DNA Replication Overview and Review
advertisement

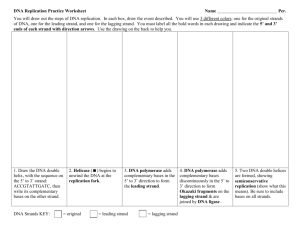
DNA Replication Overview and Review Name: ____________________________________________ 1. What is the complete name of DNA? 2. The two sides of the DNA helix are held together by _________________ bonds. 3. On the diagram below, do the following: a. Label the 3' and 5' ends on both backbones. b. Circle a single nucleotide. c. Label the sugars and phosphates with “S” and “P”. d. Label the bases that are not already labeled (A, T, C, G). 11. Why do the two strands of the helix have to be elongated by two slightly different mechanisms? 12. Chargaff’s rule states that the DNA of any species contains equal amounts of _________________ & _________________ and also equal amounts of _________________ & _________________. 13. What enzyme unzips the parent strand of DNA? 14. DNA replication happens only in the _____ to ______ direction. 15. What is the non-continuous backbone of the new DNA called? 16. Explain elongation stage of replication – you answer should include a discussion of leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki pieces and RNA primer. Use at least two sentences. 17. Draw a picture of the replication fork and include all of the following: helicase, leading strand, lagging strand, single strand binding proteins, DNA polymerase III, DNA primers, Okazaki fragment, and RNA primase. 4. Replication means: 5. DNA strands are complementary. How does this allow DNA to replicate itself? 6. Create a matching (complementary) DNA sequence for the following strand: 18. How are Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand joined into one continuous strand? 19. How do eukaryotes speed the process of replication – since they have multiple long chromosomes? 20. Why is DNA replication called semiconservative? 7. List the proteins/enzymes involved in the process of replication. 8. How does replication start? What prevents the unwound DNA for twisting back? 9. What enzyme synthesizes the new DNA strand? 21. What is the role of DNA polymerase (III)? 22. What is a primer? 10. What is the importance of DNA polymerase? 23. Which enzyme removes primers between Okazaki fragments? 24. Which enzyme joins the Okazaki fragments together on the lagging strand? 25. You will draw out the steps of the S phase of Interphase, DNA replication. In each box, draw the event described. You will use 3 different colors: one for the original strands of DNA, one for the leading strand, and one for the lagging strand. You must label all the bold words in each drawing. Use the drawing on the back to help you. 1. Draw the DNA double helix, with this sequence on the 5’ to 3’ strand: ACCGTATTGATC Label 5’ and 3’ on each strand. 2. Draw Helicase as it begins to unwind and separate the DNA at the replication fork, creating two single backbones from one double backbone. 3. Draw the beginning of replication as primers are added to the appropriate places on each backbones and the correct enzymes begin to do their jobs. Pay attention to leading & lagging strands. 4. Draw the end of the process. Include the final nucleotides being added and the primers being removed. Show the binding of the fragments by ligase. 5. Draw the two DNA double helices that are formed, showing semiconservative replication.