The Chemical Context of Life
advertisement

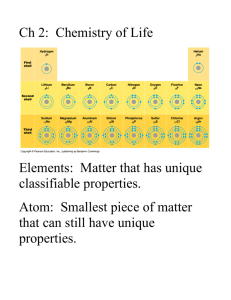
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life What is an element? What is a compound? The basic form of matter that cannot be broken down Two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio What is an atom? The smallest unit of an element that still has the properties of that element. Subatomic particles neutrons protons no charge found in the nucleus mass of 1 amu positive charge found in the nucleus mass of 1 amu electrons negative charge found outside the nucleus little mass Characteristics of Elements Atomic number: Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number: Number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus Isotope: An element that has a different mass than normal due to a change in the normal number of neutrons Electrons Located outside of the nucleus Unless otherwise indicated the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons Potential energy of electrons increases as their distance from the nucleus increases Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels Electron Energy Levels Electron Energy Levels The first energy level contains how many electrons? The second energy level contains how many electrons? 2 8 The third energy level contains how many electrons? 8 An element whose valence shell is complete is said to be what? Inert or unreactive Electron Orbitals Electron Configurations of First 18 Elements Chemical Bonds Covalent bond Non-Polar Covalent bond Sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms Equal sharing of electrons Polar Covalent bond Unequal sharing of electrons What sort of covalent bonds are seen here? Ionic Bonds Ion - transfer of electrons between atoms Ionic bond – attraction between two oppositely charged ions Cation – positively charged ion (lost electron) Anion – negatively charged ion (gained electron) Hydrogen Bonds Oxygen is one of the most electronegative elements In a water molecule electronegative oxygen “hogs” electrons. This “hogging” of electrons results in which type of bond between oxygen and hydrogen within the water molecule? Polar covalent Hydrogen Bond Hydrogen bonds occur between two polar molecules, or between different polar regions of one large macromolecule. One “relatively” negative region is attracted to a second “relatively” positive region. Van der Waals Interactions Weak attractions that occur when atoms and molecules are very close together May occur in regions of a single large molecule such as a protein Shape and function Molecular shape determines how molecules recognize and respond to one another Molecules with shapes similar to brain signal molecules can affect mood and pain perception Ex: morphine and heroin mimic endorphins in the brain Chemical Reactions Starting materials are known as Ending materials are known as reactants products Matter can only be ______________ not created or ______________ When forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, ______________ has been established Ionic bond, cation, anion