Winds Winds are caused by differences in temperature and air
advertisement

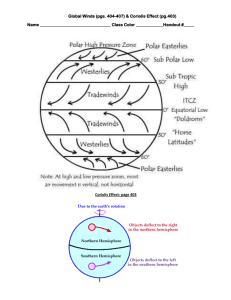
N am e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ D at e_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Winds Winds are caused by differences in temperature and air pressure. When there is a difference in pressure between two air masses, movement begins between them. The air moves from the area of high pressure to the area of low pressure until the pressure is equal. The greater the differences in pressure, the stronger the wind will be. The earth doesn’t heat evenly. Some places on earth are warmer than others. The sun shines more directly on the equator than it does on the poles. This makes the equator much warmer. Warm air rises. Cold, denser (or heavier) air moves in from below to take its place. Cool air sinks. In addition, the earth spins. This spinning causes air to be turned in the direction of the spin. In general, warm air rises at the equator. At the poles, cold air sinks. However, instead of circulating in a single loop in each hemisphere, the motion divides into three circulation loops in the Northern Hemisphere and three in the Southern Hemisphere. There are regions of sinking air at about 30 and at about 60 degrees latitude, north and south. At the North and South Pole, there is a constant area of high pressure where air sinks. Over some areas around the earth, winds blow mostly in one direction throughout the year. These wind systems help move heat more evenly around the earth. The wind systems of the earth blow from areas of high pressure toward lowpressure areas. Because of the earth’s rotation, air is turned to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This is known as the Coriolis Effect. These global air circulation patterns or wind systems include the Polar Easterlies, the Prevailing Westerlies, and the Trade Winds. Winds are named by the direction they are blowing from. There are jet streams that occur at the boundaries of these winds. The jet streams are like horizontal rivers of fast moving air high in the atmosphere. The Polar Easterlies blow from the northeast to the southwest. This wind zone is between 60 degrees latitude and the poles. The Polar Easterlies move cold, polar air from an area of high pressure southward. Because of the Coriolis Effect, it is turned toward the right or to the southwest. Between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, there is a second wind system. It is called the Prevailing Westerlies. In this zone, the winds blow toward the poles from the west. These winds cause most of the weather movement across the United States. This area was called “the horse latitudes” by sailors. The name came from the days when Spanish sailing vessels carried horses to the West Indies. Ships would often become becalmed in mid-ocean in this latitude. The Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb N am e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ D at e_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Winds (cont’d) ships could not move without enough wind. Water shortages made it necessary for the crew to throw their horses overboard. By the way, most of the world’s deserts can be found around 30 degrees latitude. This is because evaporation tends to be greater than rainfall at this latitude. Rainfall in desert areas is less than ten inches per year. The third area of movement is known as the Trade Winds. Located between the equator and 30 degrees north or south, this area of low pressure has been called the doldrums. Because this area receives most of the sun’s direct rays, it causes intense heating of the land and water around the equator. This heating causes warm, moist air to rise. The air pressure is low. Sailors long ago named the area the doldrums because their ships could be trapped there for weeks with little or no winds. Hurricanes form in this area. Severe thunderstorms or squalls often occur. There is a lot of rain. This is why there are rainforests along the equator. At 30 degrees either north or south of the equator, the air has cooled. The sinking air creates high pressure that produces very light winds. It begins to move back toward the equator. Jet streams are like rivers of air high above the earth. They occur at the boundaries between the wind systems. There is a big difference in temperature and pressure at the upper levels. This causes winds that blow over 100 miles per hour high above the earth. Because of the earth’s rotation, they blow from west to east. The subtropical jet stream is between the trade winds and the prevailing westerlies. The polar jet stream separates the polar easterlies from the prevailing westerlies. The jet streams produce large weather systems that move cold and warm air around. The jet stream can move in a northerly or southerly direction. It can even split into two branches. Whichever way it moves, the weather systems move with it. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb N am e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ D at e_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Winds Questions Questions 1. What causes wind? a. differences in temperature and air pressure b. differences in sea level c. differences in the earth’s spin 2. Where are the trade winds located? a. at the poles b. between the equator and 30 degrees latitude c. between 30 and 60 degrees latitude 3. What are winds called that blow between 30 and 60 degrees latitude? a. the Trade Winds b. the Prevailing Westerlies c. the Polar Easterlies 4. What kind of air do the polar easterlies bring? a. warm tropical air b. warm polar air c. cold polar air 5. Where are most of the world’s deserts found? a. 30 degrees latitudes b. 60 degrees latitudes c. 90 degrees latitudes d. the equator 6. Where are jet streams? a. horizontal rivers of air high above earth b. boundaries between wind systems c. producers of large weather systems d. all of the above 7. How fast are the winds in the jet streams? a. 30 miles per hour b. 60 miles per hour c. 90 miles per hour d. over 100 miles per hour Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb N am e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ D at e_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Winds Questions (cont’d) True or False: 1. Winds are moving air. 2. Air moves because of differences in temperature and pressure. 3. The smaller the differences, the stronger the wind will be. 4. If there were no winds, the North Pole would be too cold for animals to live there. 5. Warm air sinks, and cold air rises. 6. The Coriolis Effect explains why winds don’t blow north to south. 7. Because of the Coriolis Effect, air is turned toward the left in the Northern Hemisphere. 8. Warm air rises at the equator. 9. Air sinks at 30, 60, and 90 degrees (the poles) latitude. 10. Winds are named for the direction they are blowing toward. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb N am e _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ D at e_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Winds Answers Multiple Choice: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. a b b c a d d True/False 1. True 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. False 6. True 7. False 8. True 9. True 10. False Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb