Print › Ch. 9 - Endocrine System | Quizlet
advertisement
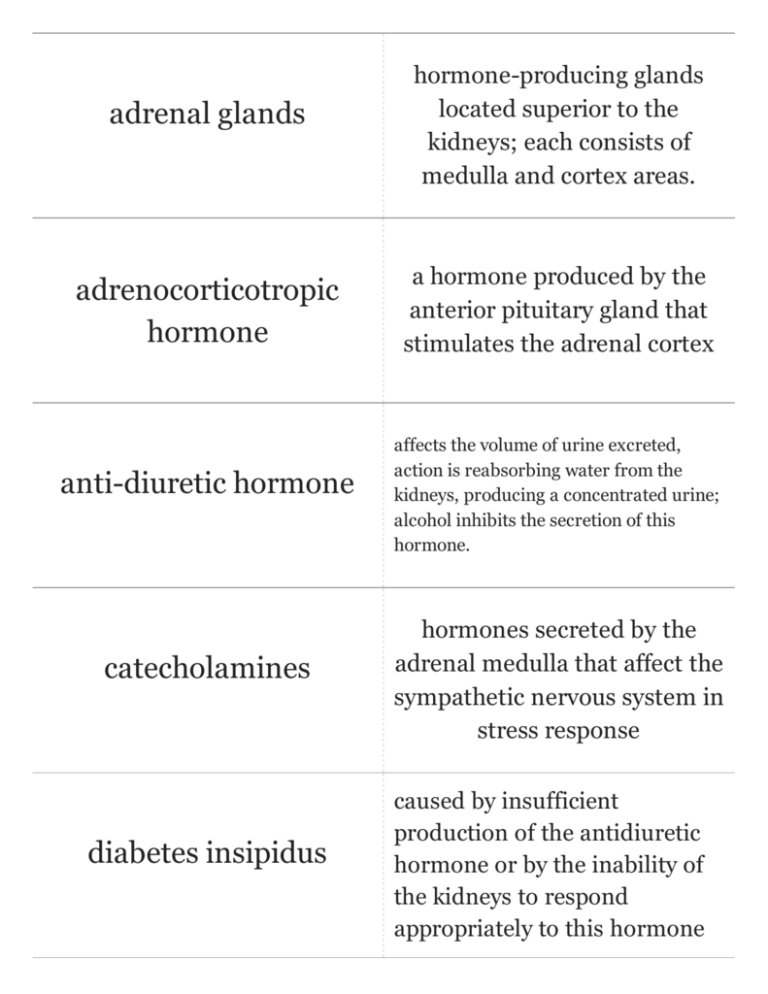
adrenal glands hormone-producing glands located superior to the kidneys; each consists of medulla and cortex areas. adrenocorticotropic hormone a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal cortex anti-diuretic hormone catecholamines diabetes insipidus affects the volume of urine excreted, action is reabsorbing water from the kidneys, producing a concentrated urine; alcohol inhibits the secretion of this hormone. hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla that affect the sympathetic nervous system in stress response caused by insufficient production of the antidiuretic hormone or by the inability of the kidneys to respond appropriately to this hormone diabetes mellitus epinephrine erythropoiesis follicle-stimulating hormone glucocortocoids condition that occurs when the pancreas produces too little insulin, resulting in an increase in the level of blood glucose a catecholamine secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress; fight or flight response process of erythrocyte formation a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that promotes growth of ovarian follicles in the female and sperm in the male secreted by the adrenal cortex and enables body to resist long term stress by increasing blood glucose levels; cortisone goiter gonadotropins growth hormone hypothalamus islets of Langerhans enlargement of the thyroid gland Hormones that stimulate the activities of the testes and ovaries; a collective term for follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. A hormone released by the anterior pituitary that targets most cells of the body; stimulates bone and muscle growth region of the brain that is the "master control center" of the endocrine system; functions in maintaining homeostasis by regulating temperature, blood pressure, and other conditions cell clusters in the pancreas that form the endocrine part of that organ; also called the pancreatic islets. luteinizing hormone melatonin mineralocorticoids A protein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary that stimulates ovulation in females and androgen production in males. hormone released by the pineal gland in response to daily cycles of light and dark One of the major groups of steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. It regulates water and electrolyte balance in extracellular fluid, mainly by regulating sodium reabsorption by the kidney tubules. Chiefly aldosterone. pancreas produces insulin and glucagon; produces both endocrine and exocrine secretions. parathyroid glands two paired glands located on the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland in the neck; secrete parathyroid hormone prostaglandins renin thymus gland biologically active lipids which produce many effects in the body, including smooth muscle contractions, inflammation, and pain enzyme that is produced by the kidney; important for blood pressure and volume regulation; catalyzes the conversion of circulating angiotensinogen to angiotensin I Endocrine gland active in immune response. thyroid gland located in front of the neck, functioning to secrete triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin tropic hormone A hormone that regulates the function of another endocrine organ.