Medical Terminology
advertisement

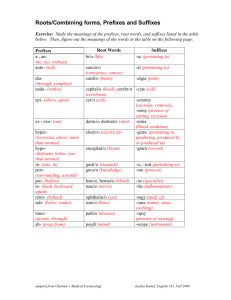
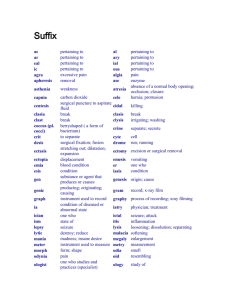
Medical Terminology lecture 4 Prefixes and suffixes Ultra, super, supra hyper The prefix pre- means before. Preoperative means before or preceding an operation. The prefix peri- (pehr-e) means around. Perioperative means pertaining to the period around an operation or the period before, during, and after an operation. The prefix post- means after. Postoperative means after an operation. Pe Epi M et Prefixes are added to the beginning of a word or root to modify its meaning. For example, the term operative can be modified using various prefixes. a Prefixes r Inter Intra Extra Trans Infra Sub, hypo Many prefixes have another prefix whose meaning is opposite of its own. Initially, when learning prefixes it is helpful to learn them in these pairs or in similar groups (Table 1–1 and Figure 1–1). TABLE 1–1 Contrasting Prefixes Without a prefix the root emetic means pertaining to vomiting. dys- (dihs) means difficult, painful, or bad. dysphagia means difficulty eating or swallowing. a- (ah or ā) means without or no. atraumatic means without injury. an- (ahn) means without or no. anuria means absence of urine. ad- (ahd) means toward. adduction means move toward the midline. anti- (ahn-tı̄ or ahn-tih) means against. antiemetics work against or prevent vomiting. eu- (yoo) means good, easy, or normal. euthyroid means having a normally functioning thyroid endo- (ehn-dō) means within or inside. ex- (ehcks) or exo- (ehcks-ō) means without, out of, endocrine means to secrete internally. endo- means within or inside. endoparasite is an organism that lives within the body of exocrine means to secrete externally (via a duct). ecto- (ehck-tō) means outside. ectoparasite is an organism that lives on the outer surface Without a prefix the root traumatic means pertaining to injury. Without a prefix the root uria means urination. ab- (ahb) means away from. abduction means to take away from midline. gland. outside, or away from. the host. hyper- (hı̄-pər) means elevated or more than normal. hyperglycemia means elevated amounts of blood glucose. inter- (ihn-tər) means between. intercostal means between the ribs. poly- (pohl-ē) means many. polyuria means elevated amount or frequency of urination. of the host. hypo- (hı̄-pō) means depressed or less than normal. hypoglycemia means depressed amounts of blood glucose. intra- (ihn-trah) means within. intramuscular means within the muscle. oligo- (ohl-ih-gō) means scant or little. oliguria means depressed amount or frequency of urination. pre- (prē) means before. preanesthetic means pertaining to before anesthesia. sub- (suhb) means below, under, or less. post- (pōst) means after. postanesthetic means pertaining to after anesthesia. super- (soo-pər) and supra- (soo-prah) mean above, sublingual means under the tongue. supernumerary means more than the regular number. suprascapular means above the shoulder blade. beyond, or excessive. 1 Medical Terminology TABLE 1-2 Directional Prefixes and Their Meanings Prefix epi extra hyper Pronunciation (eh-pē) (ehcks-trah) (hi-pər) hypo infra inter intra meta per sub super (hı̄-pō) (ihn-frah) (ihn-tər) (ihn-trah) (meht-ah) (pər) (suhb) (soo-pər) supra (soo-prah) trans ultra (trahnz) (uhl-trah) Definition upper outside above, increased, or more than normal below, under, or decreased below or beneath between within beyond throughout below, under, or decreased above, increased, or more than normal above, increased, or more than normal across above, increased, or more than normal The suffix -ectomy means surgical removal or excision. Gastrectomy is surgical removal of the stomach. Many suffixes can be grouped together by meaning or by the category they modify. Initially, when learning suffixes it is easiest if the learner groups them by meaning or category. “PERTAINING TO” SUFFIXES -ac (ahck), as in cardiac (pertaining to the heart) -al (ahl), as in renal (pertaining to the kidney) -an (ahn), as in ovarian (pertaining to the ovary) -ar (ahr), as in lumbar (pertaining to the loin) -ary (ahr-ē), as in alimentary (pertaining to the gastrointestinal tract) -eal (ē-ahl), as in laryngeal (pertaining to the larynx) -ic (ihck), as in enteric (pertaining to the intestines) -ine (ihn), as in uterine (pertaining to the uterus) -ous (uhs), as in cutaneous (pertaining to the skin) -tic (tihck), as in nephrotic (pertaining to the kidneys) SURGICAL SUFFIXES -ectomy (ehck-tō-mē) surgical removal, as in mastectomy, surgical removal of the breast or mammary glands -pexy (pehck-sē) suture to stabilize, as in gastropexy, surgically stabilizing the stomach to the abdominal wall -plasty (plahs-tē) surgical repair, as in rhinoplasty, surgical repair of the nose -stomy (stō-mē) surgically created opening, as in colostomy, a surgically created opening between the colon and body surface -tomy (tō-mē) cutting into, as in laparotomy, an incision into the abdomen PROCEDURAL SUFFIXES 2 -centesis (sehn-tē-sihs) surgical puncture to remove fluid or gas (either for diagnosis or to remove excess fluid or gas), as in cystocentesis, a surgical puncture of the urinary bladder with a needle to remove fluid (urine) -gram (grahm) record of, as in electrocardiogram, the electrocardiographic hard copy record -graph (grahf) instrument that records (or used as record), as in electrocardiograph, the machine that records the electrical activity of the heart -graphy (grahf-ē) procedure that records, as in electrocardiography, the procedure used to record the electrical activity of the heart -lysis (lı̄-sihs) separation or breakdown, as in Prefixes and suffixes urinalysis, separation of the urine into its constituents -scope (skōp) instrument to visually examine, as in endoscope, an instrument used to visually examine inside the body -scopy (skōp-ē) procedure to visually examine, as in endoscopy, the procedure of visually examining inside the body -therapy (thehr-ah-pē) treatment, as in chemotherapy, treatment with chemical substances or drugs DOUBLE “R” SUFFIXES -rrhagia or -rrhage (rā-jē-ah or rihdj) bursting forth, as in hemorrhage, bursting forth of blood from the vessels -rrhaphy (rahf-ē) to suture, as in enterorrhaphy, suturing of the intestines -rrhea (rē-ah) flow, discharge, as in diarrhea, complete discharge of the bowels -rrhexis (rehck-sihs) rupture, as in myorrhexis, rupture of the muscle CONDITIONAL SUFFIXES -algia and -dynia (ahl-jē-ah or dihn-ē-ah) pain, as in arthralgia and arthrodynia, or joint pain -itis (ı̄-tihs) inflammation, as in hepatitis, inflammation of the liver -malacia (mah-lā-shē-ah) abnormal softening, as in osteomalacia, abnormal softening of bone -megaly (mehg-ah-lē) enlargement, as in cardiomegaly, enlargement of the heart -osis (ō-sihs) abnormal condition, as in cardiosis, an abnormal condition of the heart -pathy (pahth-ē) disease, as in enteropathy, disease of the intestines -sclerosis (skleh-rō-sihs) abnormal hardening, as in arteriosclerosis, abnormal hardening of the arteries -um (uhm) structure, as in pericardium, the structure surrounding the heart 3 Noun Suffix Adjective Suffix cyanosis -osis cyanotic -tic anemia -emia anemic -ic mucus -us mucous -ous ilium -um iliac -ac condyle -e condylar -ar carpus -us carpal -al FIGURE 1–2 Suffix variation depending on usage Suffixes may change the part of speech of a word. Different suffixes may change the word from a noun (naming people, places, or things) to an adjective (descriptor) (Figure 1-2). Examples of this include cyanosis is a noun meaning condition of blue discoloration, whereas cyanotic is an adjective meaning pertaining to blue discoloration anemia is a noun meaning a blood condition of deficient red blood cells or hemoglobin, whereas anemic is an adjective meaning pertaining to a blood condition of deficient red blood cells or hemoglobin mucus is a noun meaning a slime-like substance that is composed of glandular secretion, salts, cells, and leukocytes, whereas mucous is an adjective meaning pertaining to mucus ilium is a noun meaning a part of the hip, whereas iliac is an adjective pertaining to the hip condyle is a noun meaning a rounded projection on a bone, whereas condylar is an adjective meaning pertaining to a rounded projection on a bone carpus is a noun meaning the joint between the radius and ulna and metacarpal bones, whereas carpal is an adjective meaning pertaining to the joint between the radius and ulna and metacarpal bones Medical Terminology Specialties and Specialists Suffixes that indicate specialties and/or specialists are presented throughout the study of medical terminology, particularly as you learn more about specialties, subspecialties, and the physicians who choose to pursue these specialties as lifelong careers. By the time a physician has earned the title of Board Certified or Diplomate in a particular field of study, this person may have invested as much as three to seven years studying beyond the basic medical degree. The following list identifies the most frequently used suffixes that denote specialties and/or specialists. Suffix Meaning Example -ician specialist in a field of study obstetrician (specialist in the field of study of pregnancy and childbirth) -iatrics relating to medicine, physicians, or medical treatment pediatrics (field of medicine that deals with children) -iatry medical treatment, medical profession psychiatry (field of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illness) -iatrist one who treats; a physician psychiatrist (specialist in the study, treatment, and prevention of mental illness) -ian specialist in a field of study geriatrician (specialist in the field of study of the aging) -ist practitioner pharmacist (one who is licensed to prepare and dispense medications) -logist one who specializes in the study of biologist (one who specializes in the study of living things) -logy the study of biology (the study of living things) 4