Optical Materials and Devices Homework Sheet 1
advertisement
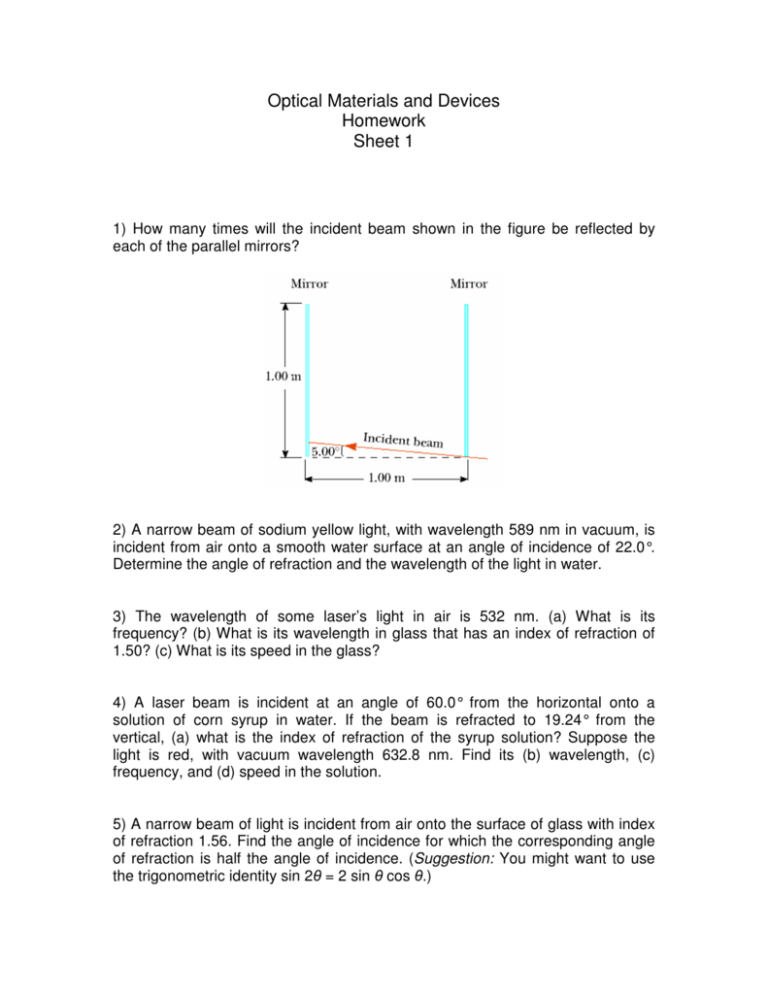
Optical Materials and Devices Homework Sheet 1 1) How many times will the incident beam shown in the figure be reflected by each of the parallel mirrors? 2) A narrow beam of sodium yellow light, with wavelength 589 nm in vacuum, is incident from air onto a smooth water surface at an angle of incidence of 22.0°. Determine the angle of refraction and the wavelength of the light in water. 3) The wavelength of some laser’s light in air is 532 nm. (a) What is its frequency? (b) What is its wavelength in glass that has an index of refraction of 1.50? (c) What is its speed in the glass? 4) A laser beam is incident at an angle of 60.0° from the horizontal onto a solution of corn syrup in water. If the beam is refracted to 19.24° from the vertical, (a) what is the index of refraction of the syrup solution? Suppose the light is red, with vacuum wavelength 632.8 nm. Find its (b) wavelength, (c) frequency, and (d) speed in the solution. 5) A narrow beam of light is incident from air onto the surface of glass with index of refraction 1.56. Find the angle of incidence for which the corresponding angle of refraction is half the angle of incidence. (Suggestion: You might want to use the trigonometric identity sin 2 = 2 sin cos .) 6) Consider a hydrogen atom, one proton, one electron, and get the BohrFormula for the energy levels. Hint: Start with energy conservation for the electron and use Bohr’s quantization of the angular momentum. Why does this formula tell us that there are discrete electron orbits in atoms? 7) Four possible transitions for a hydrogen atom are as follows: (i) ni = 2; nf = 5 (iii) ni = 7; nf = 4 (ii) ni = 5; nf = 3 (iv) ni = 4; nf = 7 (a) In which transition is light of the shortest wavelength emitted? (b) In which transition does the atom gain the most energy? (c) In which transition(s) does the atom lose energy? 8) A photon is emitted as a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from the n = 6 state to the n = 2 state. Calculate (a) the energy, (b) the wavelength, and (c) the frequency of the emitted photon. 9) A monochromatic beam of light is absorbed by a collection of ground-state hydrogen atoms in such a way that six different wavelengths are observed when the hydrogen relaxes back to the ground state. What is the wavelength of the incident beam?











