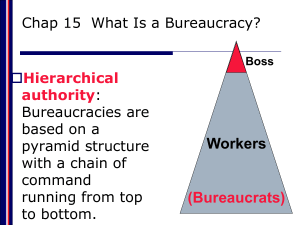
The Bureaucracy
advertisement

THE FEDERAL BUREAUCRACY JOBS • Spoils party System - The hiring of loyalists to the newly elected • Patronage - Jobs, grants, or other special favors that are given as rewards to friends and allies for their support • Merit System - A system of employment based on qualifications, test scores, and ability • Pendleton Act - Reform law that established federal employment based on open, competitive exams. Created the Civil Service Commission • Civil Service System - The merit system by which many federal bureaucrats are selected GROWTH • Most early growth in the bureaucracy was due to commerce • 1887 - Congress created the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC). Was the first Independent Regulatory Commission • TR created the Department of Commerce and Labor in 1901 and Wilson split it into 2 departments in 1913. Congress then created the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). • The 16th amendment and the creation of the Income Tax in 1913 allowed for greater government revenue, and therefore more spending and programs • The Great Depression saw the rise of more govt agencies and programs such as Social Security. Even more have been added since. BUREAUCRATS • There are 2.7 million federal employees working in 2000 different units of the federal government. • Some departments have a problem with being able to fill positions, especially in dangerous areas so the govt has hired private contractors to fill those positions. • In 2008 $538bn was spent on contractors ORGANIZATION • There are about 1,150 civilian government agencies • They fall into 4 categories: • Cabinet Departments - Major administrative units • Government Corporations - Businesses established by the government • Independent Executive Agencies - Like cabinet departments but with a narrower, service-based focus • Independent Regulatory Commissions - Designed to regulate specific activities free from partisan influence HOW IT WORKS • Implementation - The process by which a law or policy is put into operation • Iron Triangles - The relatively stable relationships and patterns of interaction that occur among agencies, interest groups, and congressional committees or subcommittees • Issue Networks - The loose and informal relationships that exist among a large number of actors who work in broad policy areas • Interagency Councils - Working groups created to facilitate coordination of policy making and implementation across a host of governmental agencies MAKING POLICY • Administrative Discretion - The ability of bureaucrats to make choices concerning the best way to implement congressional or executive intentions • Rule Making - A quasi-legislative process that results in regulations that have the characteristics of a legislative act • Regulations - Rules that govern the operation of all government programs that have the force of law • Administrative Adjudication - A quasi-judicial process in which a bureaucratic agency settles disputes between two parties in a manner similar to the way courts resolve disputes • Agencies are subject to Congressional and Judicial oversight