Male Anatomy - CNR WEB SITE
advertisement

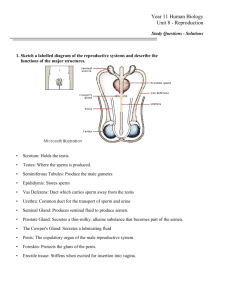
Reproductive system Male Anatomy Male reproductive is made up of a pair of testicles, vas deferens, urethra and penis with its associated organs. Spermatic cord Source: http://animalsciences.missouri.edu/reprod/Notes/male/anatomy.htm Symphasis of the pelvis - immovable bone in the median plane of the body Rectum - posterior end of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract Scrotum - external sac that holds testicles outside of the body to keep sperm at 4-5oF cooler than the body temperature for effective sperm production except in elephant and rooster in which testicles are located inside body Testicles - the primary male organs of reproduction (testis is singular; testes is plural) Functions of the testicles: 1. To produce sperm in the seminiferous tubules 2. To secrete testosterone in the Leydig cells; this is the male sex hormone that stimulates the development of the male sex characteristics. Anatomy /Reproductive system/ 08 1 Seminiferous tubules - glandular part of testicles containing the sperm producing cells Epididymis - a common path sperm take after formation in the seminiferous tubules; sperm mature and accumulate here prior to ejaculation. Functions of the epididymis: 1. Provide passageway for sperm out of the seminiferous tubules 2. Storage for sperm 3. Fluid secretion to nourish sperm 4. Place for sperm maturation Vas Deferens - slender tube from epididymis to urethra, which moves sperm to the urethra at ejaculation Spermatic Cord - vas deferens, cremester muscle, spermatic artery, spermatic vain and spermatic nerves Bladder - storage for urine Urethra - long tube from bladder to penis; passageway for urine and sperm out of the body Accessory Glands: Seminal vesicles - lobe type organ near the end of the vas deferens Function of the seminal vesicles: add fructose and citric acid to nourish the sperm Prostate Gland - located at the neck of the bladder Functions of the prostate gland: 1. Cleans the urethra prior to and during ejaculation 2. Provides minerals for sperm 3. Provides the medium for sperm transport 4. Provides the characteristic odor of semen Bulbourethral gland - paired organs To clean the urethra prior to semen passage Penis retractor muscle - allows extension and retraction of the penis; sigmoid flexure extends in copulation (taut - sexual rest; relaxed - sexual excitement) Penis - male organ of copulation, which conveys semen and urine out of the body Clinical importance Phimosis inability of penis to protrude out of sheath Paraphimosis inability of penis to retract into the sheath after protrusion Penile fracture seen in dogs because of presence of bone in penis Scrotal hernia migration of internal organ into scrotum Brucellosis bacterial disease affecting testicles Anatomy /Reproductive system/ 08 2 Female Anatomy Female reproductive tract is made up of a pair of ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina and vulva. Reproductive tract of cow is shown below Source: http://old.cvm.msu.edu/courses/AP/bessie/cowrepro.htm Ovary - the ovary is comparable to the male testicle and is the site of gamete production. A bovine animal has 20,000 potential eggs per ovary, (Ova are fully developed at puberty and are not continuously produced as in the male). All species contain two functional ovaries except for the hen, which has only a left functioning ovary. The ovaries have three major functions: 1. To produce gametes 2. Secrete estrogen Estrogen is the hormone responsible for the secondary sex characteristics in the female: o Absence of muscle development o Development of mammary glands o Development of reproductive systems and external genitalia o Fat deposition on hips and stomach (source of energy) o Triggering of estrous cycle at puberty o Triggering of heat 3. Form the corpus leutum That releases progesterone, which is required for the maintenance of pregnancy if animal get pregnant Anatomy /Reproductive system/ 08 3 Infundibulum - the flared portion of the fallopian tube near the ovary that catches the ovulated egg. Cilia movement and muscle contractions push the ovum into the fallopian tube. Fallopian Tubes (or Oviducts) - pair of small cilliated tubes leading from the ovaries to the horns of the uterus (5 - 6 inches). Fertilization occurs in the upper 1/3 of the oviduct. Egg travels from ovary to uterine horn in 3 - 4 days. Uterine Horn - the anterior, divided end of the uterus in cow, ewe, and mare. Sow has only 2 horns, no body; woman has no horns, only body. Uterus - the muscular sac connecting the fallopian tubes to the cervix. This organ can have two parts (the body and the horns). The uterus has three major functions: 1. Sustains the sperm and aids in its transport to oviduct 2. Supports embryo and fetus during gestation 3. Expels fetus at parturition Cervix - restricted area between the uterus and vagina, which opens at estrus and parturition. Otherwise, it remains closed to protect the uterus (2 -3 inches). Vagina - the female organ of copulation Functions of the vagina: 1. Admits penis 2. Receives semen (except in sow) 3. Passageway for fetus at parturition Bladder - storage organ for urine. Urethra - opening of bladder into vagina Vulva - extended genitalia; opening for both urinary and genital tracts Clitoris - located just inside vulva, rudimentary male organ Reproductive Functions of the Female The female has several major functions during reproduction: 1. produce gamete (ova or ovum) Anatomy /Reproductive system/ 08 4 ovulation - release of egg(s) from graafian follicle into oviduct where fertilization can occur if sperm are present. Ovulation Rates by Species cow 1 egg per estrus ewe 1 - 3 eggs per estrus sow 10 - 20 eggs per estrus mare 1 egg per estrus hen ~ 28 eggs per month At ovulation, the ruptured follicle, or corpus luteum, becomes a temporary endocrine organ, secreting progesterone The infundibulum pushes the ovum into the fallopian tube If not, an ectopic pregnancy may occur. The egg is fertilized in the upper 1/3 of the oviduct and then moves to the uterus. 2. Develop embryo in uterus from fertilization to parturition (this period is gestation) 3. Expel fully developed young at birth (parturition) Species Act of giving birth Offspring Cow Yak Calving Calf Buffalo Ewes Lambing Lamb Sows farrowing Piglet Hens Hatching Chick Mares Foaling Foal Doe Kidding Kid Bitch Whelping Pup Queen Kittening Kitten 4. Produce milk (lactation) to nourish young Clinical importance 1. Under developed genital tract due to poor nutrition may result in late onset of estrus 2. Freemartinism may result in permanent sterility 3. Ovarian cysts may result in infertility 4. Mishandling during calving may cause uterine prolapse 5. AI gun may go into urinary bladder http://nongae.gsnu.ac.kr/~cspark/teaching/chap3.html Anatomy /Reproductive system/ 08 5