ppt for test 116
advertisement

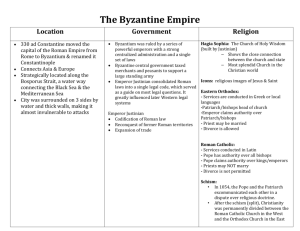
The Byzantine Empire 330-1453 AD Rise of the Byzantine Empire Roman Emperor Constantine moves the capital from Rome to eastern city of Byzantium Western half of old Roman Empire falls into “Dark Ages” Eastern half of Roman Empire becomes Byzantine Empire Byzantine Culture Cultural Tradition from Greeks Christianity center of Byzantine art, education, and life The Golden Age of Byzantine 527 AD Emperor Justinian takes power Not popular at start of his rule High taxes—due Justinian Code Formal Code of law that Governed the Empire A improved version of Roman Law Significance ***Justinian’s Code would become the basis for European law in the future*** Byzantine Religion Byzantine Empire brings drastic Change for Christianity Rome no longer important city to the Byzantine people and rulers Breakdown in authority over the church Byzantine Religion Continued Religion in East controlled by ruling emperor and Patriarch Patriarch a term for Lead Bishop in the East Byzantine Emperors and Patriarchs often conflict with Pope Icons Icons used by Christians in the east to aid in worship Controversy over use Some saw it as idol worship Leo III banned Icon use in 730AD Icon Controversy King Leo III’s ban on Icon led to period of Iconoclasm (Icon smashing) Smash Icons to end improper worship Pope claimed an Emperor had no authority to deal in issues of the Christian church Emperor’s Response Claimed authority over religious decisions within his empire Great Schism 1054 AD the Christian Church Splits The patriarch and Pope excommunicate each other East forms the Eastern Orthodox church Pope and western churches remain the Roman catholic church The two Churches Roman Catholic Eastern Orthodox Services Conducted in Services Conducted in Latin Pope has authority over all bishops Pope has authority over all kings and emperors Priests can not marry Greek Patriarch and other bishops head the church Emperor has authority over Patriarch Priests can marry Spread of EOC Opening up trade with Russia Eastern Orthodox missionaries spread EOC to Slavs (Russians) St. Cyril and St. Methodius most successful missionaries Cyrillic Alphabet St. Cyril and St. Methodius Designed Cyrillic Alphabet Allowed Slavs to read bible in native language Decline of the Byzantine Empire Black plague hit Empire during Emperor Justinian rein around 540 AD Killed large percentage of population From the Start of the Empire it was under constant attack Over time Empire lost more and more territory Empire Under Justinian Byzantine Empire At the End The Crusades 1204 AD the fourth crusade ends with Christians sacking the city of Constantinople Attacks from Islamic and Russian armies shrunk the empire Empire officially dies with the fall of Constantinople to the Turks in 1453 Legacy of Byzantine Empire Preserved Culture of the Greeks and Romans Great Schism split Christianity into Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Legacy Continued Justinian’s Code preserved Roman laws Be basis for creation of laws in future European countries Cyrillic Alphabet allowed for spread of Eastern Orthodox Christianity into Russia