The Chemical Context of Life: Atoms, Bonding, Molecules Structure
advertisement

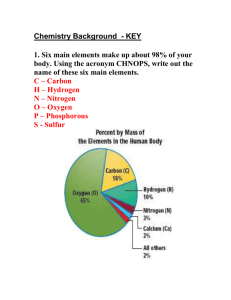
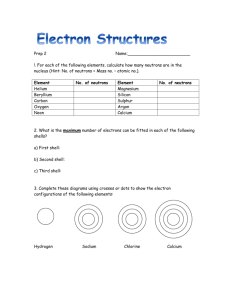
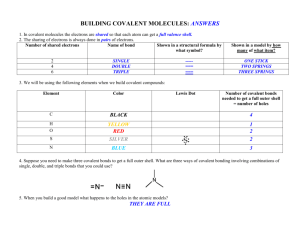
The Chemical Context of Life: Atoms, Bonding, Molecules Today s Topics: • Atomic Structure and bonding Matter Compounds Elements Two or more types of atoms bonded together in a fixed ratio Made up of only One type of atom Now a NEW SUBSTANCE – Periodic Table • Ionic Bonds • Covalent Bonds • Hydrogen Bonds (if time) + Figure 2.2 Sodium Sep 2, 2015 Chlorine Sodium Chloride Electrons are arranged in SHELLS Structure of Atoms Helium Potassium: 1 outer shell electron Fluorine: 7 outer shell electrons Atoms differ by the number of protons and electrons Electrons are – Nucleus Figure 2.11+ Electron Shells arranged in First shell (2 electrons maximum) shells Hydrogen (H) – – – – – – – – – – – Second – – 6+ – – 7+ – – 8+ – shell (8 electrons – – – maximum) Carbon (C) Nitrogen (N) Oxygen (O) shell 8 Third X (18 electrons maximum) – – – – – –– – – – 15+ – – – – – – – – Various ways to draw molecules – – – – – – 16+ – – – – – – – – Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) H O H O H H H-O | H 2O H 1 • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for all the elements Hydrogen 1H Atomic mass First shell Lithium 3Li Beryllium 4Be Boron 3B Carbon 6C 2 He 4.00 Atomic number Helium 2He Element symbol Electron-shell diagram Nitrogen 7N Oxygen Fluorine 8O 9F Neon 10Ne Second shell Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur 13Al 16S 11Na 12Mg 14Si 15P Chlorine 17Cl Argon 18Ar Third shell Isotopes differ in the number of neutrons Bonding: Ionic Bonding 12C 99% 1% tiny bit 13C Are these isotopes charged? 14C Do they have different chemical bonding properties? When atoms have very different Electronegativities, form an Ionic Bond Hydrogen 1H Atomic mass First shell Lithium 3Li Second shell Beryllium 4Be Weak ElectroNegativity Boron 3B Carbon 6C 2 He 4.00 Nitrogen 7N Third shell Theft Sharing Figure 2.6 Ionic Attraction between Sodium and Chlorine Atomic number Helium 2He Element symbol Electron-shell diagram Strong ElectroNegativity Oxygen Fluorine 8O 9F Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur 13Al 16S 11Na 12Mg 14Si 15P Nearly Empty Outer Shells Covalent Bonding Chlorine NearlyCl Full Outer shells 17 Electronically Stable Neon 10NeFull Outer Shells Argon NON18Ar Sodium atom (Na) (11 protons, 11 electrons) Chlorine atom (Cl) (17 protons, 17 electrons) Ionic attraction + _ REACTIVE Sodium ion (Na+) (11 protons, 10 electrons) Chloride ion (Cl–) (17 protons, 18 electrons) 2 What are some other ionic compounds? Covalent Bonds Form between atoms of similar electronegativity Hydrogen 1H Atomic mass First shell Lithium 3Li Beryllium 4Be Boron 3B Carbon 6C Atomic number Helium 2He 2 He 4.00 Nitrogen 7N Element symbol Hydrogen 1H Electron-shell diagram Oxygen Fluorine 8O 9F First shell Neon 10Ne Lithium 3Li Second shell Beryllium 4Be Boron 3B Carbon 6C Chlorine 17Cl Argon 18Ar Element symbol Electron-shell diagram Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine 8 9F O N Intermediate ElectroNegativity Second shell Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur 13Al 16S 11Na 12Mg 14Si 15P Atomic number Helium 2He 2 He 4.00 Atomic mass 7 Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur 13Al 16S 11Na 12Mg 14Si 15P Third shell Chlorine 17Cl Neon 10Ne Argon 18Ar Third shell Figure 2.8 Figure 2.8 Covalent Bonding: Sharing Covalent Bonds have a Specific Geometry Same electronegativity H Name (molecular formula) H • Full outer shells • Atoms overlap • Physically connected with fixed geometry H-H Molecules have covalent bonds Structural formula Electron-shell diagram Water (H2O). Spacefilling model H O H Methane (CH4). H H C H H H2 Fig. 2-12b Double Bonds Name and Molecular Formula ElectronLewis Dot distribution Structure and Diagram Structural Formula Oxygen (O2) These oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons. Spacefilling Model Missing 2 3 4 electrons always makes 2 3 4 bonds water cytosine 3 Fig. 2-18 Molecular Shape determines Function Key Natural endorphin Molecular Shape Determines Function Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Sulfur Oxygen Morphine Natural endorphin Morphine Endorphin receptors Two Types of Covalent Bonds Polar covalent bonds Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen Non-polar δ– Polar δ+ H Polar covalent bonds δ– O Partial negative charge on the oxygen; H δ+ Partial positive charge on the hydrogen. Like little magnets: S N S N S + N + + + + + Hydrogen Bonds + Liquid water + 4