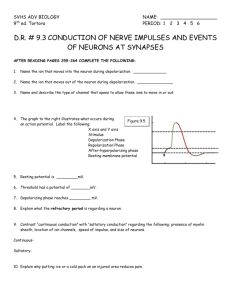
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Study
advertisement
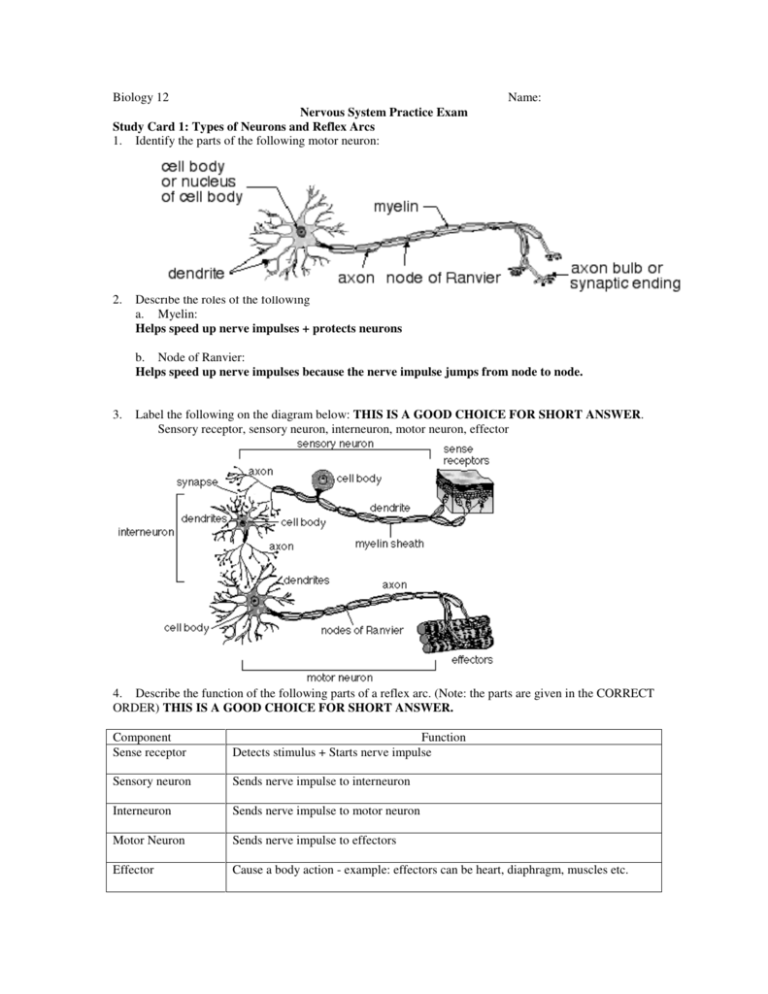
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Study Card 1: Types of Neurons and Reflex Arcs 1. Identify the parts of the following motor neuron: 2. Describe the roles of the following a. Myelin: Helps speed up nerve impulses + protects neurons b. Node of Ranvier: Helps speed up nerve impulses because the nerve impulse jumps from node to node. 3. Label the following on the diagram below: THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORT ANSWER. Sensory receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector 4. Describe the function of the following parts of a reflex arc. (Note: the parts are given in the CORRECT ORDER) THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORT ANSWER. Component Sense receptor Function Detects stimulus + Starts nerve impulse Sensory neuron Sends nerve impulse to interneuron Interneuron Sends nerve impulse to motor neuron Motor Neuron Sends nerve impulse to effectors Effector Cause a body action - example: effectors can be heart, diaphragm, muscles etc. 5. Label the following diagram. W Y = dendrite of sensory neuron W = cell body of sensory neuron X = axon of interneuron Z = axon of motor neuron 6. In the diagram, X indicates the a) dendrite of an interneuron b) cell body of the motor neuron c) axon of a sensory neuron d) dendrite of a motor neuron 7. Neurons which carry nerve impulses toward the central nervous system are called a) inter neurons b) motor neurons c) sensory neurons d) sympathetic neurons 8. In the diagram, X indicates a) Cell body of motor neuron b) Cell body of interneuron c) Cell body of sensory neuron d) Axon of sensory neuron 9. A collection of cell bodies in the location labeled as X is called a) Ventral root b) Dorsal root ganglion c) Spinal cord d) Medulla oblongata 10. Considering the direction of the nerve impulse, what is structure X? a) dendrite b) synapse c) cell body d) axon 11. Considering the direction of the nerve impulse, what is structure Y? a) dendrite b) synapse c) cell body d) axon 12. Considering the direction of the nerve impulse, what type of cell is the second neuron? a) sensory neuron b) motor neuron c) interneuron d) schwaan cell Study Card 2: Action Potential and Nerve Impulse 13. Explain the transmission of a nerve impulse through a neuron, using the following terms: Term Description Resting potential inside neuron is -60 mVolts and Na+ is pumped to the outside of the neuron and K+ pumped to the inside of the neuron Action potential Na+ diffuses into the neuron and K+ diffuses out of the neuron. (depolarization + repolarization) Depolarization Na+ gate opens and Na+ diffuses into the neuron Repolarization K+ gate opens and K+ diffuses out of the neuron Recovery (refractory) period Na+ is pumped to the outside of the neuron and K+ pumped to the inside of the neuron - this requires the Na+/K+ pump which requires ATP. A nerve impulse will be generated if the neuron is depolarized to a threshold value. Threshold (all or none response) 14. What is the role of myelin in a myelinated nerve fibre? Protects neurons and helps speed up nerve impulse – nerve impulse jumps from node to node. 15. Name and describe the events at each stage of the graph below 1 = resting potential: inside neuron is -60 mVolts and Na+ is pumped to the outside of the neuron and K+ pumped to the inside of the neuron – requires Na+/K+ pump and ATP 2 = depolarization: Na+ gate opens and Na+ diffuses into the neuron (+40 mvolts) 3 = repolarization: K+ gate opens and K+ diffuses out of the neuron (-60 mvolts) 4 = recover (refractory) phase: Na+ is pumped to the outside of the neuron and K+ pumped to the inside of the neuron - this requires the Na+/K+ pump which requires ATP. 16. Explain how a nerve impulse (action potential) is transmitted along a neuron. Action potential travels like a wave down a neuron 17. In the diagram of a nerve impulse above, the area from 5-6 milliseconds would represent a) sodium gates opening and sodium ions leaving the neuron cytoplasm b) sodium gates opening and sodium ions entering the neuron cytoplasm c) potassium gates opening and potassium ions leaving the neuron cytoplasm d) active transport of sodium and potassium ions 18. The diagram shows part of a dendrite. A role of structure X is to a) Secrete the myelin sheath. b) Identify the cell to phagocytes. c) Move sodium across the membrane. d) Release calcium at the synaptic ending. 19. If potassium ions could not diffuse out of the axon, which of the following would result? a) Repolarization would not occur. b) A neurotransmitter would be released. c) The length of the recovery phase would be reduced. d) The frequency of action potentials would be increased. 20. Why can an impulse traveling along an axon not reverse its direction? a) The myelin sheath will only permit one-way travel of an impulse. b) Sodium gates remain closed until the impulse reaches the synapse. c) The threshold required to create an action potential behind the impulse is increased. d) The sodium-potassium pump has not restored the resting potential immediately behind the action potential. 21. Use the graph below to describe how a neuron would respond to increased stimulation of the membrane. Frequency of nerve impulses would increase 22. If X is an interneuron, Y must be? a) b) c) d) effector sensory neuron motor neuron myelin Study Card 3 - Synapse 23. Identify the major components of a Synapse. (THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORT ANSWER) 24. Explain the process by which impulses are transmitted across a Synapse. Include the role of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and the role of enzymes. (THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORT ANSWER) 1. When an action potential reaches a synaptic ending it causes the vesicles with neurotransmitters to fuse with the pre synaptic membrane and neurotransmitters are released through exocytosis. Government exam Writers: the action potential causes calcium ions to diffuse into the pre-synaptic ending. The calcium ions interact with contractile proteins which causes them to pull the synaptic vesicles to the edge of the membrane where they then burst to release their contents. 2. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft and attach to receptor sites on the post synaptic membrane in a lock and key manner. 3. Neurotransmitters can have either an excitatory or inhibitory effect. excitatory effect - action potential generated in post synaptic membrane. (Na+ gates (channels) open on post synaptic membrane) inhibitory effect - action potential does not continue in post synaptic membrane. (K+ gates (channels) open causing hyperpolarization of post synaptic membrane) 4. Enzymes on the post synaptic membrane, breakdown the neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft and the receptor sites. This stops excitatory or inhibitory stimulation of postsynaptic membranes. 25. Explain why neurons carry an impulse (action potential) in only one direction. Only axon has vesicles with neurotransmitter and receptor sites found only on post synaptic membrane. 26. To which other neuron(s) would the action potential be passed if neuron 2 were stimulated at point X? a) 1 only b) 3 only c) 1 and 3 d) neither 1 nor 3 27. How does the molecule indicated by X move across the space below? a) Osmosis. b) Diffusion. c) Active transport. d) Facilitated transport. 28. In order for a nerve impulse to be transmitted across the synapse, the amount of excitatory neurotransmitter must exceed the amount of inhibitory neurotransmitter. Which of the following conditions would reach the threshold and cause the firing of a neuron? Neuron C – (75 + 20 = 95 inhibitory) and (55 + 45 = 100 excitatory) Type of Synapse Amount of Neurotransmitter Released inhibitory 75 units inhibitory 20 units excitatory 55 units excitatory 45 units Study Card 4: The brain and autonomic nervous system 29. Contrast the locations and functions of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems. Nervous System Components Central Brain + spinal cord Peripheral Spinal + cranial nerves Autonomic Motor neurons Types of neurons Spinal cord – relays sensory impulses to the brain and relays motor nerve impulses to effectors Brain – thinking, learning etc. Spinal nerves + cranial nerves – contain sensory + motor neurons to take nerve impulses to and from the CNS Motor nerves to smooth muscle and internal organs involuntary 30. Differentiate between the functions of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Nervous Functions System Divisions promotes reaction to “fight or flight” situations or emergency Sympathetic accelerate heart beat (rate) increase breathing rate dilation of pupils inhibit digestion decrease peristalsis decrease enzyme secretion decrease blood flow to intestines promotes all those internal response we associate with a relaxed state Parasympathetic slow heart beat (rate) slow breathing rate contraction of pupils digestion of food increase peristalsis increase enzyme secretion increase blood flow to intestines 31. Identify the source gland for adrenalin (epinephrine) and explain its role in the "fight or flight" response. Trigger - sympathetic nervous system Source - adrenal gland (adrenal medulla - inner part of adrenal gland) Action - fight or flight responses 32. Identify and give functions for each of the following brain structures: (THIS IS A GOOD CHOICE FOR SHORT ANSWER) Structure Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Corpus callosum Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Function Control reflexes – heart rate, breathing rate Controls balance and muscle coordination Gatekeeper – relays sensory nerve impulses to correct area of brain Control body temperature Produces and releases hormones Produces and releases hormones Bridge between right and left hemispheres of cerebrum Connects the 2 hemispheres of cerebrum Thinking, speech, hearing, personality Right hemisphere controls left side of body, left hemisphere controls right side of body Top layer of cerebrum – higher level thinking 33. A drug was observed to have the following effects: • accelerated heart rate • dilation of pupils • reduced peristalsis The nervous system affected by this drug is the a) central b) somatic c) peripheral d) sympathetic 34. A person shows signs of uncoordinated movements. The part of the brain affected is the a) cerebrum b) cerebellum c) medulla oblongata d) thalamus 35. Which of the following activities would be the most difficult for a person with a damaged cerebellum? a) reading b) breathing c) gymnastics d) conscious thought