN 50 0 -2 26 5 -3 36 5 -4 46 5 -5 56 5 -6 66 5 -7 5 75 + 16 testosterone) - reduction in symptoms when pregnant Schizophrenia 9 10 and genetic risk, fewer coping skills taught, less access to health care 1.9 2) DOWNWARD DRIFT 1.3 0.9 3) VIRUS and PREGNANCY PROBLEMS 08 0.8 schizophrenics hi h i births bi th higher hi h in i late l t winter i t & early l spring i andd this is reversed in southern climates. Small increase 5-50% above expectancy, poorer health care 0.4 Lower Schizophrenia WHY? 1) HIGHER STRESS - psychologically, increased biological Economic Status and Schizophrenia 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 2) WOMEN HAVE MORE MOOD SYMPTOMS AND YOUNG MALES MORE O AGG AGGRESSIVE SS 4) BIOLOGICAL FACTORS (estrogen, Age at onset % o f R is k Numbee r of indiv iduals EXPLANATION FOR GENDER DIFFERENCES 1) SOCIAL ROLES - problems or differences 150 Lowermiddle Middle Schizophrenia Uppermiddle Upper 11 Schizophrenia 12 3 Minor Physical Anomalies Schizophrenia Minor Physical Anomalies 13 Minor Physical Anomalies Schizophrenia 14 RELAPSE ISSUES • Families high in expressed emotion (EE) are defined by: – emotional over involvement with a patient; and – a tendency to become hostile and make negative patient comments to the p Schizophrenia 15 Schizophrenia 16 4 RELAPSE ISSUES • High expressed emotion: – predicts schizophrenic relapse; and – is probably both a cause and consequence of patients’ p symptoms. y p schizophrenic Schizophrenia 17 5