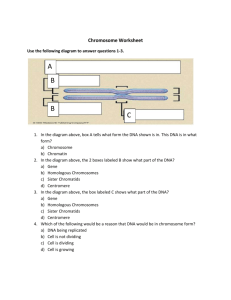
Chromosomes, homologous pairs, chromatids and DNA
Chromosomes, homologous pairs, chromatids and DNA molecules
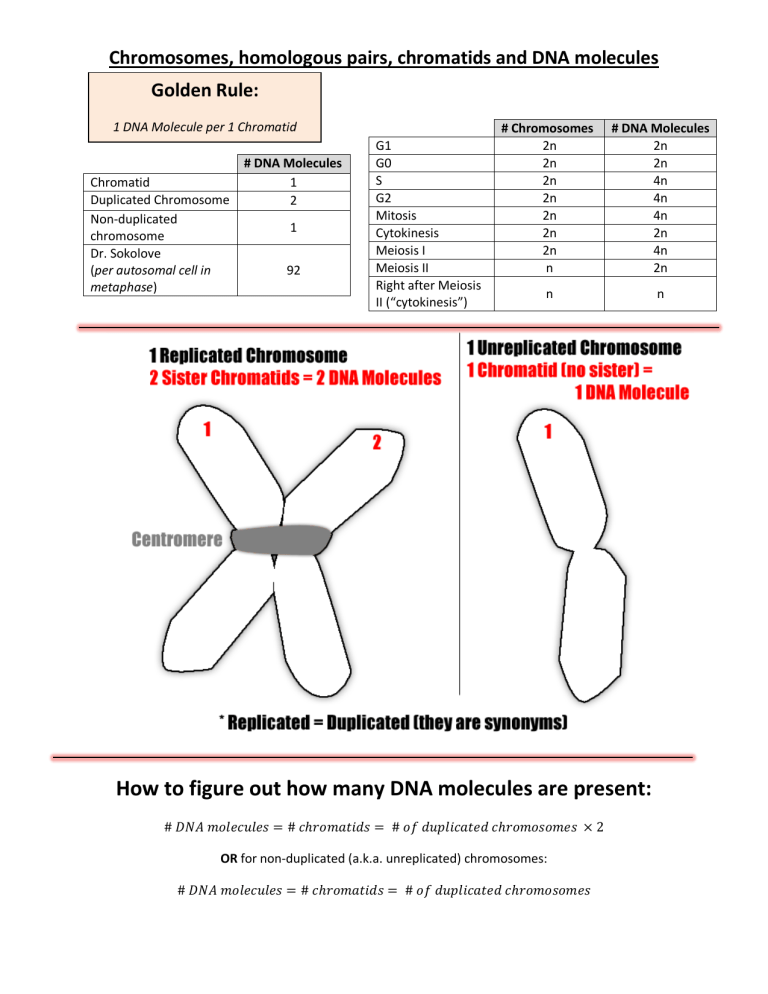
Golden Rule:
1 DNA Molecule per 1 Chromatid
Chromatid
Duplicated Chromosome
Non-duplicated chromosome
Dr. Sokolove
( per autosomal cell in metaphase )
# DNA Molecules
1
2
1
92
G1
G0
S
G2
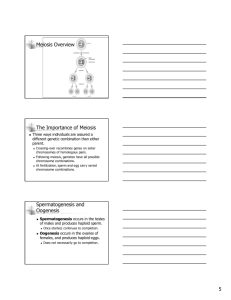
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
Right after Meiosis
II (“cytokinesis”)
# Chromosomes # DNA Molecules
2n 2n
2n
2n
2n
2n
2n
4n
4n
4n
2n
2n n
2n
4n
2n n n
How to figure out how many DNA molecules are present:
OR for non-duplicated (a.k.a. unreplicated) chromosomes:
Chromosomes, homologous pairs, chromatids and DNA molecules
Each number corresponds to an unreplicated homologous pair of chromosomes
Each number corresponds to a replicated homologous pair of chromosomes
What’s the difference between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes?
Sister chromatids are (mostly) identical! It’s basically a copy (“replicate”) of the original chromatid.
Homologous chromosomes only share the same size and shape – they may contain the same genes, but they may or may not be the same version in each chromosome of the pair. One comes from the father and one from the mother. Crossing over occurs between these (NOT between sister chromatids).